Abstract
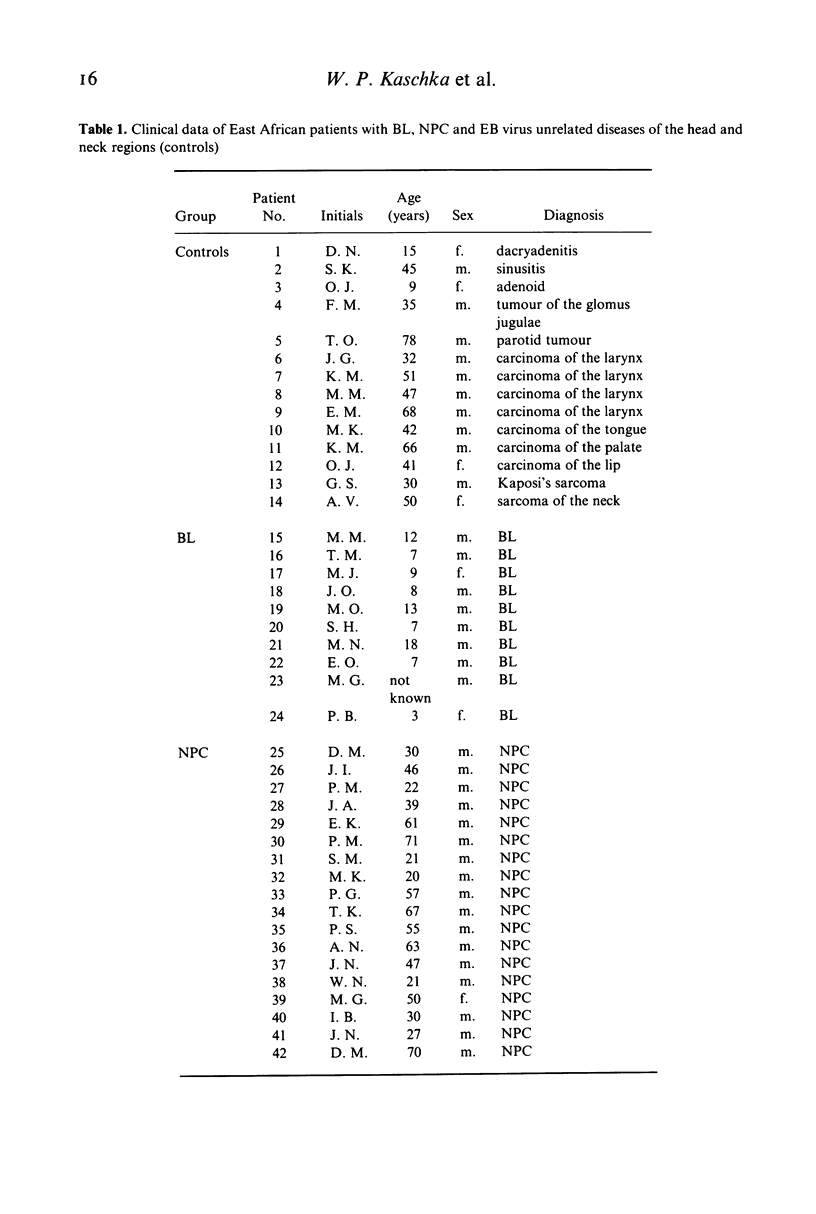
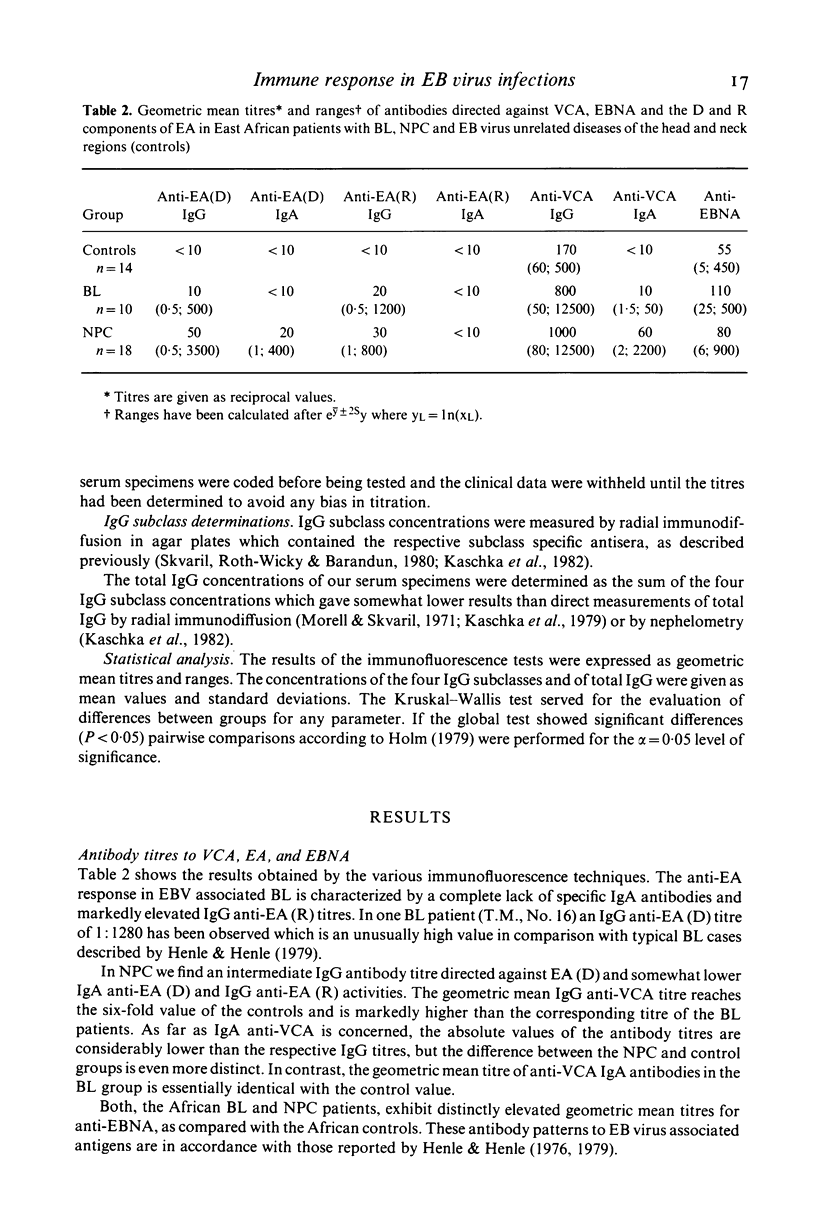
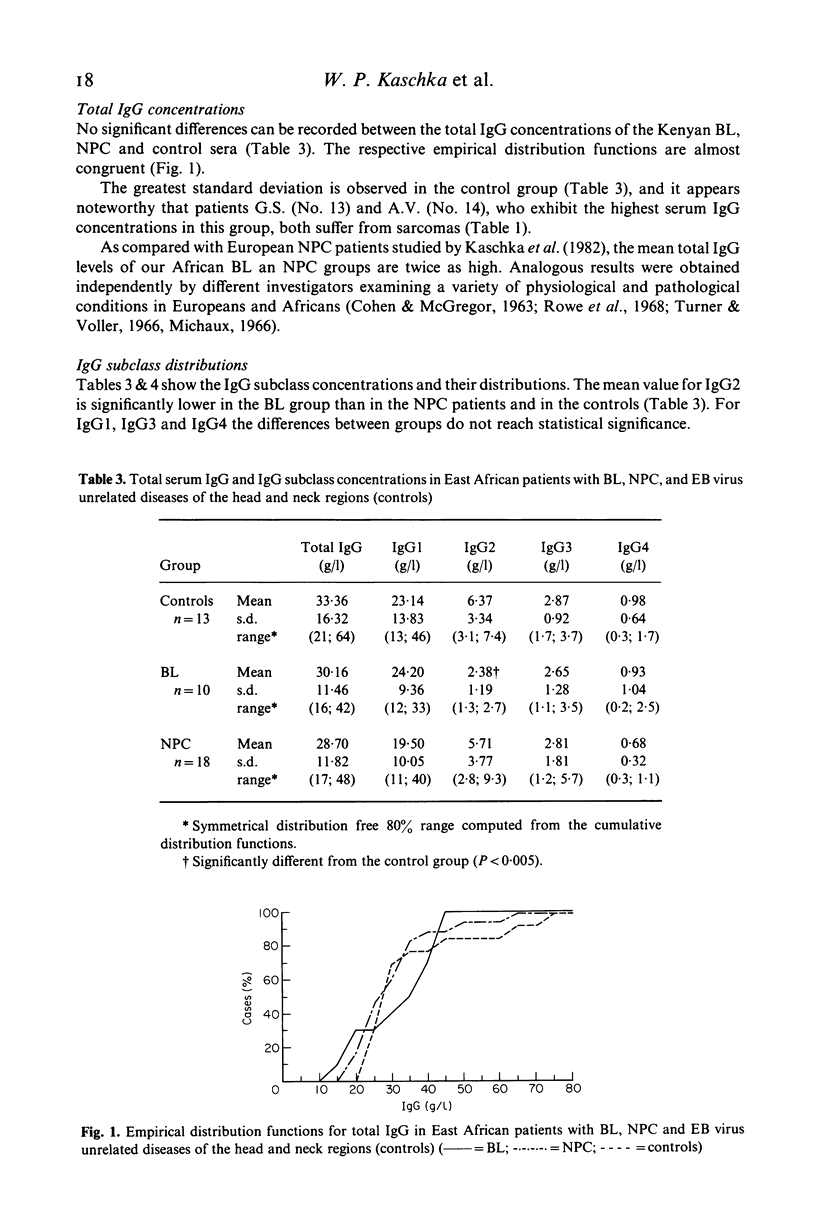
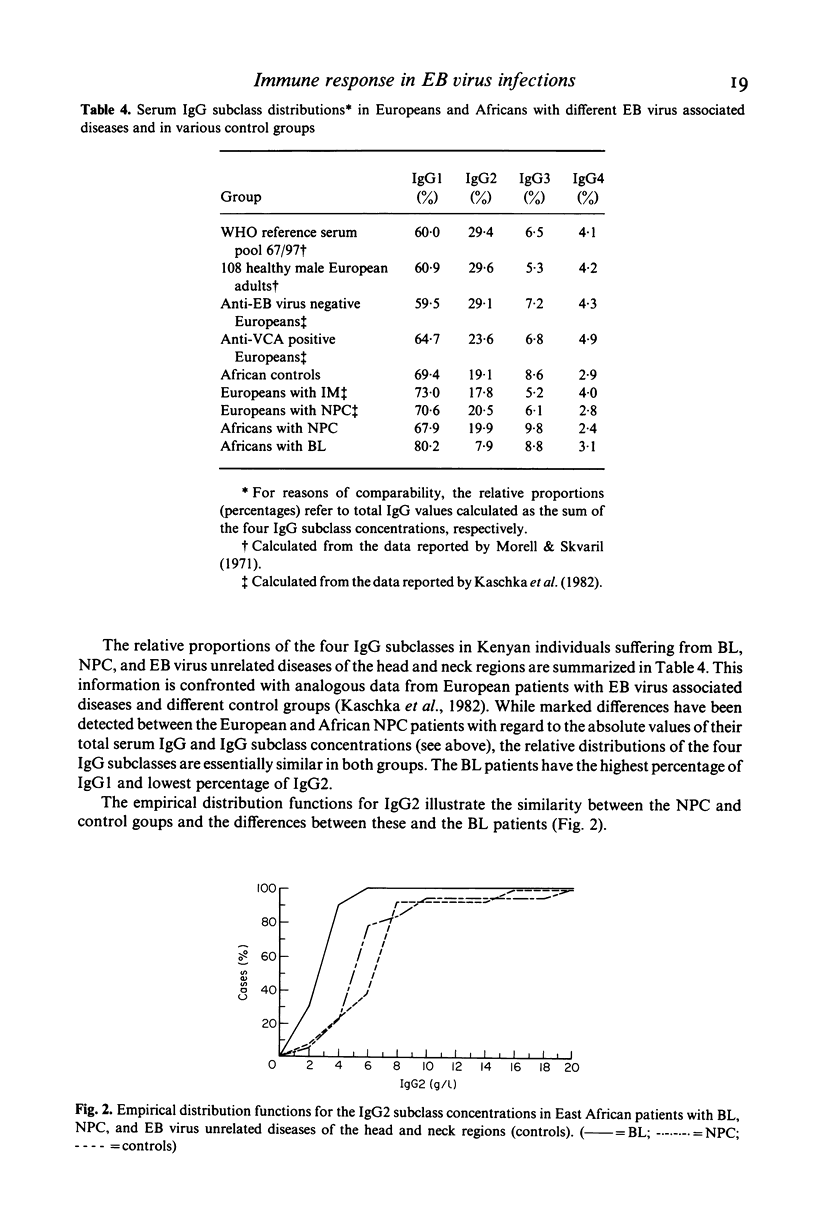
Native Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients from Kenya were examined with regard to the serum concentrations and distribution of the four IgG subclasses, total IgG, and antibody activities to Epstein-Barr (EB) virus associated antigens. The results were compared with corresponding data of an African control group. As revealed by indirect immunofluorescence techniques, the patients displayed a pattern of IgG and IgA antibodies to EB virus associated antigens which is characteristic for these diseases. No significant differences could be detected between the total IgG levels of the diagnostic groups. The mean total IgG concentrations of our Kenyan patients were two to three times as high as those found in four different groups of Europeans, which is consistent with results of previous studies on Gambian, Nigerian, and Congolese Bantu populations. Quantitative determination of the four IgG subclasses by radial immunodiffusion revealed a unique pattern in the BL group which was characterized by a decreased proportion of IgG2 and significantly lower absolute IgG2 values as compared with the controls. The IgG subclass distribution pattern in the African NPC sera was essentially identical with that of European NPC and African control sera. The pathogenetic implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURKITT D. A children's cancer dependent on climatic factors. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:232–234. doi: 10.1038/194232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKITT D., WRIGHT D. H. A LYMPHOMA SYNDROME IN TROPICAL AFRICA WITH A NOTE ON HISTOLOGY, CYTOLOGY, AND HISTOCHEMISTRY. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1963;2:67–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth K., Burkitt D. P., Bassett D. J., Cooke R. A., Biddulph J. Burkitt lymphoma in Papua, New Guinea. Br J Cancer. 1967 Dec;21(4):657–664. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1967.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G., Barr Y. M., Zajac B., Henle G., Henle W. Morphological and virological investigations on cultured Burkitt tumor lymphoblasts (strain Raji). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Oct;37(4):547–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Klein E., Klein G., Clifford P., Singh S. Immunoglobulin and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase as markers of cellular origin in Burkitt lymphoma. J Exp Med. 1973 Jul 1;138(1):89–102. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunvén P., Klein G., Henle G., Henle W., Clifford P. Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Antibodies to EBV associated membrane and viral capsid antigens in Burkitt lymphoma patients. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1053–1056. doi: 10.1038/2281053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Clifford P., Diehl V., Kafuko G. W., Kirya B. G., Klein G., Morrow R. H., Munube G. M., Pike P. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt's lymphoma and control groups. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Nov;43(5):1147–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Klein G. Demonstration of two distinct components in the early antigen complex of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. Int J Cancer. 1971 Sep 15;8(2):272–282. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Ho H. C., Burtin P., Cachin Y., Clifford P., de Schryver A., de-Thé G., Diehl V., Klein G. