Abstract
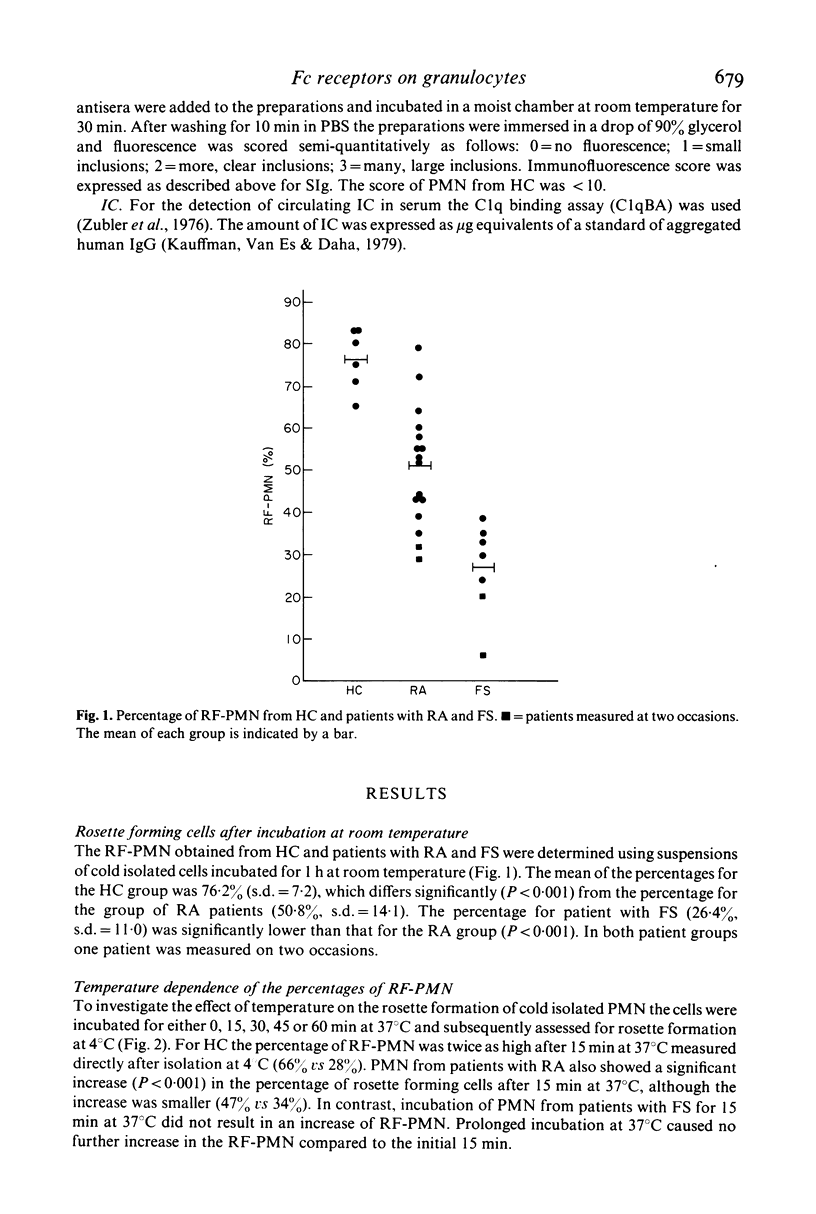
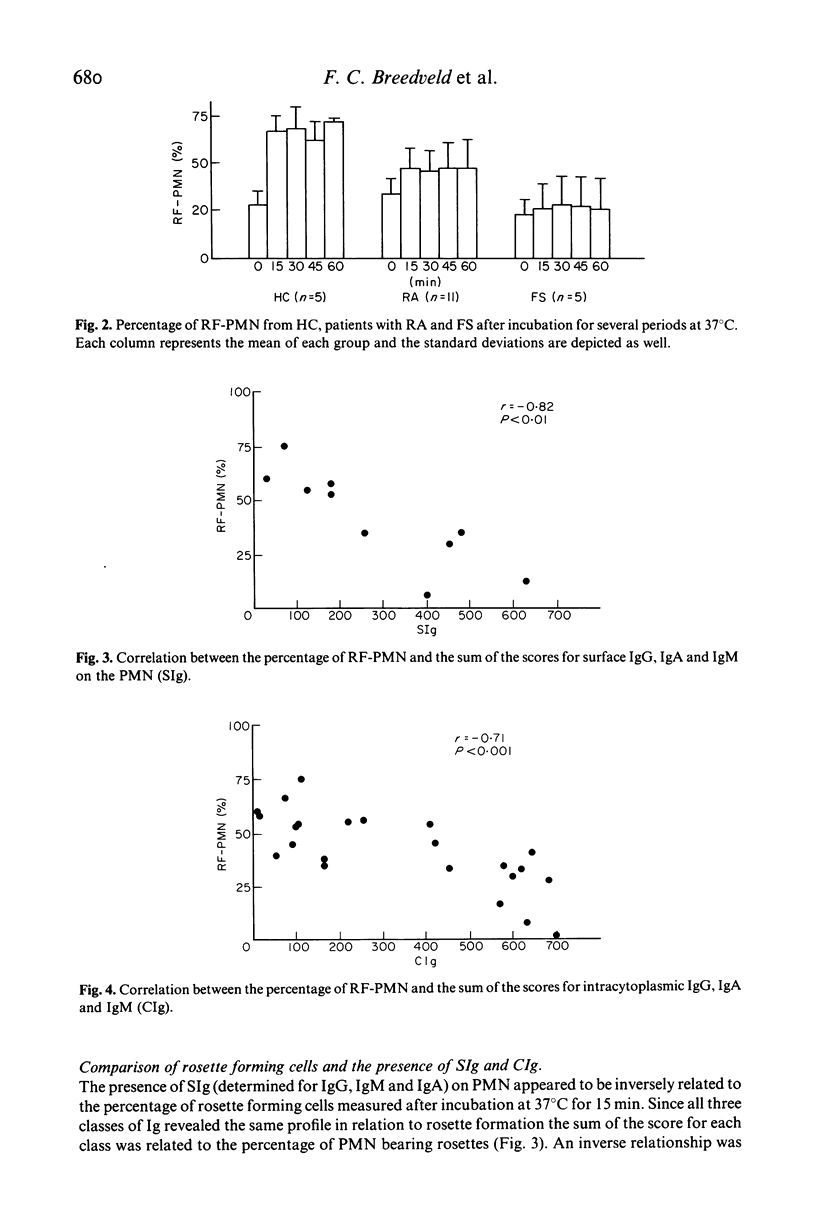
Receptors for the Fc part of IgG on polymorphonuclear cells (FcR) of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Felty's syndrome (FS) and healthy controls (HC) were studied by means of a rosetting technique with rabbit IgG coated ox erythrocytes. When cold isolated polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) were incubated at room temperature the percentage of rosette forming PMN (RF-PMN) from HC was more than twice that measured directly after isolation at 4 degrees C. The same phenomenon was observed for PMN from patients with RA although the RF-PMN increased by only 1/3. In contrast warming of PMN from patients with FS did not influence the RF-PMN. The presence of surface bound immunoglobulins and intracytoplasmic immunoglobulins was measured by immunofluorescence and appeared to be inversely related to the RF-PMN. A good correlation between the results of the C1q binding assay (C1qBA) and the immunofluorescence score was observed but no correlation existed between the C1qBA and the RF-PMN. These results indicate that the number of PMN expressing FcR in patients with RA and FS is decreased presumably because of the phagocytosis of immune complex like material. The decrease in the availability of FcR may influence the functions of the PMN.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum J. Infection in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Jan-Feb;14(1):135–137. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bültmann B., Geitner R., Seibold H., Kratsch G., Haferkamp O. Interaction of circulating immune complexes with granulocyte function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Klin Wochenschr. 1980 Jul 15;58(14):727–732. doi: 10.1007/BF01478460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cats A., Lafeber G. J., Klein F. Immunoglobulin phagocytosis by granulocytes from sera and synovial fluids in various rheumatoid and nonrheumatoid diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Apr;34(2):146–155. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.2.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cnossen J., Lafeber G. J., Damsteeg W. J., Meijer C. J. Mixed rosette assay for the detection of T mu and T gamma lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., van Es L. A. The role of cellular Fc and C3 receptors on the complement-dependent degradation of stable soluble immunoglobulin aggregates by normal and trypsin-treated peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1982 Sep;47(1):203–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Collins L. A. Increased expression of C3b receptors on polymorphonuclear leukocytes induced by chemotactic factors and by purification procedures. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F. Education for outcome. J Rheumatol. 1978 Spring;5(1):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr Effects of soluble immune complexes on Fc receptor- and C3b receptor-mediated phagocytosis by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):905–919. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Laforce F. M., Mills D. M. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte inclusions and impaired bacterial killing in patients with Felty's syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Aug;88(2):183–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hed J., Stendahl O. Differences in the ingestion mechanisms of IgG and C3b particles in phagocytosis by neutrophils. Immunology. 