Abstract
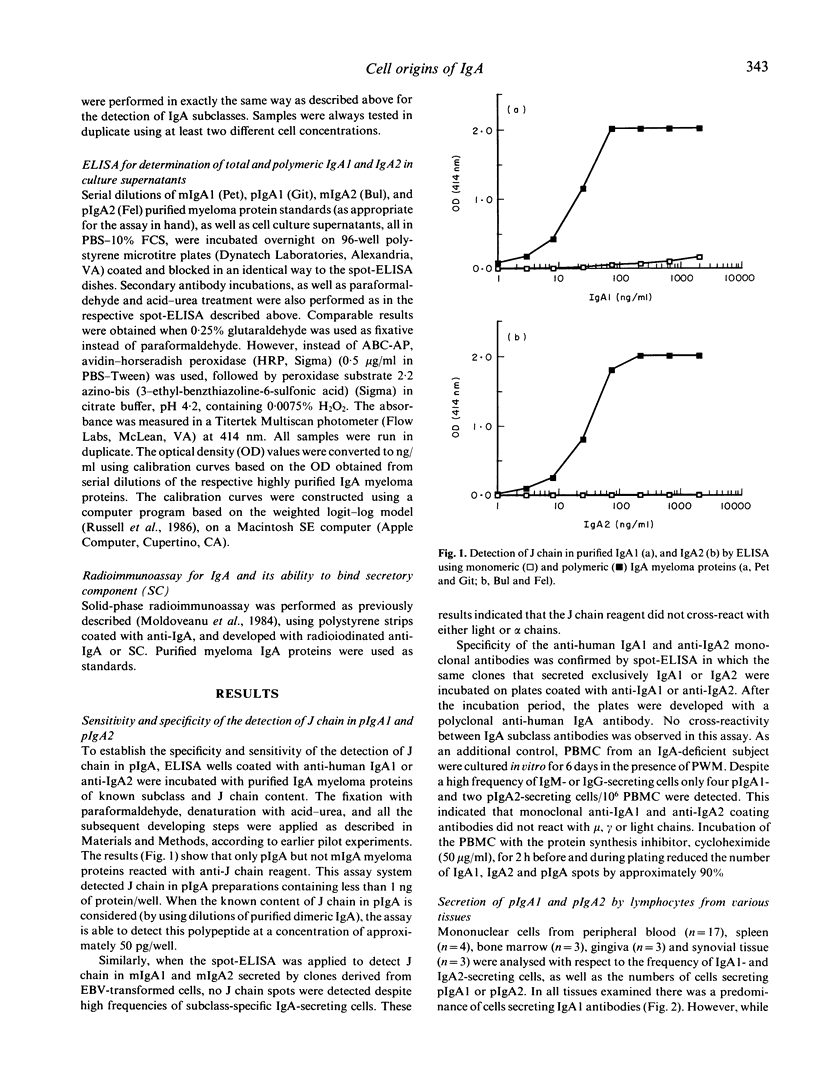
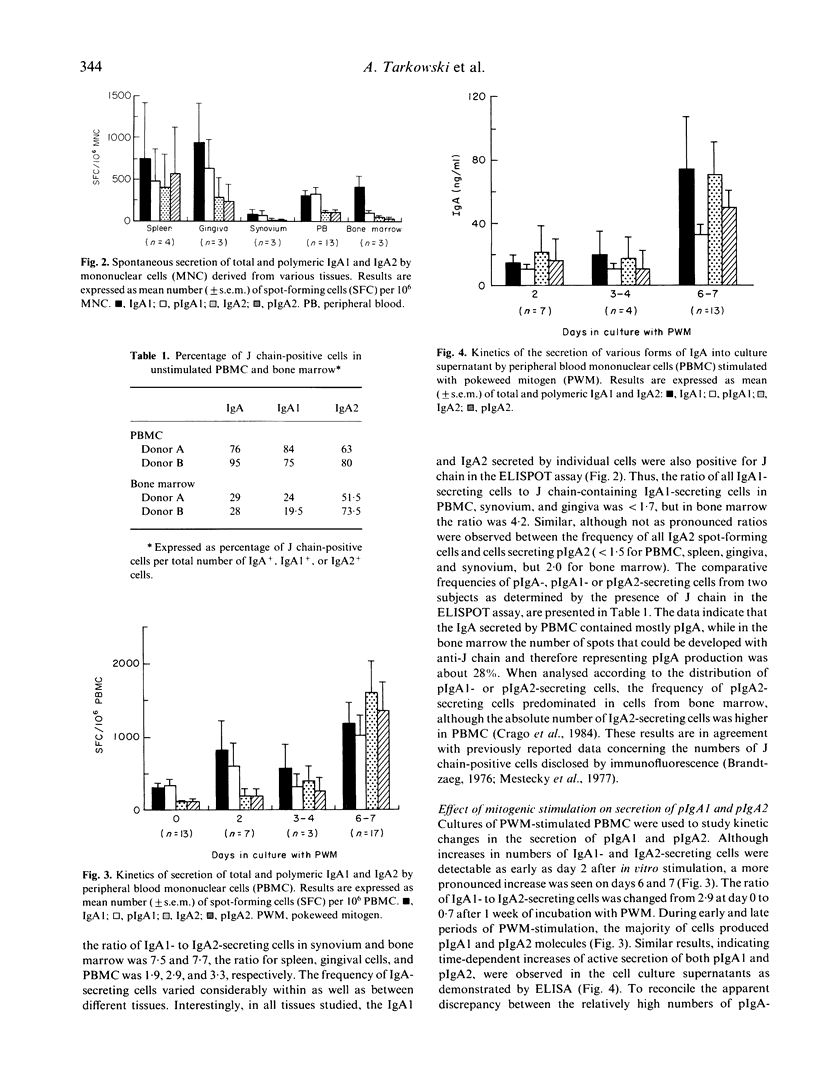
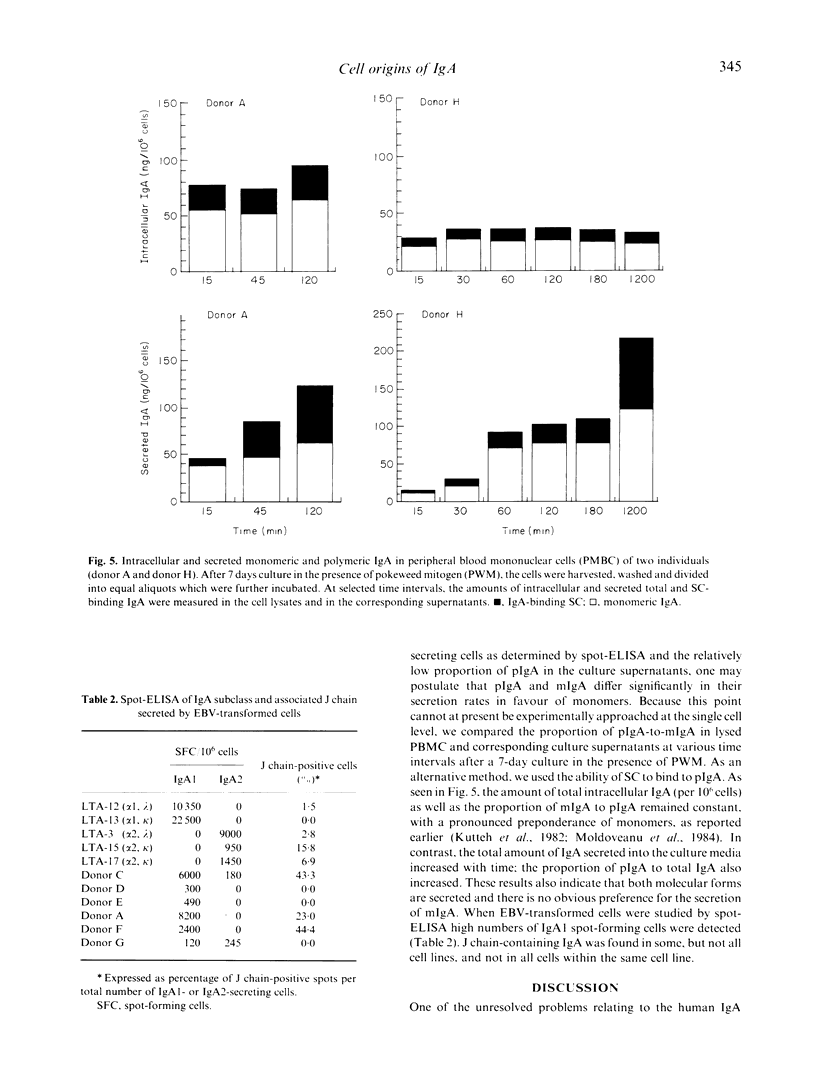
Using modified ELISA and spot-ELISA, which permit the parallel determination of heavy chain subclass and the presence of covalently linked J chain, we analysed IgA found in cell culture supernatants or secreted by individual cells from peripheral blood, spleen, bone marrow, gingiva and synovial tissue, with respect to its polymeric or monomeric IgA form (pIgA, mIgA) and IgA1 or IgA2 subclass. The ELISA for determination of J chain in tissue culture supernatants was specific and highly sensitive (detection limit in pg). The results demonstrated that IgA1-producing cells predominated in the tissues examined, and that J chain could be detected in association with the majority of IgA1 and IgA2 secreted by individual cells. With respect to the frequency of cells secreting polymeric, J chain-containing IgA, only 20-30% of cells from the bone marrow were engaged in the synthesis of PIgA. In other tissues the frequency of cells secreting pIgA1 and pIgA2 was considerably higher. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells secreting pIgA2 were easily inducible during stimulation with T cell-dependent pokeweed mitogen, whereas Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cells secreted preferentially mIgA1. When the frequencies of pIgA-, pIgA1- or pIgA2-secreting cells (determined by spot-ELISA technique) from different tissues were correlated with the proportion of pIgA to mIgA (and IgA subclasses) secreted in tissue culture supernatants, data obtained suggest that many individual IgA-producing cells could be engaged in simultaneous secretion of mIgA and pIgA.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargellesi A., Periman P., Scharff M. D. Synthesis, assembly, and secretion of globulin by mouse myeloma cells. IV. Assembly of IgA. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):126–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Berdal P. J chain in malignant human IgG immunocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(4):403–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Studies on J chain and binding site for secretory component in circulating human B cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):50–58. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Two types of IgA immunocytes in man. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 30;243(126):142–143. doi: 10.1038/newbio243142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Murphy B. R., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Mestecky J. Subclass distribution and molecular form of immunoglobulin A hemagglutinin antibodies in sera and nasal secretions after experimental secondary infection with influenza A virus in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):259–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.259-264.