Abstract
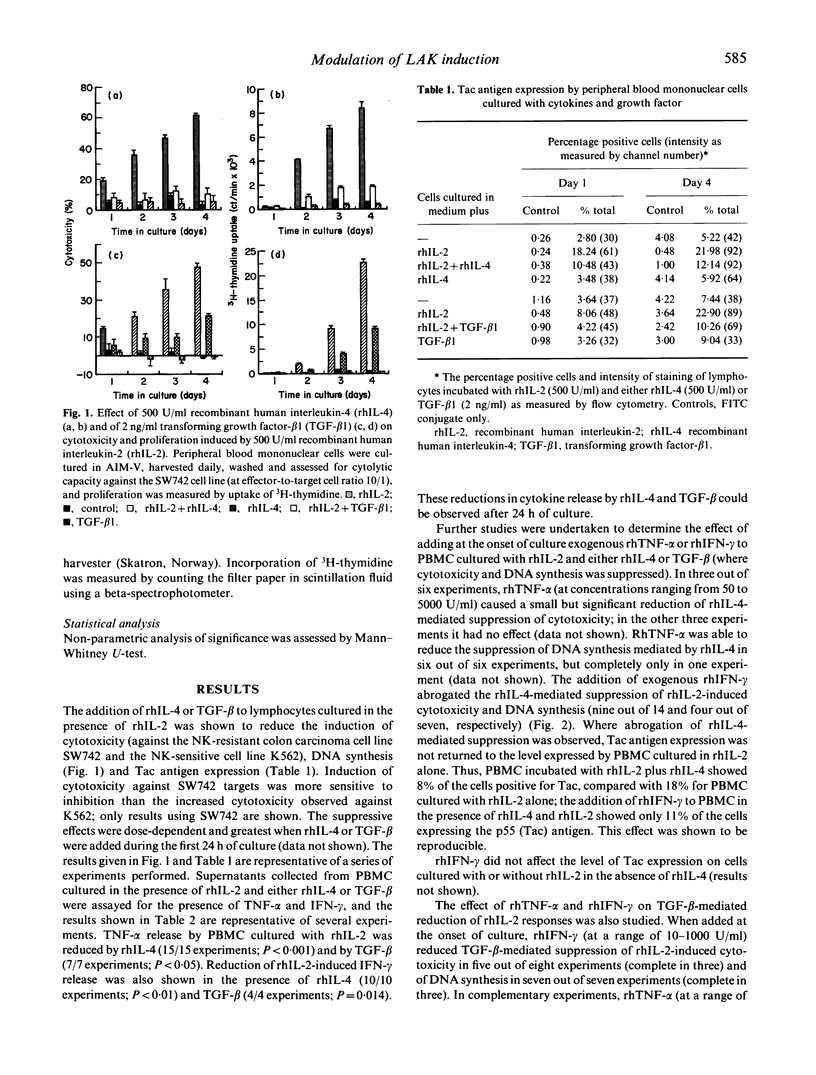
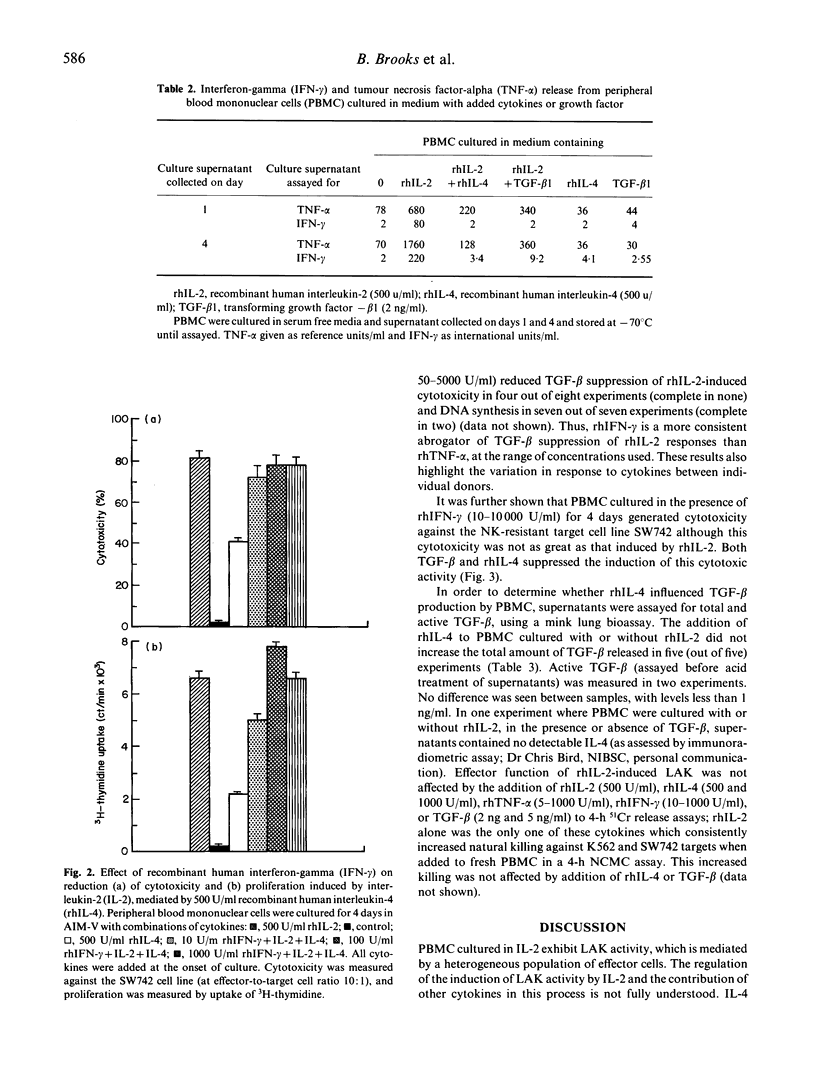
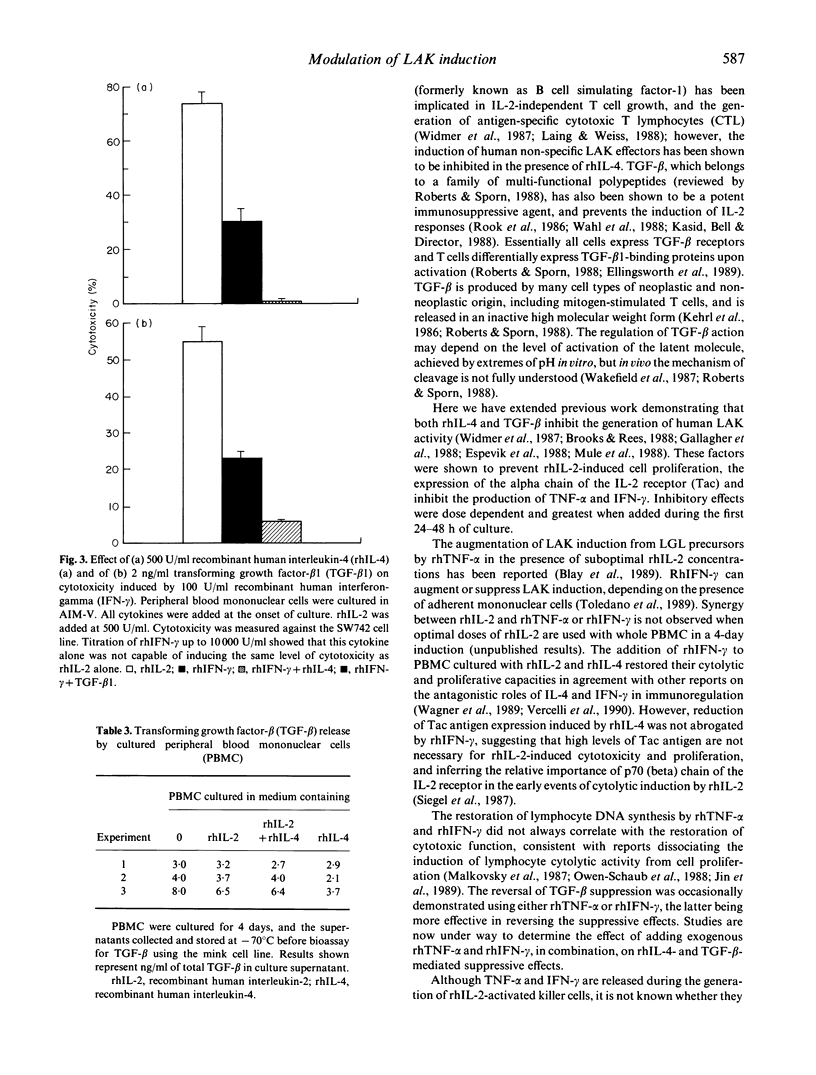
Recombinant human interleukin-4 (rhIL-4) and transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) suppressed the induction of lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) activity induced by recombinant human interleukin-2 (rhIL-2) in peripheral blood lymphocytes. DNA synthesis and the expression of the p55 alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor (Tac antigen) were also inhibited. The inhibitory effect was greatest when these factors were added during the first 48 h of a 4-day culture, with reduced cytolytic activity against both natural killer (NK) resistant and NK-sensitive tumour cell line targets. The suppressive action of both cytokines was accompanied by a reduction in tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) levels in lymphocyte culture supernatants. Recombinant human IFN-gamma (rhIFN-gamma), but not recombinant human TNF-alpha (rhTNF-alpha) was able to overcome the inhibitory effect of recombinant human interleukin-4 (rhIL-4) on LAK induction and DNA synthesis but not Tac antigen expression. However, cytotoxicity induced by rhIFN-gamma alone was also suppressed by rhIL-4 and TGF-beta 1, inferring that rhIFN-gamma-mediated abrogation of rhIL4 suppression was not simply a direct IL-2-independent effect on cytotoxicity. In addition, rhIL-4 did not increase TGF-beta production from rhIL-2-activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, suggesting that rhIL-4 did not mediate reduction of rhIL-2 responses through the induction of TGF-beta release.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blay J. Y., Bertoglio J., Fradelizi D., Chouaib S. Functional interactions of IL2 and TNF in the differentiation of LGL into LAK effectors. Int J Cancer. 1989 Oct 15;44(4):598–604. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braakman E., van Tunen A., Meager A., Lucas C. J. IL-2- and IFN gamma-enhanced natural cytotoxic activity: analysis of the role of different lymphoid subsets and implications for activation routes. Cell Immunol. 1986 May;99(2):476–488. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B., Rees R. C. Human recombinant IL-4 suppresses the induction of human IL-2 induced lymphokine activated killer (LAK) activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):162–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmas S. E., Meager A., Moore M. Production of interferon and tumour necrosis factor by cloned human natural cytotoxic lymphocytes and T cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Aug;69(2):441–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump W. L., 3rd, Owen-Schaub L. B., Grimm E. A. Synergy of human recombinant interleukin 1 with interleukin 2 in the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Doyle L. V., Bradley E. C. Interleukin 2-activated human killer cells are derived from phenotypically heterogeneous precursors. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2814–2822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Doyle L. V. Interleukin-2 activated human killer lymphocytes: lack of involvement of interferon in the development of IL-2-activated killer lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 1987 Oct 15;40(4):519–524. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou J. S., McBride W. H., Essner R., Rhoades K., Golub S., Holmes E. C., Morton D. L. Tumour necrosis factor production by IL-2-activated macrophages in vitro and in vivo. Immunology. 