1982 Apr;45(4):727–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. The adherence of leucocytes and platelets induced by fixed IgG antibody or complement. Immunology. 1969 Jan;16(1):107–121. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe G. B., Fordham J. N., Brown K. A., Currey H. L. Polymorphonuclear cell function in rheumatoid arthritis and in Felty's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Aug;40(4):370–375. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.4.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällgren R., Håkansson L., Venge P. Kinetic studies of phagocytosis. I. The serum independent particle uptake by PMN from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jan-Feb;21(1):107–113. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann R. H., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Aggregated human immunoglobulin G stabilized by albumin: a standard for immune complex detection. J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(1-2):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann R. H., de Rooy-Dijk H. H., Klein F., Lafeber G. J., Cats A., van Es L. A. The significance of immunofluorescent immunoglobulin inclusions in polymorphonuclear leucocytes for the detection of circulating immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):203–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay N. E., Bumol T. F., Douglas S. D. Effect of phagocytosis and Fc receptor occupancy on complement-dependent neutrophil chemotaxis. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 May;91(5):850–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Participation of immunoglobulins and complement components in the intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by human granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):714–724. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.714-724.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Jelinek J. Receptors for human gamma G globulin on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2165–2171. doi: 10.1172/JCI106435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. A., Brunner C. M., Sandusky W. R., Leavell B. S. Felty's syndrome: long-term follow-up after splenectomy. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Sep;75(3):381–385. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-3-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal F. D., Beeley J. M., Gelsthorpe K., Doughty R. W. White-cell antibodies and the aetiology of Felty's syndrome. Q J Med. 1974 Apr;43(170):187–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scribner D. J., Fahrney D. Neutrophil receptors for IgG and complement: their roles in the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):892–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkebaum G., Arend W. P., Nardella F. A., Gavin S. E. Characterization of immune complexes and immunoglobulin G antibodies reactive with neutrophils in the sera of patients with Felty's syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Aug;96(2):238–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkebaum G., Jimenez R. A., Arend W. P. Effect of immune complexes on human neutrophil phagocytic function. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