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull D. M., Bienenstock J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Studies on human intestinal immunoglobulin A. Gastroenterology. 1971 Mar;60(3):370–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J. N., Zolla S., Scharff M. D., Franklin E. C. The synthesis and assembly of immunoglobulins by malignant human plasmacytes. 3. Heterogeneity in IgA polymer assembly. Eur J Immunol. 1974 May;4(5):367–369. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Koopman W. J. In vitro regulation of IgA subclass synthesis. I. Discordance between plasma cell production and antibody secretion. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1615–1621. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crago S. S., Kutteh W. H., Moro I., Allansmith M. R., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Mestecky J. Distribution of IgA1-, IgA2-, and J chain-containing cells in human tissues. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):16–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crago S. S., Mestecky J. Secretory component: interactions with intracellular and surface immunoglobulins of human lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):906–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C. C., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H., Ouchterlony O., Tarkowski A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Dive C., Rambaud J. C., Vaerman J. P. IgA subclasses in various secretions and in serum. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):383–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Elkom K. B., Geubel A. P., Hodgson H. F., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. Changes in size, subclass, and metabolic properties of serum immunoglobulin A in liver diseases and in other diseases with high serum immunoglobulin A. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):358–367. doi: 10.1172/JCI110777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangakis M. V., Koopman W. J., Kiyono H., Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R. An enzymatic method for preparation of dissociated murine Peyer's patch cells enriched for macrophages. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikata M., Tachibana K., Imai M., Naito S., Oinuma A., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Immunoglobulin A antibody against hepatitis B core antigen of polymeric and monomeric forms, as well as of IgA1 and IgA2 subclasses, in acute and chronic infection with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 1986 Jul-Aug;6(4):652–657. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam K. B., Hassan M. S., Engström P. E., Hammarström L., Smith C. I. Transcription, translation and secretion of both IgA subclasses in polyclonally activated human lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):977–982. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kett K., Brandtzaeg P., Radl J., Haaijman J. J. Different subclass distribution of IgA-producing cells in human lymphoid organs and various secretory tissues. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3631–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland M. E. The coming of age of the immunoglobulin J chain. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:425–453. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H., Koopman W. J., Conley M. E., Egan M. L., Mestecky J. Production of predominantly polymeric IgA by human peripheral blood lymphocytes stimulated in vitro with mitogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1424–1429. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H., Moldoveanu Z., Prince S. J., Kulhavy R., Alonso F., Mestecky J. Biosynthesis of J-chain in human lymphoid cells producing immunoglobulins of various isotypes. Mol Immunol. 1983 Sep;20(9):967–976. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H., Prince S. J., Mestecky J. Tissue origins of human polymeric and monomeric IgA. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):990–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue C., Tarkowski A., Mestecky J. Systemic immunization with pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine induces a predominant IgA2 response of peripheral blood lymphocytes and increases of both serum and secretory anti-pneumococcal antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3793–3800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Beale M. G., Alley C. D., Nash G. S., Bertovich M. J., Bragdon M. J. Synthesis and secretion of IgA, IgM, and IgG by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in human disease states, by isolated human intestinal mononuclear cells, and by human bone marrow mononuclear cells from ribs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:498–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascart-Lemone F. O., Duchateau J. R., Oosterom J., Butzler J. P., Delacroix D. L. Kinetics of anti-Campylobacter jejuni monomeric and polymeric immunoglobulin A1 and A2 responses in serum during acute enteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1253–1257. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1253-1257.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascart-Lemone F., Carlsson B., Jalil F., Hahn-Zoric M., Duchateau J., Hanson L. A. Polymeric and monomeric IgA response in serum and milk after parenteral cholera and oral typhoid vaccination. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Oct;28(4):443–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., McGhee J. R. Immunoglobulin A (IgA): molecular and cellular interactions involved in IgA biosynthesis and immune response. Adv Immunol. 