1989 Aug;67(4):514–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellingsworth L., Nakayama D., Dasch J., Segarini P., Carrillo P., Waegell W. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) receptor expression on resting and mitogen-activated T cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Apr;39(4):489–500. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Figari I. S., Ranges G. E., Palladino M. A., Jr Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha reciprocally regulate the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cell activity. Comparison between natural porcine platelet-derived TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2, and recombinant human TGF-beta 1. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2312–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher G., Stimson W. H., Findlay J., al-Azzawi F. Interleukin-6 enhances the induction of human lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1990;31(1):49–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01742495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher G., Wilcox F., al-Azzawi F. Interleukin-3 and interleukin-4 each strongly inhibit the induction and function of human LAK cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Nov;74(2):166–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Zhang H. Z., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1823–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Shiiba K., Shimizu Y., Suzuki R., Kumagai K. Generation of activated killer (AK) cells by recombinant interleukin 2 (rIL 2) in collaboration with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3124–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin B., Scott J. L., Vadas M. A., Burns G. F. TGF beta down-regulates TLiSA1 expression and inhibits the differentiation of precursor lymphocytes into CTL and LAK cells. Immunology. 1989 Apr;66(4):570–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasid A., Bell G. I., Director E. P. Effects of transforming growth factor-beta on human lymphokine-activated killer cell precursors. Autocrine inhibition of cellular proliferation and differentiation to immune killer cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):690–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami Y., Custer M. C., Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T. IL-4 regulates IL-2 induction of lymphokine-activated killer activity from human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3452–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Jakowlew S., Alvarez-Mon M., Derynck R., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Production of transforming growth factor beta by human T lymphocytes and its potential role in the regulation of T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1037–1050. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs E. J., Beckner S. K., Longo D. L., Varesio L., Young H. A. Cytokine gene expression during the generation of human lymphokine-activated killer cells: early induction of interleukin 1 beta by interleukin 2. Cancer Res. 1989 Feb 15;49(4):940–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing T. J., Weiss A. Evidence for IL-2 independent proliferation in human T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1056–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitz A., Stinson J. C., McCombs W. B., 3rd, McCoy C. E., Mazur K. C., Mabry N. D. Classification of human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976 Dec;36(12):4562–4569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limb G. A., Meager A., Woolley J., Wadhwa M., Biggerstaff J., Brown K. A., Wolstencroft R. A. Release of cytokines during generation of lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells by IL-2. Immunology. 