Abstract
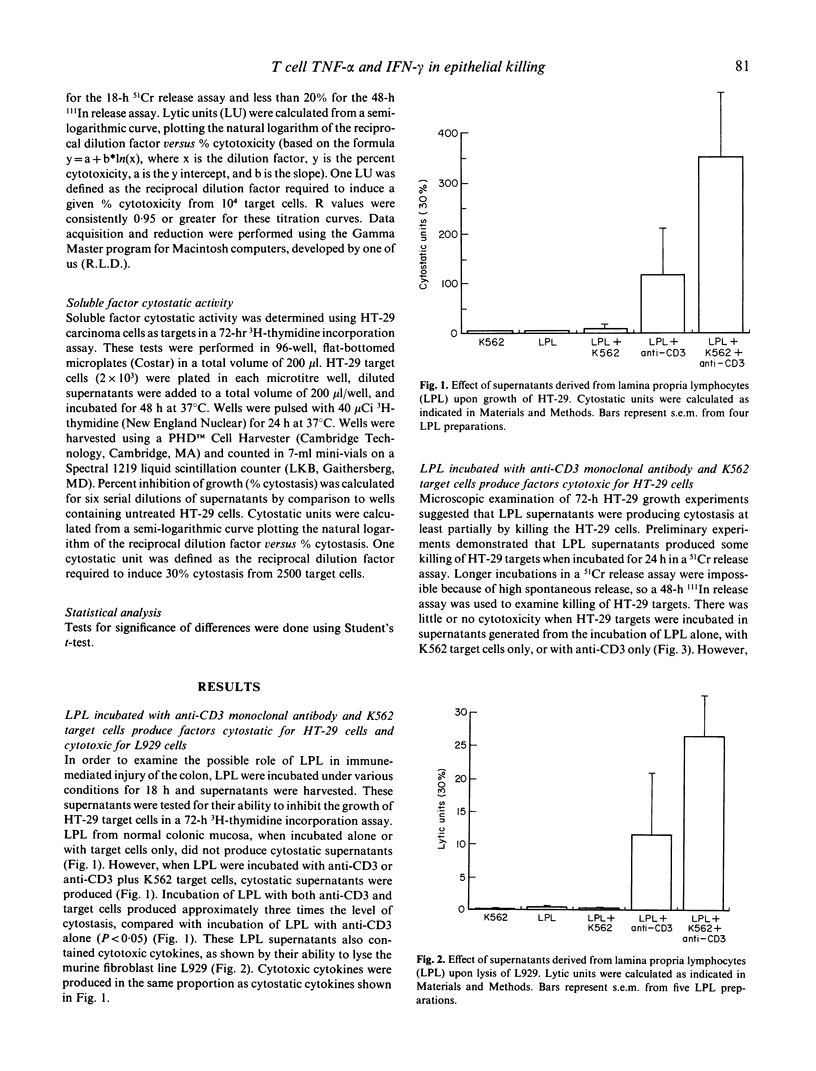
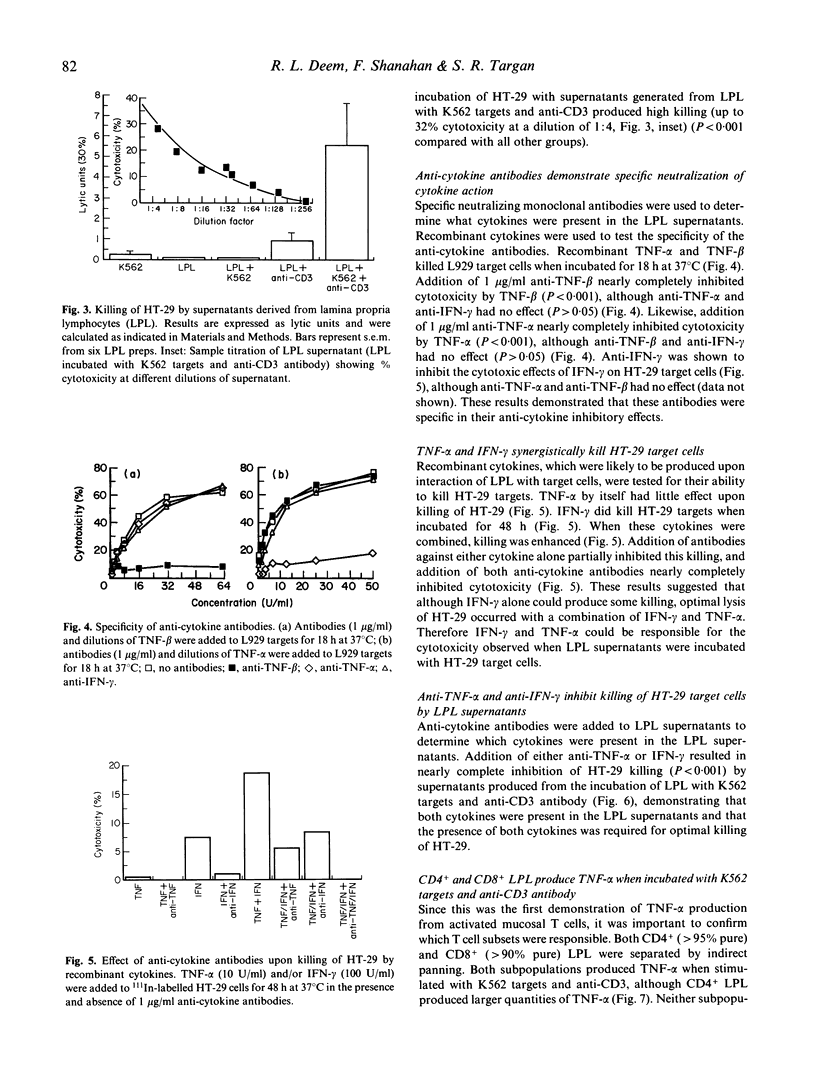
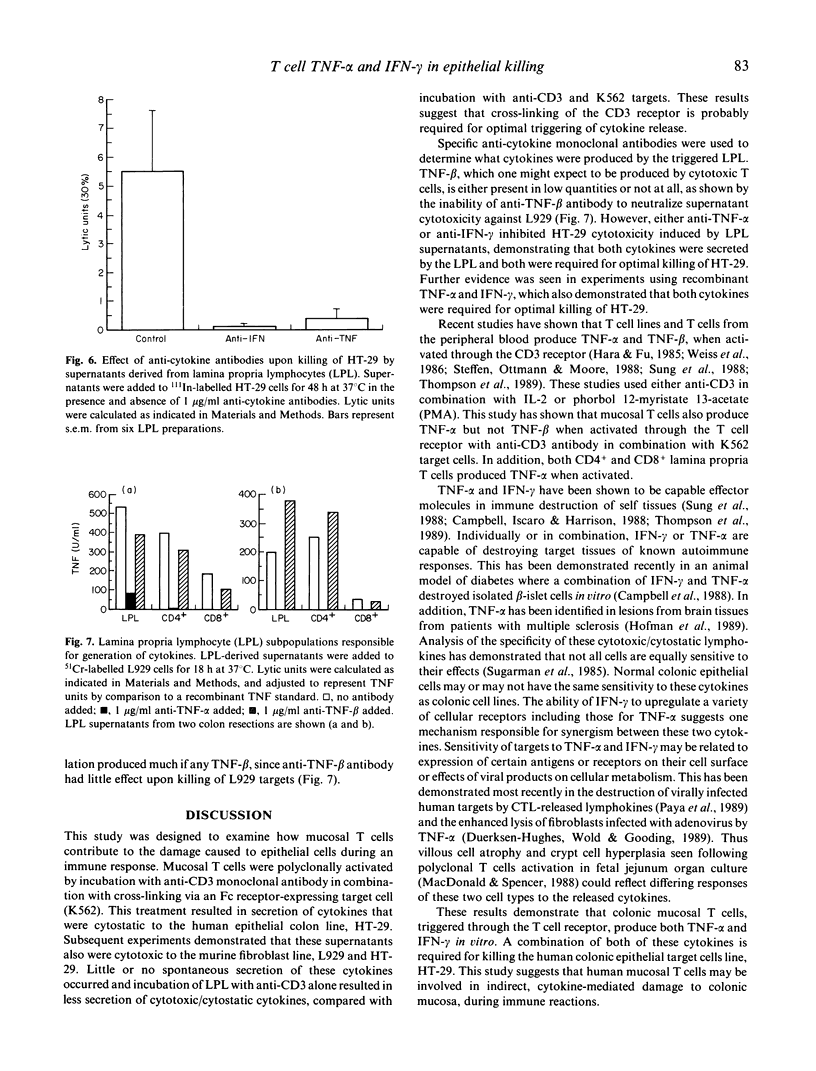
T cell activation can lead to local tissue injury in organ culture studies of human fetal jejunum, either directly through cytotoxicity or indirectly by the release of cytotoxic cytokines. The goal of this study was to establish in vitro whether cytotoxic cytokines can be released by isolated colonic T cells and what cytokine interactions are required for killing of human colonic epithelial cells. Cytokine-containing supernatants were induced by incubating unseparated lamina propria lymphocytes (LPL) or mucosal T cell subpopulations (separated by indirect panning) with anti-CD3 and/or K562 target cells for 18 h at 37 degrees C. Cytokines were measured by cytotoxicity assays using L929 (murine fibroblast) and HT-29 (human colonic tumour) lines as target cells in combination with blocking anti-cytokine antibodies. Supernatants derived from unseparated, CD4+ (greater than 95% pure) and CD8+ (greater than 90% pure) LPL were cytotoxic to L929 targets (350 U/ml, 230 U/ml and 100 U/ml tumour necrosis factor-alpha, respectively). All or nearly all of the cytotoxicity was due to the presence of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (little or no tumour necrosis factor-beta was detected). These same supernatants were cytotoxic (up to 32% lysis at 1/4 dilution) to HT-29 targets in a 48-h 111In release assay. Recombinant tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma alone produced minimal killing of HT-29, but together killed the HT-29 target cells. Anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha or anti-interferon-gamma alone blocked killing of HT-29 target cells by LPL-derived supernatants, although anti-tumour necrosis factor-beta had no effect upon killing of HT-29. These results demonstrate that human LPL T cells, triggered by addition of anti-CD3 and target cells, produce tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma, both of which are required for optimal killing of HT-29. Simultaneous release of these cytokines in the vicinity of epithelial cells during immune responses could play an important role in the mucosal damage in chronic inflammatory states such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bull D. M., Bookman M. A. Isolation and functional characterization of human intestinal mucosal lymphoid cells. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):966–974. doi: 10.1172/JCI108719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. A two-phase system for removal of red cells with methylcellulose as erythrocyte-aggregating agent. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:9–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Iscaro A., Harrison L. C. IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cytotoxicity to murine islets of Langerhans. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2325–2329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deem R. L., Targan S. R. Sequential substages of natural killer cell-derived cytolytic factor (NKCF)-mediated cytolysis as defined by glutaraldehyde modulation of the target cell. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1836–1840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerksen-Hughes P., Wold W. S., Gooding L. R. Adenovirus E1A renders infected cells sensitive to cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4193–4200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation. I. Monocyte-independent activation and proliferation induced by anti-T3 monoclonal antibodies in the presence of tumor promoter 12-o-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13 acetate. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):641–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Jung L. K., Bjorndahl J. M., Fu S. M. Human T cell activation. III. Rapid induction of a phosphorylated 28 kD/32 kD disulfide-linked early activation antigen (EA 1) by 12-o-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate, mitogens, and antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1988–2005. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Austin R. K., Hubert J. J., Bernardin J. E., Kasarda D. D. Possible role for a human adenovirus in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1544–1557. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Spencer J. Evidence that activated mucosal T cells play a role in the pathogenesis of enteropathy in human small intestine. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald G. B., Jewell D. P. Class II antigen (HLA-DR) expression by intestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory diseases of colon. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;40(3):312–317. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.3.