Abstract
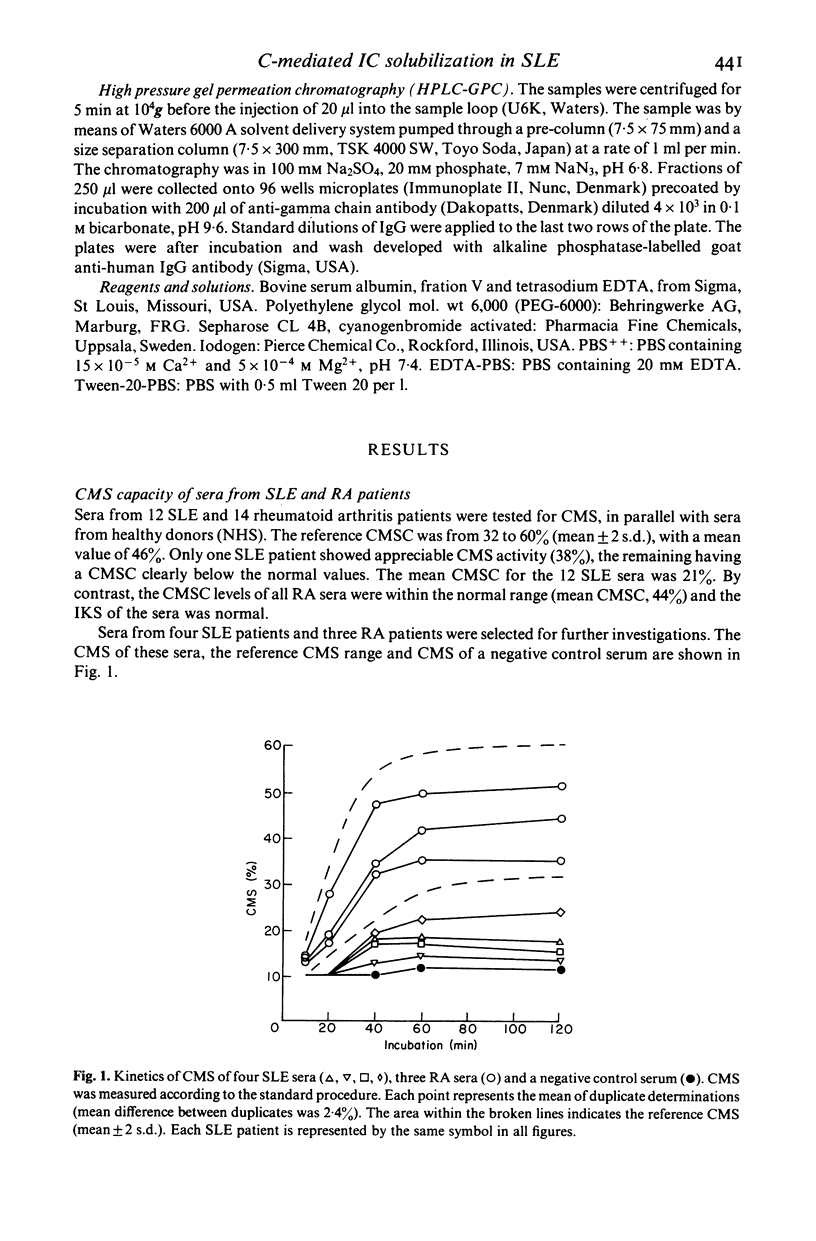
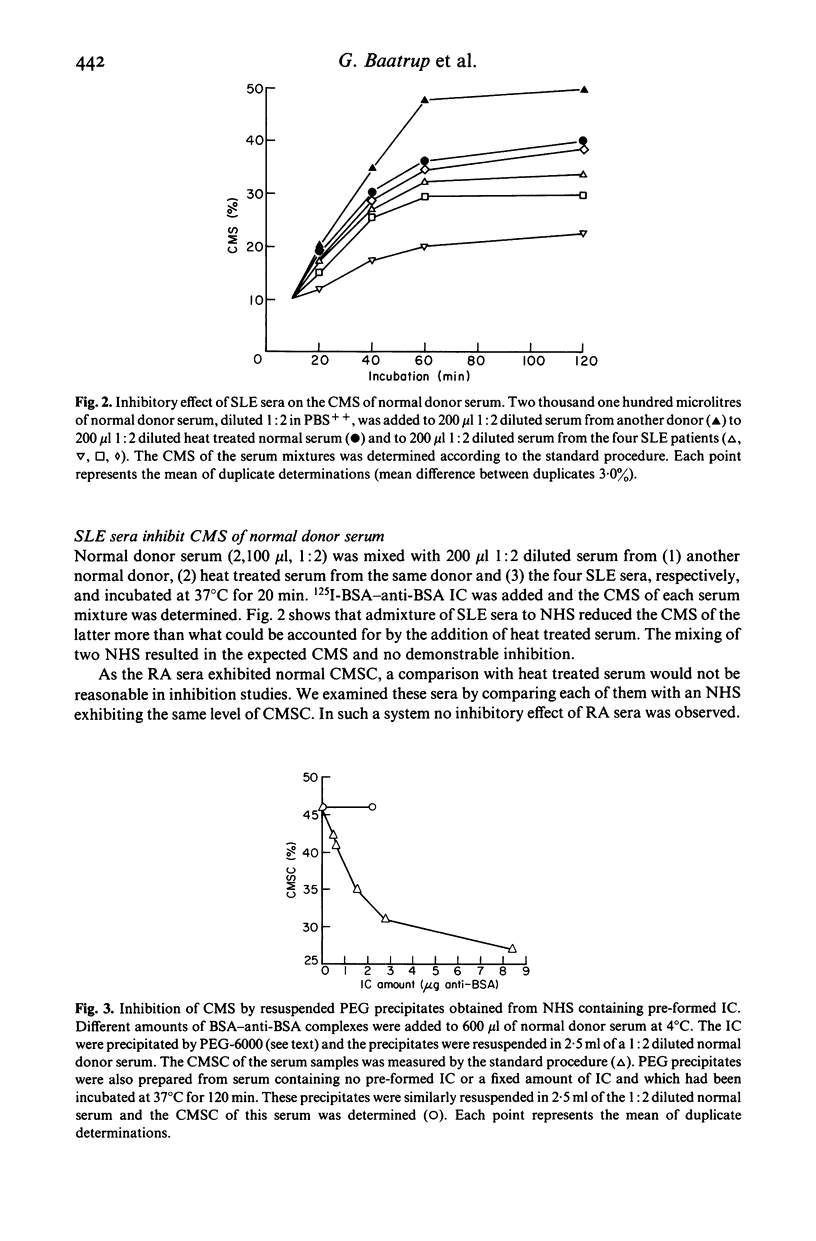
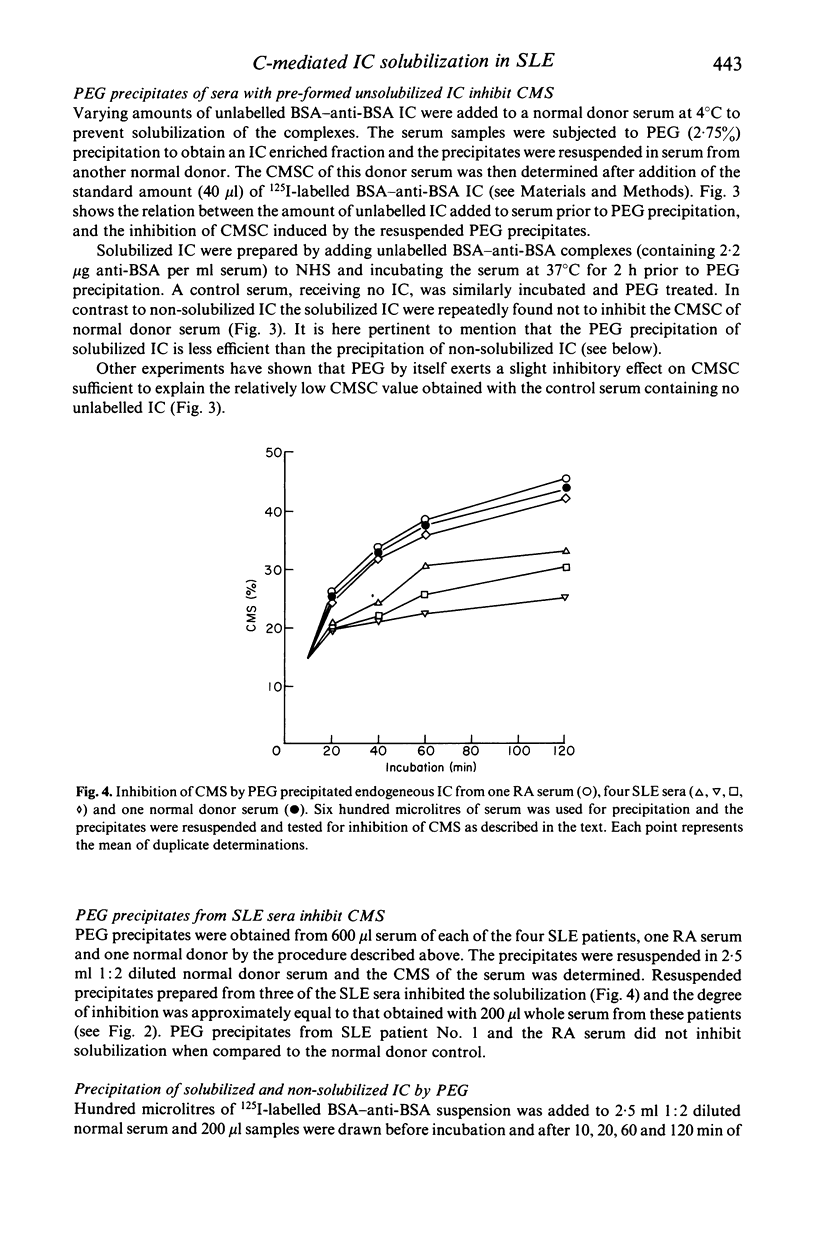
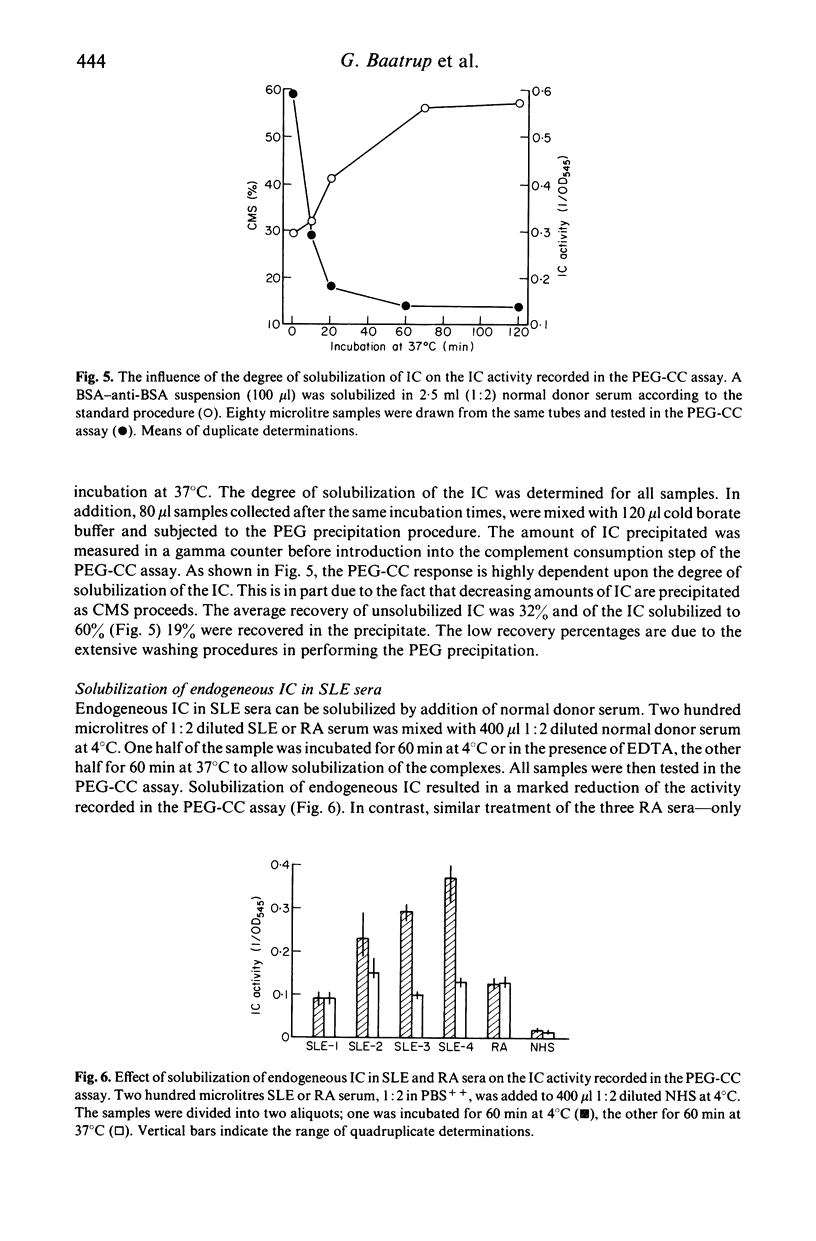
Reduced complement-mediated solubilization (CMS) of pre-formed immune complexes (IC) was demonstrated in sera from 11 out of 12 SLE patients. The presence of incompletely solubilized endogeneous IC in SLE sera was indicated by the following findings: (1) When IC positive SLE sera with reduced CMS capacity were mixed with normal donor sera they inhibited the CMS of the latter sera. (2) Resuspended PEG (2.75%) precipitates obtained from SLE sera inhibited the CMS of normal donor sera. (3) Non-solubilized or incompletely complement solubilized IC in SLE sera give a strong response in the PEG-CC assay for IC. The IC activity of SLE sera was clearly reduced in this assay when the endogeneous IC were solubilized prior to testing. In contrast, sera of 14 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients exhibited normal CMS. IC which could be further solubilized by complement were not demonstrable although all RA sera were IC positive.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrass C. K., Nies K. M., Louie J. S., Border W. A., Glassock R. J. Correlation and predictive accuracy of circulating immune complexes with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Mar;23(3):273–282. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguado M. T., Perrin L. H., Miescher P. A., Lambert P. H. Decreased capacity to solubilize immune complexes in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Oct;24(10):1225–1229. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguado M. T., Perrin L. H., Ramirez R., Miescher P. A., Lambert P. H. Evaluation of alternative pathway and factor B haemolytic activities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: correlations with the alternative pathway regulatory proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):495–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyave C. M., Wilson M. R., Tan E. M. Serum factors activating the alternative complement pathway in autoimmune disease: description of two different factors from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):821–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandslund I., Siersted H. C., Jensenius J. C., Svehag S. E. Detection and quantitation of immune complexes with a rapid polyethylene glycol precipitation complement consumption method (PEG-CC). Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):551–571. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano P. O., Jerry L. M., Sladowski J. P., Osterland C. K. Circulating immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Aug;29(2):197–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J., Nussenzweig V. Studies on the mechanism of solubilization of immune precipitates by serum. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):615–630. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P., Cumming R. H., Verrier-Jones J. Relationship between anti-DNA antibodies complement consumption and circulating immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 May;28(2):226–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd W., Schur P. H. Immune complexes, complement, and anti-DNA in exacerbations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 May;60(3):208–217. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198105000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Scarborough D., Miller G. Ability of complement to release systemic lupus erythematosus immune complexes from cell receptors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 May;44(2):416–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Nussenzweig V. A new complement function: solubilization of antigen-antibody aggregates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):418–422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Fujita T., Kono I., Kabashima T., Yamane K., Tamura N., Kashiwagi H. Complement-mediated solubilization of immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):37–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Morris S. M., Dash A., Peters D. K. Complement-mediated solubilization in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, nephritis or vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):557–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Woo P., Peters D. K. Complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation. I. Role of the classical and alternative pathways. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):555–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Czop J., Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V. Mechanism of solubilization of immune aggregates by complement. Implications for immunopathology. Transplant Rev. 1976;32:121–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Brade V., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement. The role of the classical pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):349–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI109135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Hirose S. Solubilization of antigen-antibody complexes: a new function of complement as a regulator of immune reactions. Prog Allergy. 1980;27:134–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