1989 Dec;68(4):514–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Jíra M., Madar J., Malkovska V., Loveland B., Asherson G. L. Generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells does not require DNA synthesis. Immunology. 1987 Mar;60(3):471–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meager A., Parti S., Leung H., Peil E., Mahon B. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against antigenic determinants of recombinant human tumour necrosis factor (rTNF). Hybridoma. 1987 Jun;6(3):305–311. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1987.6.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason A., Overton R. Lymphokine-activated killer cells. Analysis of progenitors and effectors. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1193–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostensen M. E., Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha enhances cytolytic activity of human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Schaub L. B., Gutterman J. U., Grimm E. A. Synergy of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 2 in the activation of human cytotoxic lymphocytes: effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 2 in the generation of human lymphokine-activated killer cell cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):788–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Schaub L. B., Loudon W. G., Yagita M., Grimm E. A. Functional differentiation of human lymphokine-activated killing (LAK) is distinct from expansion and involves dissimilar interleukin 2 receptors. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jan;111(1):235–246. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa M. Z., Mulé J. J., Rosenberg S. A. Antitumor efficacy of lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin 2 in vivo: successful immunotherapy of established pulmonary metastases from weakly immunogenic and nonimmunogenic murine tumors of three district histological types. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):4973–4978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. M., Ortaldo J. R., Shalaby M. R., Svedersky L. P., Nedwin G. E., Bringman T. S., Hass P. E., Aggarwal B. B., Herberman R. B., Goeddel D. V. Natural killer-sensitive targets stimulate production of TNF-alpha but not TNF-beta (lymphotoxin) by highly purified human peripheral blood large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2592–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlinson L., Dalton B. J., Rogers K., Rees R. C. The influence of interferon alpha and gamma, singly or in combination on human natural cell mediated cytotoxicity. Biosci Rep. 1989 Oct;9(5):549–557. doi: 10.1007/BF01119797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:107–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook A. H., Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Burlington D. B., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Effects of transforming growth factor beta on the functions of natural killer cells: depressed cytolytic activity and blunting of interferon responsiveness. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3916–3920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A. Immunotherapy of cancer using interleukin 2: current status and future prospects. Immunol Today. 