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, other head and neck neoplasms, and control groups. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Jan;44(1):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaschka-Dierich C., Adams A., Lindahl T., Bornkamm G. W., Bjursell G., Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Singh S. Intracellular forms of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in human tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):302–306. doi: 10.1038/260302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaschka W. P., Hilgers R., Skvaril F. Humoral immune response in Epstein-Barr virus infections. I. Elevated serum concentration of the IgG1 subclass in infectious mononucleosis and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):149–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaschka W. P., Theilkaes L., Eickhoff K., Skvaril F. Disproportionate elevation of the immunoglobulin G1 concentration in cerebrospinal fluids of patients with multiple sclerosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):933–941. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.933-941.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Specific chromosomal translocations and the genesis of B-cell-derived tumors in mice and men. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. The role of gene dosage and genetic transpositions in carcinogenesis. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):313–318. doi: 10.1038/294313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Boyse E. A., Oettgen H. F., Harven E. D., Geering G., Williamson B., Clifford P. Precipitating antibody in human serum to an antigen present in cultured burkitt's lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1699–1704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. IgG subclass levels in infancy and childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Jan;68(1):23–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb04424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S., McGregor I. A., Smith S. J., Hall P., Williams K. Plasma immunoglobulin concentrations in a West African (Gambian) community and in a group of healthy British adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Jan;3(1):63–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Rosen F., Norman M. E. Immunoglobulin subclasses in normal children. Pediatr Res. 1979 Mar;13(3):181–183. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197903000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F., Roth-Wicky B., Barandun S. IgG subclasses in human gamma-globulin preparations for intravenous use and their reactivity with staphylococcus protein A. Vox Sang. 1980;38(3):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1980.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Hildemann W. H. Regulation of immunity toward allogeneic tumors in mice. I. Effect of antiserum fractions on tumor growth. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Oct;43(4):843–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Voller A. Studies on immunoglobulins of Nigerians. I. The immunoglobulin levels of a Nigerian population. J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 May;69(5):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Schryver A., Friberg S., Jr, Klein G., Henle W., Henle G., De-Thé G., Clifford P., Ho H. C. Epstein-Barr virus-associated antibody patterns in carcinoma of the post-nasal space. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Nov;5(5):443–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G., Clifford P., Santesson L. EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/2281056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


