Abstract
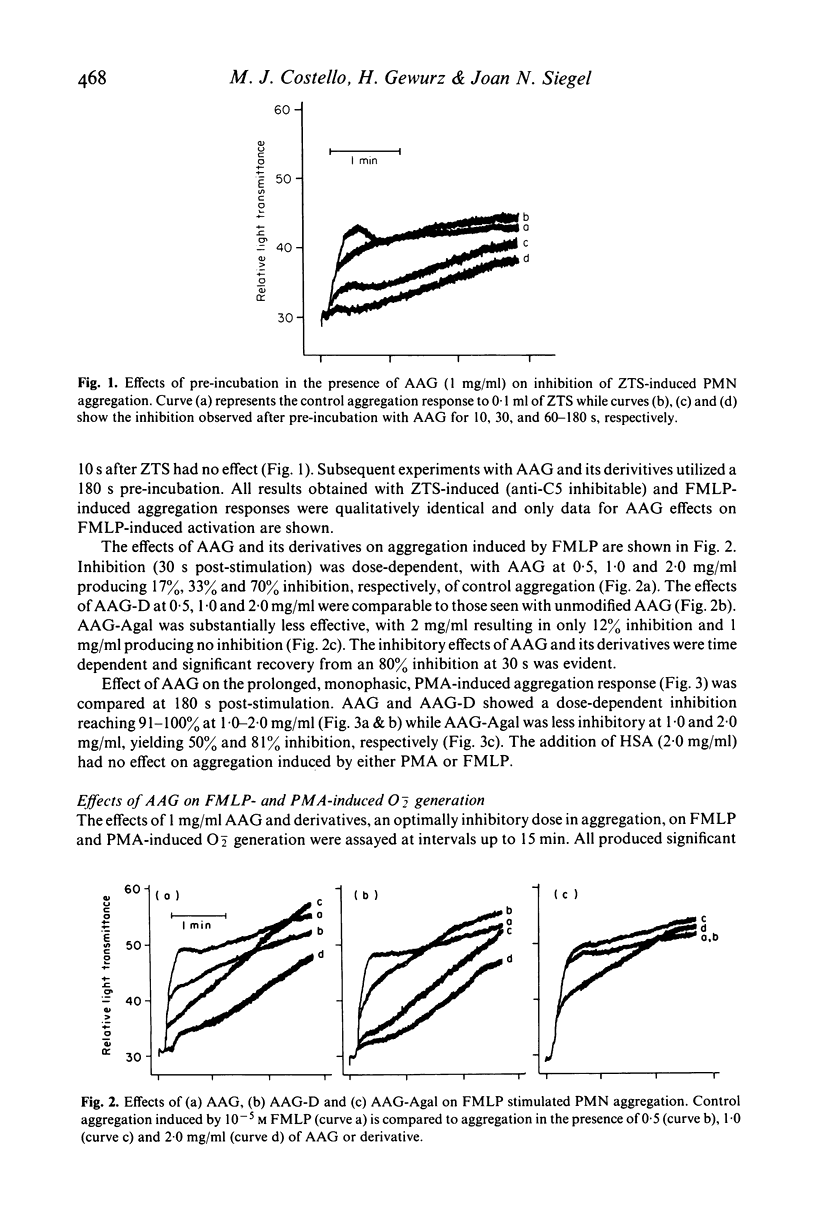
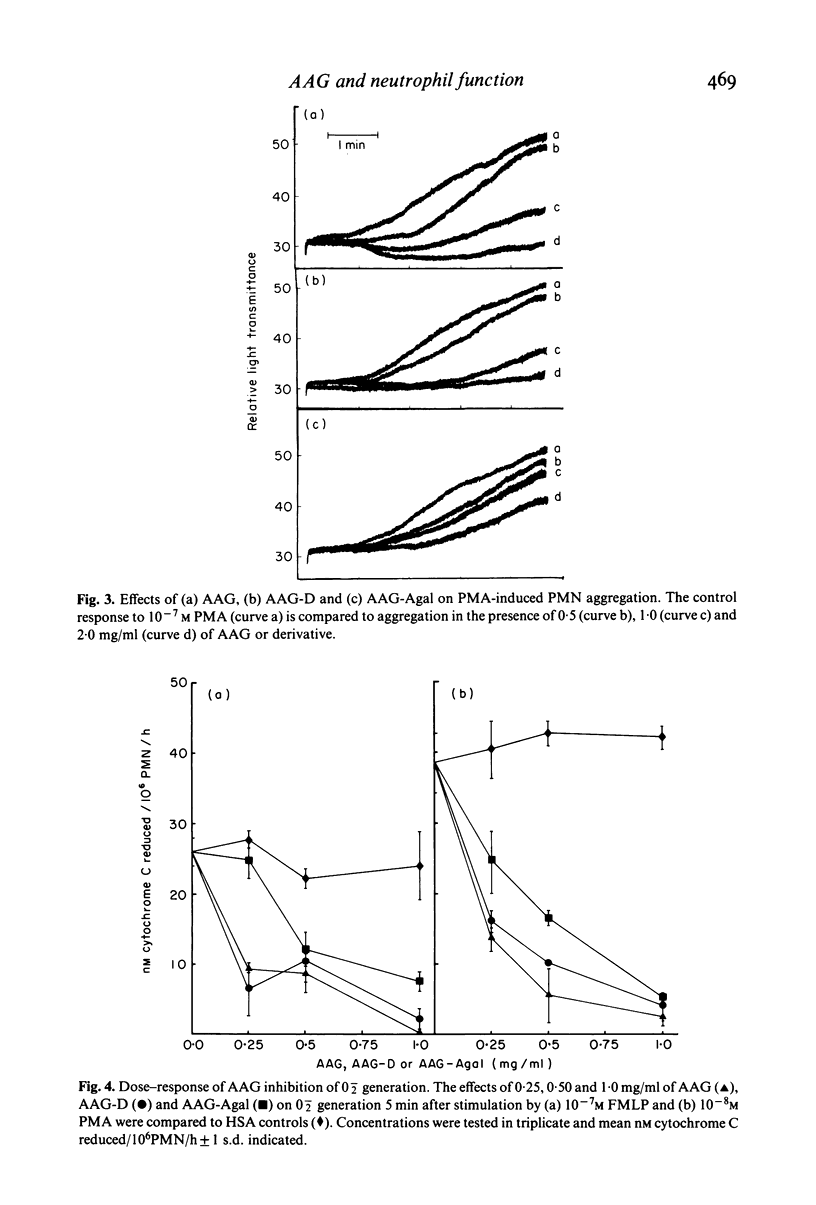
We report that alpha1-acid glycoprotein (AAG), a naturally occurring human plasma protein and acute phase reactant of uncertain biological function, inhibits human neutrophil aggregation and superoxide anion generation induced by a variety of stimuli including zymosan treated serum, formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine and phorbol myristate acetate. Inhibition was transient, directly proportional to the glycoprotein concentration and inversely proportional to the concentration of the stimulus added. Desialyzation, resulting in the removal of a substantial portion of the molecule's negative charge, did not alter the effectiveness of AAG. Removal of the penultimate galactose residues from desialyzed AAG resulted in a slight but significant reversal of inhibition, suggesting that the heteropolysaccharide units of AAG may be important for inhibition of cellular function. We therefore suggest that the acute phase glycoprotein AAG may be a significant modulator of neutrophil as well as platelet and lymphocyte function during inflammation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATHINEOS E., THORNTON M., WINZLER R. J. Comparative antigenicity of native and "desialized" orosomucoid in rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:353–356. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Schiffmann E., Day A. R., Freer R. J., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Demonstration of a receptor on rabbit neutrophils for chemotactic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M., Schmid K. Immunosuppression by human plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein: importance of the carbohydrate moiety. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6109–6113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Langham C. S., Parente L., Persico P., Russel-Smith N. C., Stone D. Glucocorticoids induce the formation and release of anti-inflammatory and anti-phospholipase proteins into the peritoneal cavity of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 May;76(1):185–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., White J. G., Jacob H. S. Potentiation of complement (C5a)-induced granulocyte aggregation by cytochalasin B. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Mar;91(3):490–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distler J. J., Jourdian G. W. The purification and properties of beta-galactosidase from bovine testes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6772–6780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau C., Schmid K., Faris B., Beldekas J., Garvin P., Kagan H. M., Baum B. J. The interaction of collagen with alpha1-acid glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 18;427(1):302–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Leukocyte surface origin of human alpha1-acid glycoprotein (orosomucoid). J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):507–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawahara K., Ikenaka T., Nimberg R. B., Schmid K. The effect of the sialyl residues on the thermodynamic and hydrodynamic properties of 1 -acid glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 21;295(2):505–513. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heide K., Schwick H. G. Chemistry and significance of the carbohydrate moieties of human serum glycoproteins. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1973 Sep;12(9):721–733. doi: 10.1002/anie.197307211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. C., Turchen B., Huebner E. Evidence for the presence of rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein in granuloma tissue: a fluorescence microscopy study. Can J Zool. 1980 Sep;58(9):1513–1517. doi: 10.1139/z80-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. S., Kim S. W. Adsorbed glycoproteins in platelet adhesion onto polymer surfaces: significance of terminal galactose units. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1979;25:124–132. doi: 10.1097/00002480-197902500-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cohen L. Receptor-mediated regulation of superoxide production in human neutrophils stimulated by phorbol myristate acetate. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1314–1320. doi: 10.1172/JCI110378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Gregoriadis G., Scheinberg I. H., Hickman J., Ashwell G. The role of sialic acid in determining the survival of glycoproteins in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicollet I., Lebreton J. P., Fontaine M., Hiron M. Evidence for alpha-1-acid glycoprotein populations of different pI values after concanavalin A affinity chromatography. Study of their evolution during inflammation in man. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 28;668(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kahane I., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated internalization of fluorescent chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.472759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piafsky K. M., Borgá O., Odar-Cederlöf I., Johansson C., Sjöqvist F. Increased plasma protein binding of propranolol and chlorpromazine mediated by disease-induced elevations of plasma alpha1 acid glycoprotein. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1435–1439. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romach M. K., Piafsky K. M., Abel J. G., Khouw V., Sellers E. M. Methadone binding to orosomucoid (alpha 1-acid glycoprotein): determinant of free fraction in plasma. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Feb;29(2):211–217. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARCIONE E. J. Sunthesis of alphal-acid glycoprotein by the isolated perfused rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Mar;100:516–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schley J., Siegert M., Müller-Oerlinghausen B. Binding of perazine to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(6):501–504. doi: 10.1007/BF00874663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Oades Z. G., Jesaitis A. J., Painter R. G., Cochrane C. G. Fluoresceinated chemotactic peptide and high-affinity antifluorescein antibody as a probe of the temporal characteristics of neutrophil stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7540–7544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S. J., Zigmond S. H. Chemotactic peptide receptor modulation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):703–711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr G. A. A macrophage receptor for (mannose/glucosamine)-glycoproteins of potential importance in phagocytic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):737–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F., Bronson P. M., Border J. R. Phagocytosis-inhibiting properties of human serum alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. Immunol Commun. 1974;3(4):321–328. doi: 10.3109/08820137409061112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


