Abstract
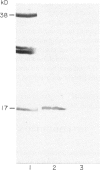
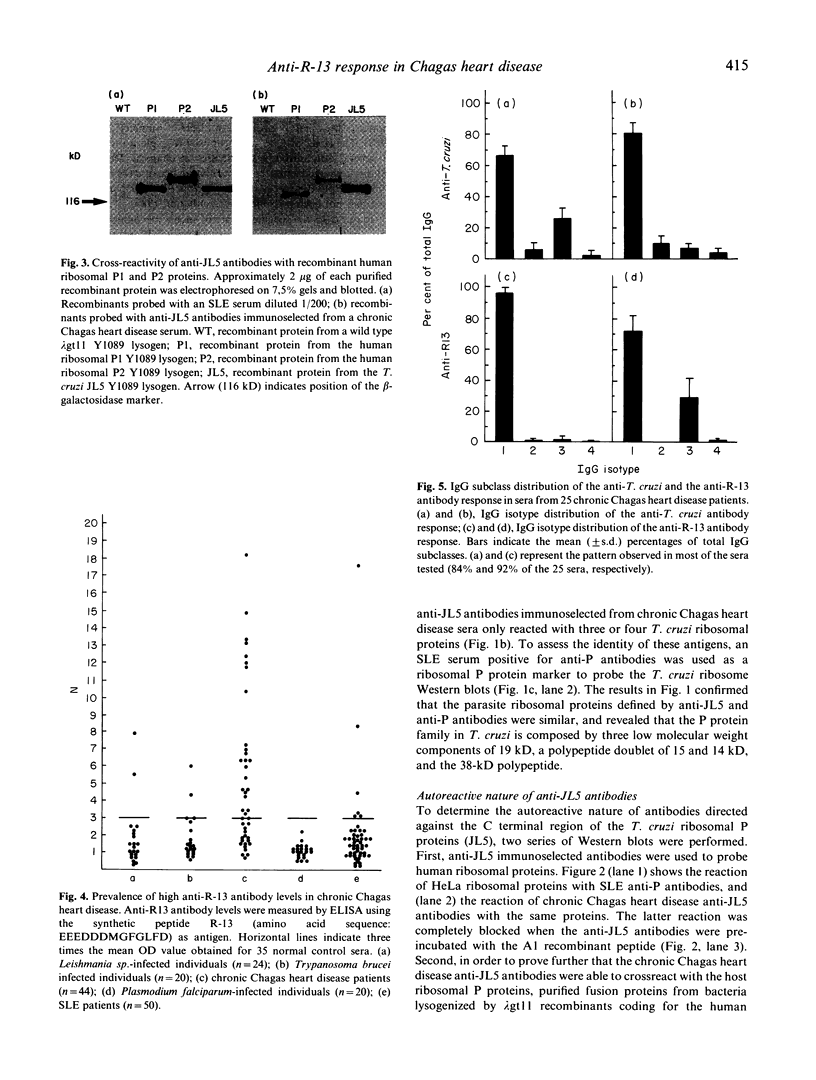
The C terminal region of a Trypanosoma cruzi ribosomal P protein, encoded by the lambda gt11 JL5 recombinant, defined a major antigenic determinant in chronic Chagas heart disease. Immunopurified anti-JL5 antibodies were tested for anti-human ribosome reactivity by immunoblotting. They recognized the parasite ribosomal P proteins and clearly reacted with the corresponding human P proteins. The peptide R-13, that comprises the 13 C terminal residues of the JL5 recombinant and defines the specificity shared between chronic Chagas heart disease anti-JL5 antibodies and the systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) anti-P antibodies, was used to study the specificity and the IgG subclass distribution of the anti-R-13 response by ELISA. The R-13 autoepitope is recognized mainly by sera from chagasic patients, but not by sera from malaria patients. Moreover, there was a significant correlation between anti-R-13 antibody levels and anti-T. cruzi antibody titres. The anti-R-13 response was mainly restricted to the IgG1 heavy chain isotype and correlated with the anti-T. cruzi isotype distribution.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acosta A. M., Sadigursky M., Santos-Buch C. A. Anti-striated muscle antibody activity produced by Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Mar;172(3):364–369. doi: 10.3181/00379727-172-41571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Elkon K. B. Clinical and serologic associations of the antiribosomal P protein antibody. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):981–985. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Llovet R., Elkon K. Immunoblot analysis of IgG subclasses of multiple lupus autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2231–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damian R. T. Molecular mimicry: parasite evasion and host defense. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;145:101–115. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74594-2_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K., Skelly S., Parnassa A., Moller W., Danho W., Weissbach H., Brot N. Identification and chemical synthesis of a ribosomal protein antigenic determinant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7419–7423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvão-Castro B., Sá Ferreira J. A., Marzochi K. F., Marzochi M. C., Coutinho S. G., Lambert P. H. Polyclonal B cell activation, circulating immune complexes and autoimmunity in human american visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):58–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R., Hyde J. E., Goman M., Simmons D. L., Hope I. A., Mackay M., Scaife J., Merkli B., Richle R., Stocker J. Major surface antigen gene of a human malaria parasite cloned and expressed in bacteria. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):379–382. doi: 10.1038/311379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. Autoimmune phenomena in chronic chagasic cardiopathy. Parasitol Today. 1985 Jul;1(1):6–9. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(85)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F. Is there autoimmunity in Chagas disease? Parasitol Today. 