Abstract
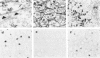
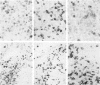
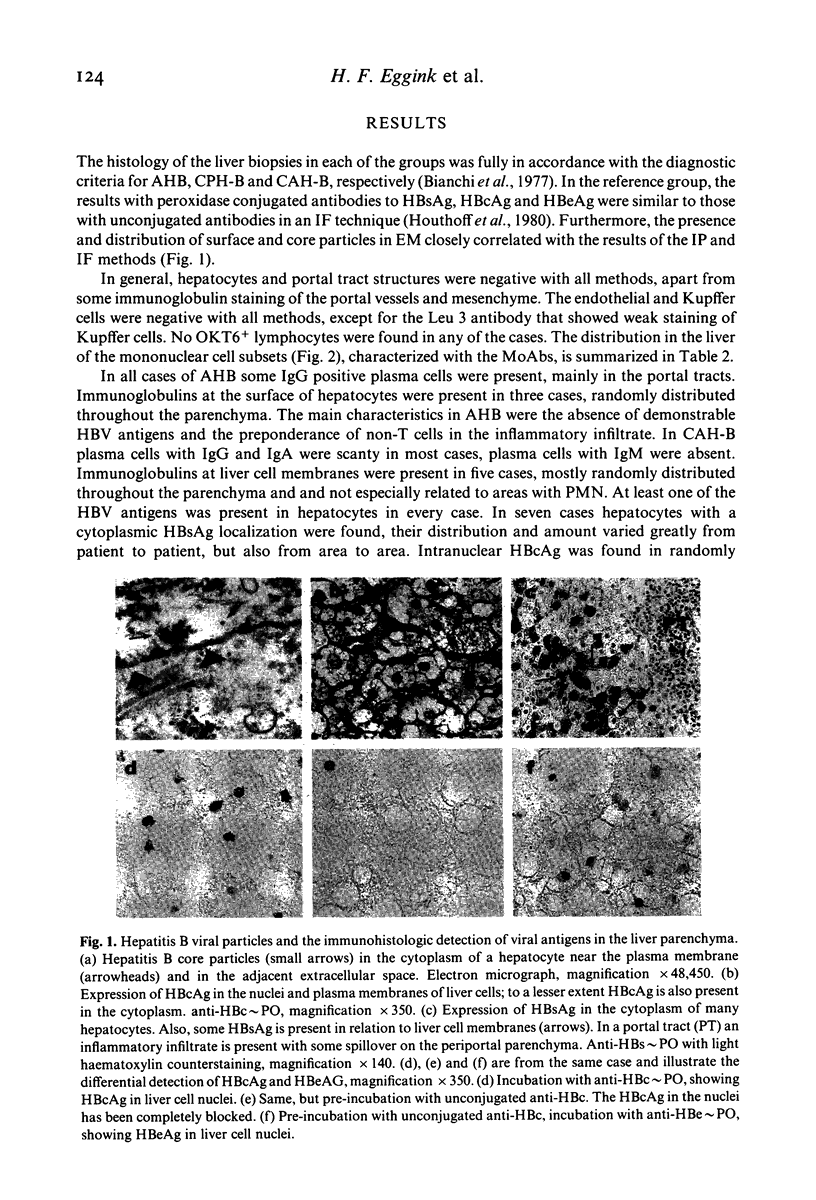
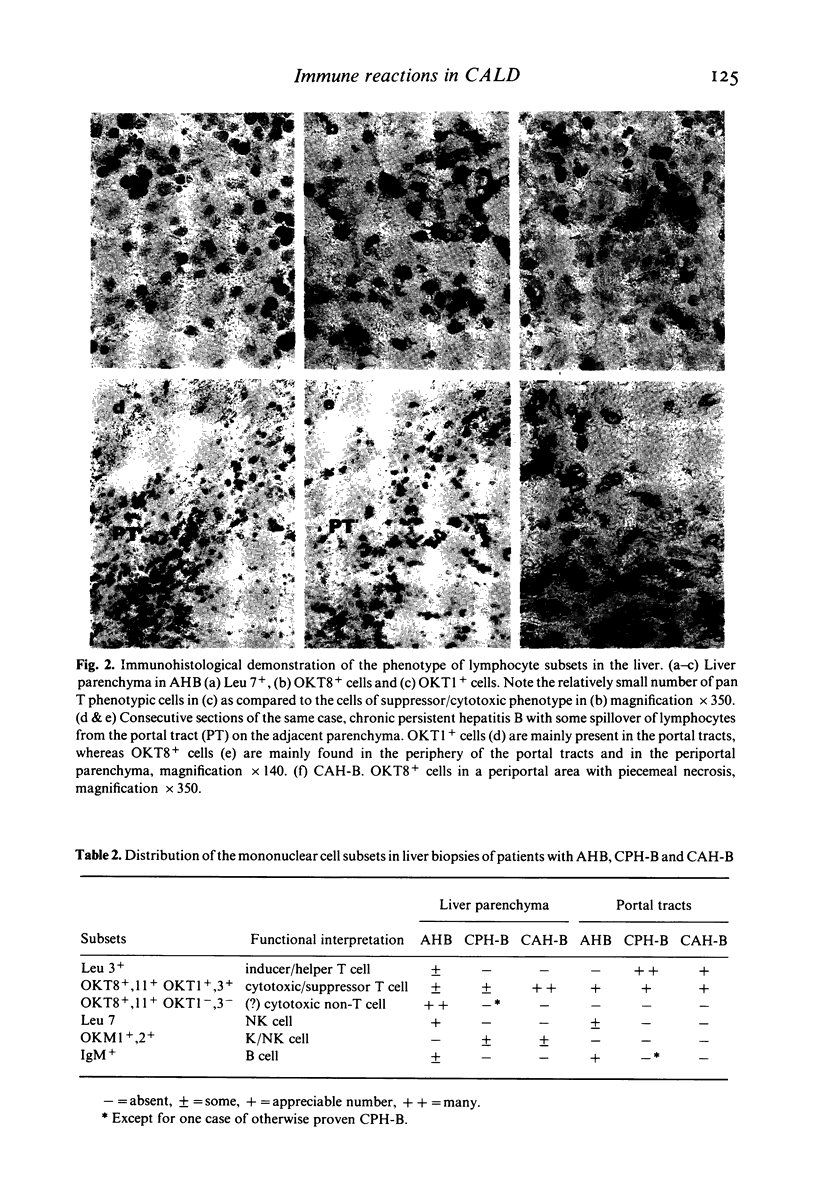
The characteristics and distribution of the inflammatory infiltrate in liver biopsies of 25 patients with hepatitis B viral (HBV) infection were studied in relation to the distribution and expression of HBV antigens. Mononuclear subsets were characterized with monoclonal (OKT, OKM, Leu) antibodies to surface antigens. For the demonstration of viral antigens directly conjugated antibodies to surface (HBsAg), core (HBcAg) and 'e' (HBeAg) antigen were used. For the study of mutual relations all methods were performed on serial cut tissue sections. In chronic active hepatitis B (CAH-B, n = 12) OKT8+ lymphocytes of T cell origin were the only cell type present in areas with liver cell degeneration and T cell cytotoxicity appears to be the only immune mechanism. In chronic persistent hepatitis B (CPH-B, n = 7) the only conspicuous feature was the presence of many Leu 3+ lymphocytes of the helper/inducer population in the portal tracts. In acute hepatitis B (AHB, n = 6) OKT8+ cells of non-T origin (OKT1-,3-) and Leu 7+ cells of presumed natural killer (NK) potential predominated in the areas with liver cell necrosis, and non-T cell cytotoxicity appears to be the predominant immune mechanism. In none of these disease entities a positive spatial relation could be established between the cytotoxic cells and the demonstrable expression of HBV antigens in hepatocytes. It is concluded that differences in immunological reaction pattern may explain the different course in the three forms of HBV infection studied.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Roder J. C., Abo W., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Natural killer (HNK-1+) cells in Chediak-Higashi patients are present in normal numbers but are abnormal in function and morphology. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):193–197. doi: 10.1172/JCI110592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acute and chronic hepatitis revisited. Review by an international group. Lancet. 1977 Oct 29;2(8044):914–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberti A., Realdi G., Bortolotti F., Rigoli A. M. T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity to HBsAg-coated target cells in hepatitis b virus infection. Gut. 1977 Dec;18(12):1004–1009. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.12.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldershvile J., Roggendorf M., Kryger P., Tage-Jensen U., Deinhardt F., Frösner G. G., Hardt F., Nielsen J. O. Anti-HBc of IgM-class, HBeAg and anti-HBe in acute and chronic hepatitis B. Liver. 1981 Dec;1(4):290–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1981.tb00045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breard J., Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1943–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickmeiss E., Soeberg B., Svejgaard A. Human cell-mediated cytotoxicity against modified target cells is restricted by HLA. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):526–528. doi: 10.1038/270526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggink H. F., Houthoff H. J., Huitema S., Gips C. H., Poppema S. Cellular and humoral immune reactions in chronic active liver disease. I. Lymphocyte subsets in liver biopsies of patients with untreated idiopathic autoimmune hepatitis, chronic active hepatitis B and primary biliary cirrhosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):17–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eleftheriou N., Thomas H. C., Heathcote J., Sherlock S. Incidence and clinical significance of e antigen and antibody in acute and chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1975 Dec 13;2(7946):1171–1173. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92657-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudat F., Bianchi L., Sonnabend W., Thiel G., Aenishaenslin W., Stalder G. A. Pattern of core and surface expression in liver tissue reflects state of specific immune response in hepatitis B. Lab Invest. 1975 Jan;32(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houthoff H. J., Niermeijer P., Gips C. H., Arends A., Hofstee N. Hepatic morphologic findings and viral antigens in acute hepatitis B. A longitudinal study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1980;389(2):153–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00439483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Horwitz D. A. Evidence by reactivity with hybridoma antibodies for a probable myeloid origin of peripheral blood cells active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):847–851. doi: 10.1172/JCI109923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Evans R. L., Lipinski M., Cunningham-Rundles C., Good R. A., Herzenberg L. A. Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T lymphocyte helper/inducer and cytotoxic/suppressor subpopulations in mouse and man. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):310–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niermeiier P., Gips C. H., Huizenga J. R., Ringers J., Verkerk S., Houthuff H. J., Houwen B., Snijder J. A., Nielsen J. O. IgM-anti-HBc as a marker of persistent and IgG-anti-HBc as a marker of past hepatitis B infection. A longitudinal study over 5 years. Acta Hepatogastroenterol (Stuttg) 1978 Oct;25(5):360–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niermeijer P., Gips C. H. Hepatitis B, report of a prospective longitudinal study. Neth J Med. 1981;24(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray M. B., Desmet V. J., Fevery J., De Groote J., Bradburne A. F., Desmyter J. Distribution patterns of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in the liver of hepatitis patients. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Feb;29(2):94–100. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.2.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevisan A., Realdi G., Alberti A., Ongaro G., Pornaro E., Meliconi R. Core antigen-specific immunoglobulin G bound to the liver cell membrane in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 1982 Feb;82(2):218–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbi W., Greaves M. F., Schneider C., Koubek K., Janossy G., Stein H., Kung P., Goldstein G. Monoclonal antibodies OKT 11 and OKT 11A have pan-T reactivity and block sheep erythrocyte "receptors". Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnatz H., Rösch W., Gerlich W., Gutmann W. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and cell-mediated cytotoxicity (CMC) to HBsAg-coated target cells in patients with hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis (CAH). Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jan;35(1):133–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]