1988 Feb;9(2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers T. J., Mason A. T., Ortaldo J. R. Regulation of human natural killer cell activity by interferon-gamma: lack of a role in interleukin 2-mediated augmentation. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2176–2180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. H., Bittner G., Storer B., Willson J. K. Synergistic antitumor effects of tumor necrosis factor and gamma-interferon on human colon carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 1;47(11):2809–2813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Sharon M., Smith P. L., Leonard W. J. The IL-2 receptor beta chain (p70): role in mediating signals for LAK, NK, and proliferative activities. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.3116668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone S., Utsugi T., Nii A., Ogura T. Differential effects of recombinant interferons alpha, beta, and gamma on induction of human lymphokine (IL-2)-activated killer activity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 May 18;80(6):425–431. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.6.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano M., Mathiot C., Michon J., Andreu G., Lando D., Brandely M., Fridman W. H. Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and interleukin-2 in the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cell cytotoxicity--IFN-gamma-induced suppressive activity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1989;30(1):57–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01665031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M., Londei M., Feldmann M. Human T cells from autoimmune and normal individuals can produce tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1807–1814. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Lauener R. P., Geha R. S. IL-4 inhibits the synthesis of IFN-gamma and induces the synthesis of IgE in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):570–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner F., Fischer N., Lersch C., Hart R., Dancygier H. Interleukin 4 inhibits the interleukin 2-induced production of its functional antagonist, interferon gamma. Immunol Lett. 1989 Jun 1;21(3):237–241. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wong H. L., Dougherty S., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Ellingsworth L., Schmidt J. A., Hall G., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor-beta is a potent immunosuppressive agent that inhibits IL-1-dependent lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3026–3032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Masui T., Harris C. C., Sporn M. B. Distribution and modulation of the cellular receptor for transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):965–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Interleukin 2 enhances natural killer cell activity through induction of gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):992–997. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.992-997.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer M. B., Acres R. B., Sassenfeld H. M., Grabstein K. H. Regulation of cytolytic cell populations from human peripheral blood by B cell stimulatory factor 1 (interleukin 4). J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Ortaldo J. R. One-signal requirement for interferon-gamma production by human large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