1985 Jul;1(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(85)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayakawa T., Louis J., Izui S., Lambert P. H. Autoimmune response to DNA, red blood cells, and thymocyte antigens in association with polyclonal antibody synthesis during experimental African trypanosomiasis. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):296–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhorne J., Kim K. J., Asofsky R. Distribution of immunoglobulin isotypes in the nonspecific B-cell response induced by infection with Plasmodium chabaudi adami and Plasmodium yoelii. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jan;90(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. J., Mesri E., Benarous R., Levitus G., Schijman A., Levy-Yeyati P., Chiale P. A., Ruiz A. M., Kahn A., Rosenbaum M. B. Identification of major Trypanosoma cruzi antigenic determinants in chronic Chagas' heart disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Nov;41(5):530–538. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. J., Rossi R., Levitus G., Mesri E., Bonnefoy S., Kerner N., Hontebeyrie-Joskowicz M. The cloned C-terminal region of a Trypanosoma cruzi P ribosomal protein harbors two antigenic determinants. Immunol Lett. 1990 Mar-Apr;24(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90038-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesri E. A., Levitus G., Hontebeyrie-Joskowicz M., Dighiero G., Van Regenmortel M. H., Levin M. J. Major Trypanosoma cruzi antigenic determinant in Chagas' heart disease shares homology with the systemic lupus erythematosus ribosomal P protein epitope. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1219–1224. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1219-1224.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBAUM M. B. CHAGASIC MYOCARDIOPATHY. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1964 Nov;7:199–225. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(64)80020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich B. E., Steitz J. A. Human acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins P0, P1, and P2: analysis of cDNA clones, in vitro synthesis, and assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4065–4074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schijman A. G., Dusetti N. J., Vazquez M. P., Lafon S., Levy-Yeyati P., Levin M. J. Nucleotide cDNA and complete deduced amino acid sequence of a Trypanosoma cruzi ribosomal P protein (P-JL5). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3399–3399. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinella S., Liegeard P., Guilbert B., Hontebeyrie-Joskowicz M. Anti-Ia treatment modulates specific and polyclonal antibody responses in Trypanosoma cruzi-infected mice. J Autoimmun. 1989 Dec;2(6):791–802. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szarfman A., Terranova V. P., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., de Fatima Lima M., Scheinman J. I., Martin G. R. Antibodies to laminin in Chagas' disease. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1161–1171. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Imperio Lima M. R., Eisen H., Minoprio P., Joskowicz M., Coutinho A. Persistence of polyclonal B cell activation with undetectable parasitemia in late stages of experimental Chagas' disease. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):353–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]