Abstract
Indirect immunofluorescence techniques employing sheep monospecific antisera to human IgG subclasses on unfixed cryostat sections have revealed the IgG subclass distribution in autoantibodies to pancreatic islets (ICA), thyroid epithelial (TMA), gastric parietal (PCA) and adrenal fasciculata (AdA) cells. Whereas antibodies were detected in all four subclasses in 21 of 27 TMA positive sera (mean IgG titre 29 +/- 5 . 2), 13 of 15 PCA (mean IgG titre 41 +/- 3 . 8) and eight of 14 AdA sera (mean IgG titre 10 +/- 3 . 1), only four of 35 ICA positive sera (mean IgG titre 45 +/- 3 . 6) reacted in all four subclasses. Approximately 50% of ICA positive sera showed a restricted polyclonal response to the 'common' pancreatic antigen and 12% of these sera reacted only with IgG2 subclass. The restriction rarely applied to co-existent thyrogastric antibodies in these sera and was independent of the ability of ICA to fix complement. Lesser subclass restrictions were observed in antibody responses to the 'common' antigen of the adrenal cortex.
Full text
PDF

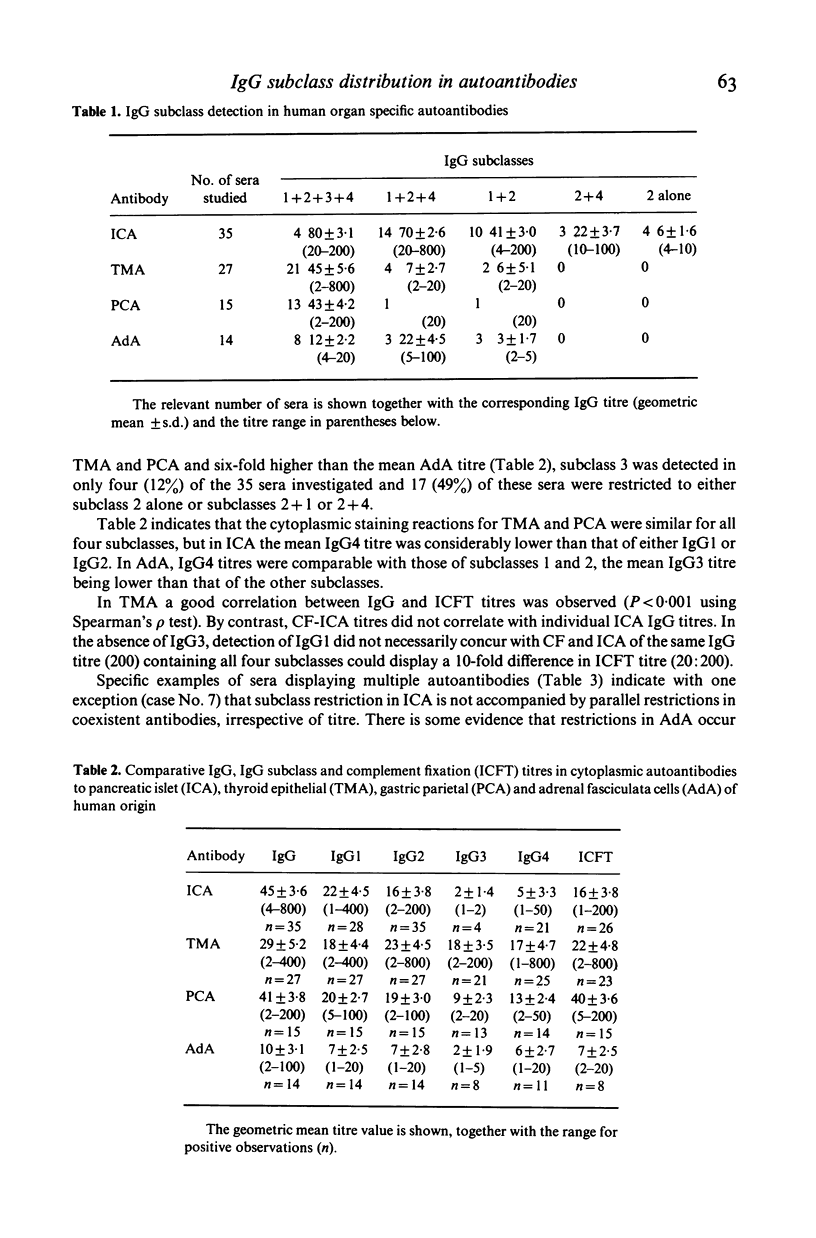
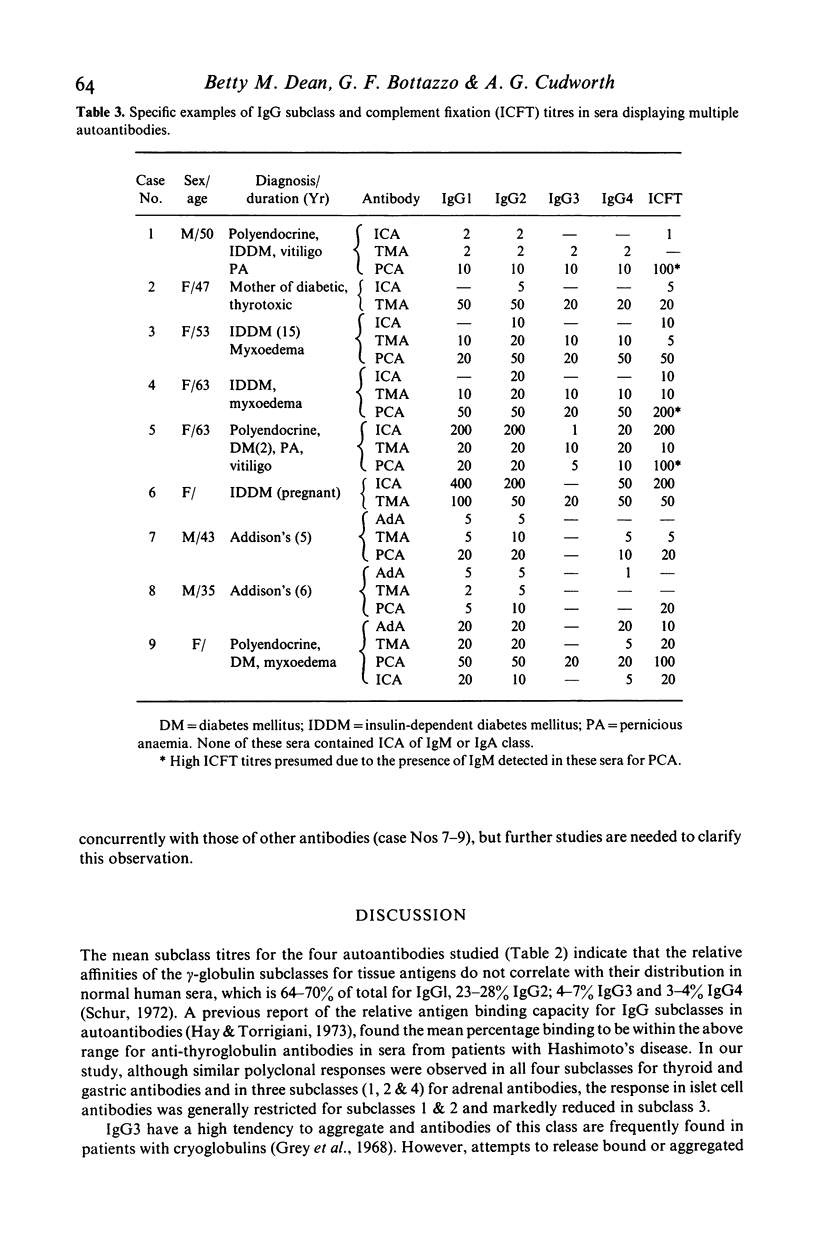


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baekkeskov S., Nielsen J. H., Marner B., Bilde T., Ludvigsson J., Lernmark A. Autoantibodies in newly diagnosed diabetic children immunoprecipitate human pancreatic islet cell proteins. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):167–169. doi: 10.1038/298167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu A., Quismorio F. P., Jr, Friou G. J., Vayuvegula B., Mirick G. IgG antibodies to double-stranded DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus sera. Independent variation of complement fixing activity and total antibody content. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jun;22(6):565–570. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky H. J., Wolf E., Cudworth A. G., Dean B. M., Nineham L. J., Bottazzo G. F., Matthews J. A., Kurtz A. B., Kohner E. M. Genetic and immunologic factors in microvascular disease in type I insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Jan;31(1):70–74. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., Gorsuch A. N., Cudworth A. G., Doniach D. Complement-fixing islet-cell antibodies in type-I diabetes: possible monitors of active beta-cell damage. Lancet. 1980 Mar 29;1(8170):668–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers J. A., Ewins A. R. Herpes gestationis: studies on the binding characteristics, activity and pathogenetic significance of the complement-fixing factor. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jan;31(1):38–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubick A., Sontheimer R. D., Gilliam J. N., Ziff M. An appraisal of tests for native DNA antibodies in connective tissue diseases. Clinical usefulness of Crithidia luciliae assay. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Aug;89(2):186–192. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-2-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Complement-fixing IgG1 constitutes a new subclass of mouse IgG. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):492–493. doi: 10.1038/281492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facer C. A. Direct antiglobulin reactions in Gambian children with P. falciparum malaria. III. Expression of IgG subclass determinants and genetic markers and association with anaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jul;41(1):81–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulpius B. W., Miskin R., Reich E. Antibodies from myasthenic patients that compete with cholinergic agents for binding to nicotinic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4326–4330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorsuch A. N., Spencer K. M., Lister J., McNally J. M., Dean B. M., Bottazzo G. F., Cudworth A. G. Evidence for a long prediabetic period in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1981 Dec 19;2(8260-61):1363–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92795-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Kohler P. F., Terry W. D., Franklin E. C. Human monoclonal gamma G-cryoglobulins with anti-gamma-globulin activity. J Clin Invest. 1968 Aug;47(8):1875–1884. doi: 10.1172/JCI105878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Torrigiani G. The distribution of anti-thyroglobulin antibodies in the immunoglobulin G subclasses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Dec;15(4):517–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman D. E., Dorrington K. J., Painter R. H. The structure and function of immunoglobulin domains. II. The importance of interchain disulfide bonds and the possible role of molecular flexibility in the interaction between immunoglobulin G and complement. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1726–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefvert A. K., Bergström K. Immunoglobulins in myasthenia gravis: effect of human lymph IgG 3 and F (ab')2 fragments on a cholinergic receptor preparation from Torpedo marmorata. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;7(2):115–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye L., Pontes de Carvalho L. C., Roitt I. M. Restrictions in the response to autologous thyroglobulin in the human. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Hansburg D., Briles D. E., Nicolotti R. A., Davie J. M. Subclass restriction of murine anti-carbohydrate antibodies. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):566–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puritz E. M., Yount W. J., Newell M., Utsinger P. D. Immunoglobulin classes and IgG subclasses of human antinuclear antibodies. A correlation of complement fixation and the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Nov;2(1):98–113. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sams W. M., Jr, Schur P. H. Studies of the antibodies in pemphigoid and pemphigus. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Aug;82(2):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Borel H., Gelfand E. W., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Selective gamma-g globulin deficiencies in patients with recurrent pyogenic infections. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 17;283(12):631–634. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009172831205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Monroe M., Rothfield N. The gammaG subclass of antinuclear and antinucleic acid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):174–182. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakib F., Stanworth D. R. Human IgG subclasses in health and disease. (A review). Part I. Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Jul-Sep;10(3):463–479. doi: 10.1007/BF02938793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer R. D., Gilliam J. N. DNA antibody class, subclass, and complement fixation in systemic lupus erythematosus with and without nephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Aug;10(4):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanislawski M., Mitard M. Recognition of two subclasses of mouse IgGl (gamma F). Immunochemistry. 1976 Dec;13(12):979–984. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY W. D., FAHEY J. L. SUBCLASSES OF HUMAN GAMMA-2-GLOBULIN BASED ON DIFFERENCES IN THE HEAVY POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS. Science. 1964 Oct 16;146(3642):400–401. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3642.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo T., Friou G. J., Spiegelberg H. L. Immunoglobulin G subclass of human antinuclear antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):145–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M., Doniach D. Quantitative distribution of human thyroglobulin autoantibodies in different immunoglobulin classes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Sep;3(7):621–630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van De Winkel M., Smets G., Gepts W., Pipeleers D. Islet cell surface antibodies from insulin-dependent diabetics bind specifically to pancreatic B cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):41–49. doi: 10.1172/JCI110601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


