Abstract
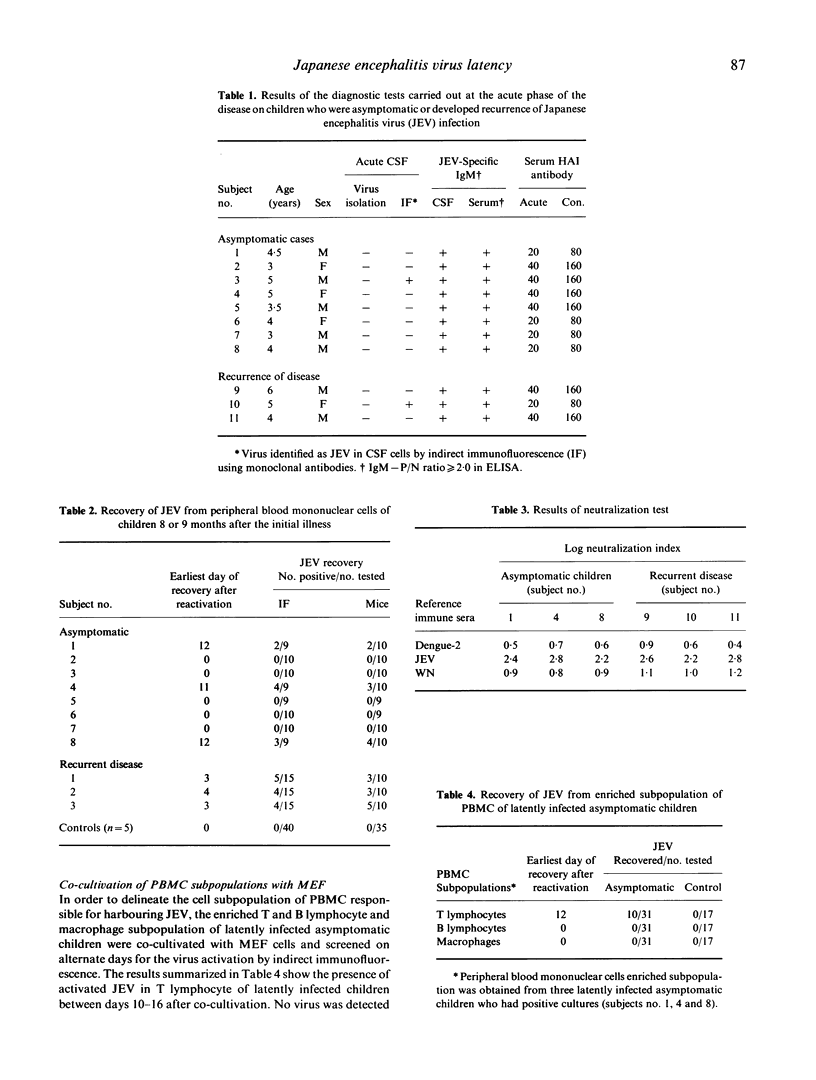
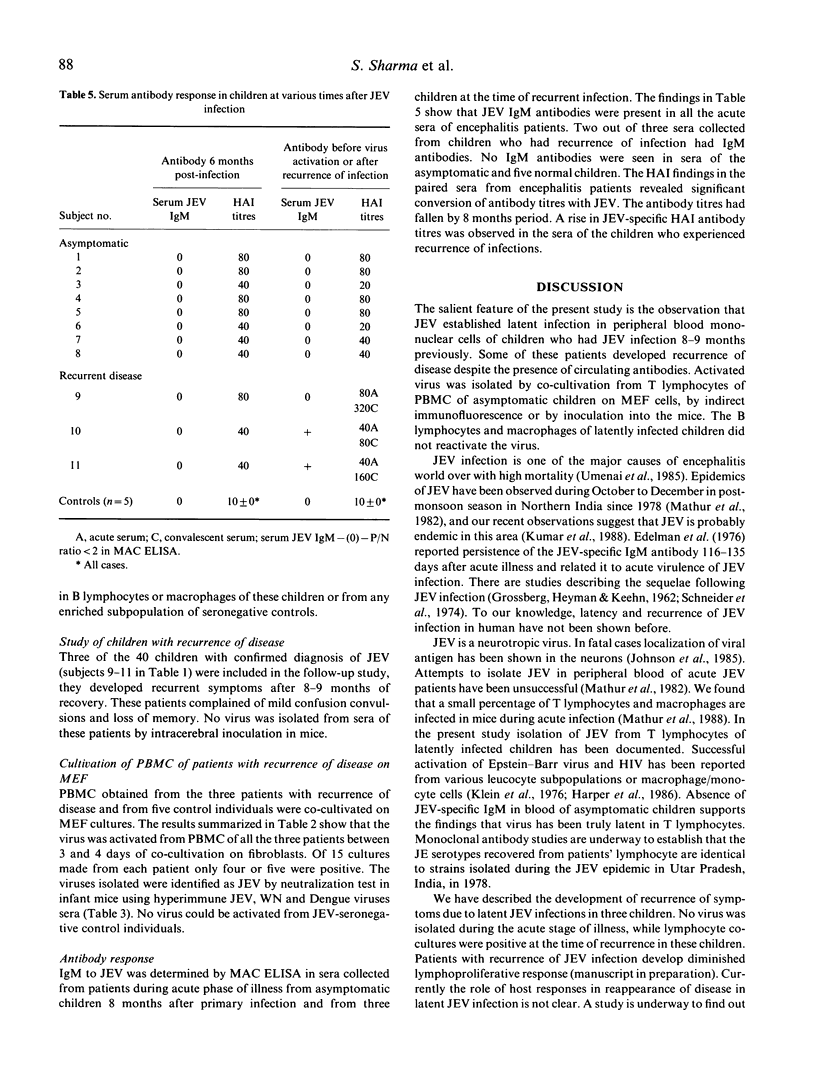
In a study group of 40 children who had been admitted to hospital with acute encephalitis, the disease was due to infection with Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). Three children developed recurrence of disease 8-9 months later. No virus had been isolated from these three patients during the acute stage of their illness, but virus was recovered from all during the recurrence phase by co-cultivation of their peripheral blood mononuclear cells in primary mouse embryo fibroblast cultures. Virus was also recovered by co-cultivation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells collected 8 months after their acute disease from three out of eight randomly selected asymptomatic children within the study group but not from similar cultures set up from JEV-seronegative children used as controls. Virus was also isolated by co-cultivation of T lymphocytes of asymptomatic children as detected by indirect immunofluorescence or by inoculation in mice.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke D. S., Nisalak A., Ussery M. A., Laorakpongse T., Chantavibul S. Kinetics of IgM and IgG responses to Japanese encephalitis virus in human serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1093–1099. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Schneider R. J., Vejjajiva A., Pornpibul R., Voodhikul P. Persistence of virus-specific IgM and clinical recovery after Japanese encephalitis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Sep;25(5):733–738. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSBERG S., HEYMAN A., KEEHN R. J. Neurologic sequelae of Japanese encephalitis. Report of a cooperative study. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1962;87:114–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Detection of lymphocytes expressing human T-lymphotropic virus type III in lymph nodes and peripheral blood from infected individuals by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):772–776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Burke D. S., Elwell M., Leake C. J., Nisalak A., Hoke C. H., Lorsomrudee W. Japanese encephalitis: immunocytochemical studies of viral antigen and inflammatory cells in fatal cases. Ann Neurol. 1985 Nov;18(5):567–573. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Svedmyr E., Jondal M., Persson P. O. EBV-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA)-positive cells in the peripheral blood of infectious mononucleosis patients. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Mathur A., Kumar A., Sharma S., Saksena P. N., Chaturvedi U. C. Japanese encephalitis--an important cause of acute childhood encephalopathy in Lucknow, India. Postgrad Med J. 1988 Jan;64(747):18–22. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.64.747.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Chaturvedi U. C. Host defence mechanisms against Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):805–811. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Rawat S., Chaturvedi U. C. Japanese encephalitis virus latency following congenital infection in mice. J Gen Virol. 1986 May;67(Pt 5):945–947. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-5-945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Arora K. L., Rawat S., Chaturvedi U. C. Persistence, latency and reactivation of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):381–385. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Bharadwaj M., Kulshreshtha R., Rawat S., Jain A., Chaturvedi U. C. Immunopathological study of spleen during Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Jun;69(3):423–432. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Chaturvedi U. C., Tandon H. O., Agarwal A. K., Mathur G. P., Nag D., Prasad A., Mittal V. P. Japanese encephalitis epidemic in Uttar Pradesh, India during 1978. Indian J Med Res. 1982 Feb;75:161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Kulshreshtha R., Chaturvedi U. C. Evidence for latency of Japanese encephalitis virus in T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):461–465. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Kulshreshtha R., Chaturvedi U. C. Induction of secondary immune response by reactivated Japanese encephalitis virus in latently infected mice. Immunology. 1987 Apr;60(4):481–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur A., Kumar R., Sharma S., Kulshreshtha R., Kumar A., Chaturvedi U. C. Rapid diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis by immunofluorescent examination of cerebrospinal fluid. Indian J Med Res. 1990 Jan;91:1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Firestone M. H., Edelman R., Chieowanich P., Pornpibul R. Clinical sequelae after japanese encephalitis: a one year follow-up study in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1974 Dec;5(4):560–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan J. F., Beck M., Smith C. C., Aurelian L. Reactivation of herpes simplex virus is associated with production of a low molecular weight factor that inhibits lymphokine activity in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1234–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umenai T., Krzysko R., Bektimirov T. A., Assaad F. A. Japanese encephalitis: current worldwide status. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(4):625–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