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallone F., Fais S., Squarcia O., Biancone L., Pozzilli P., Boirivant M. Activation of peripheral blood and intestinal lamina propria lymphocytes in Crohn's disease. In vivo state of activation and in vitro response to stimulation as defined by the expression of early activation antigens. Gut. 1987 Jun;28(6):745–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.6.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paya C. V., Kenmotsu N., Schoon R. A., Leibson P. J. Tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin secretion by human natural killer cells leads to antiviral cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):1989–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A., Sato G. Growth of embryonal carcinoma cells in serum-free medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Mason D. Y., Jewell D. P. Expression of HLA-DR antigens by colonic epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Sep;53(3):614–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan F., Brogan M., Targan S. Human mucosal cytotoxic effector cells. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jun;92(6):1951–1957. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90629-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan F., Deem R., Nayersina R., Leman B., Targan S. Human mucosal T-cell cytotoxicity. Gastroenterology. 1988 Apr;94(4):960–967. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90554-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen M., Ottmann O. G., Moore M. A. Simultaneous production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin by normal T cells after induction with IL-2 and anti-T3. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Bjorndahl J. M., Wang C. Y., Kao H. T., Fu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin by human T cell lines and peripheral blood T lymphocytes stimulated by phorbol myristate acetate and anti-CD3 antibody. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):937–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S. R., Kagnoff M. F., Brogan M. D., Shanahan F. Immunologic mechanisms in intestinal diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jun;106(6):853–870. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-6-853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Lindsten T., Ledbetter J. A., Kunkel S. L., Young H. A., Emerson S. G., Leiden J. M., June C. H. CD28 activation pathway regulates the production of multiple T-cell-derived lymphokines/cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