1987;40:153–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Russell M. W. IgA subclasses. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:277–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Winchester R. J., Hoffman T., Kunkel H. G. Parallel synthesis of immunoglobulins and J chain in pokeweed mitogen-stimulated normal cells and in lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):760–765. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Kubagawa H., Butler J. L., Cooper M. D. Ig isotypes produced by EBV-transformed B cells as a function of age and tissue distribution. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3887–3892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldoveanu Z., Egan M. L., Mestecky J. Cellular origins of human polymeric and monomeric IgA: intracellular and secreted forms of IgA. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3156–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moro I., Iwase T., Komiyama K., Moldoveanu Z., Mestecky J. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) polymerization sites in human immunocytes: immunoelectron microscopic study. Cell Struct Funct. 1990 Apr;15(2):85–91. doi: 10.1247/csf.15.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro Ponzi A., Merlino C., Angeretti A., Penna R. Virus-specific polymeric immunoglobulin A antibodies in serum from patients with rubella, measles, varicella, and herpes zoster virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):505–509. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.505-509.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Tarkowski A., McGhee M. L., Moldoveanu Z., Mestecky J., Hirsch H. Z., Koopman W. J., Hamada S., McGhee J. R., Kiyono H. Analysis of human IgG and IgA subclass antibody-secreting cells from localized chronic inflammatory tissue. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1150–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhouse R. M.E. Immunoglobulin a biosynthesis. Intracellular accumulation of 7 S subunits. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jul 15;16(1):71–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80689-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radl J., Schuit H. R., Mestecky J., Hijmans W. The origin of monomeric and polymeric forms of IgA in man. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):57–65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Brown T. A., Radl J., Haaijman J. J., Mestecky J. Assay of human IgA subclass antibodies in serum and secretions by means of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 27;87(1):87–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomana M., Kulhavy R., Mestecky J. Receptor-mediated binding and uptake of immunoglobulin A by human liver. Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):762–770. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


