Abstract
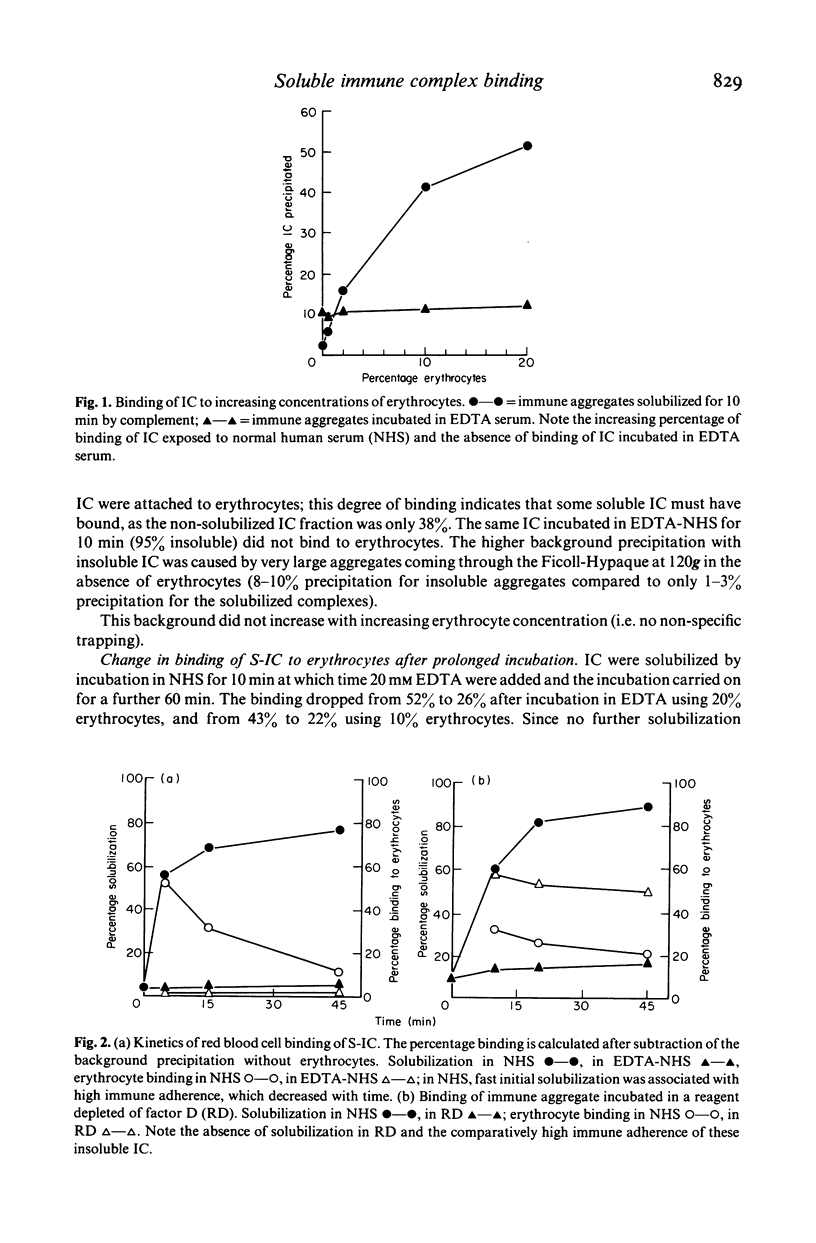
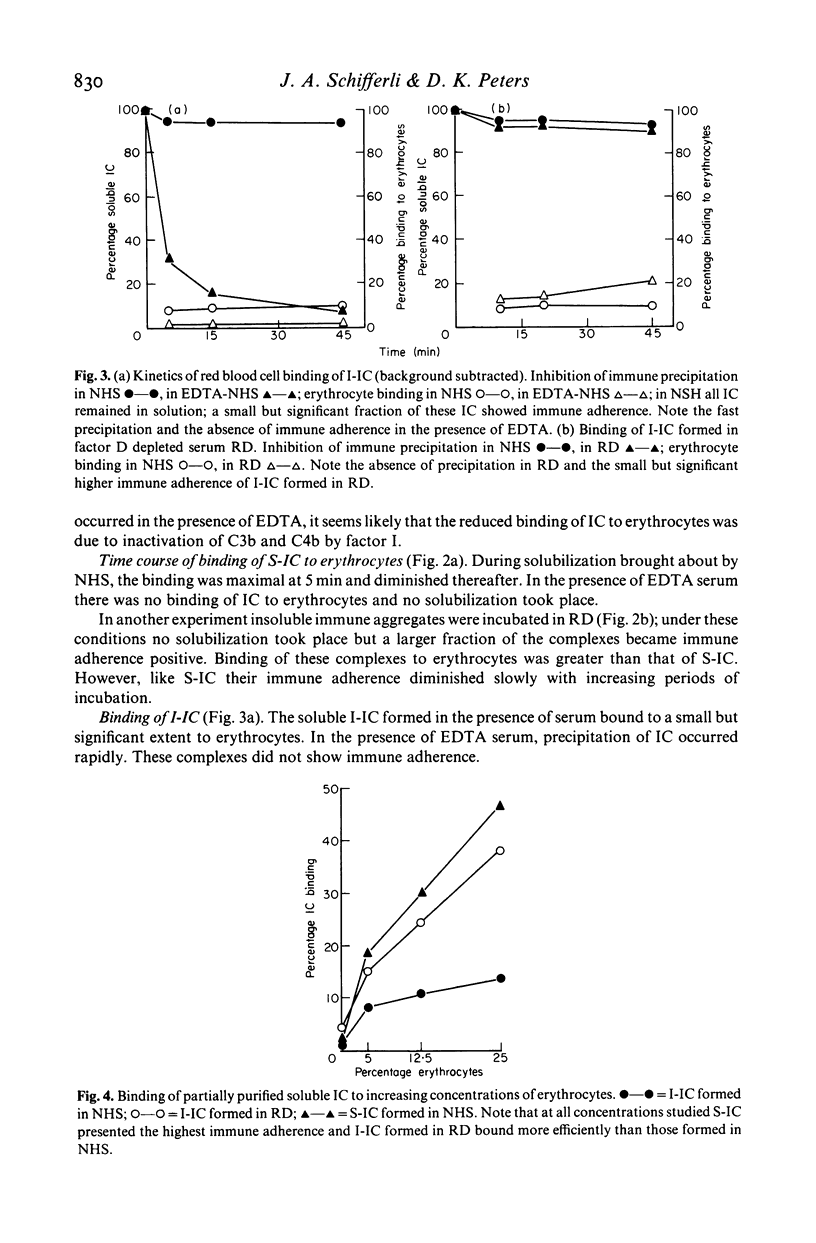
Complement has been shown to affect the solubility of antigen-antibody complexes by two mechanisms: in the first, classical pathway dependent, complement inhibits the formation of the immune precipitate; in the second, alternative pathway dependent, complement reacts with a formed precipitate to bring about its solubilization. The biological properties of complement reacted immune complexes (IC) has been assessed by studying their binding to staphylococcus protein A (SPA) and to human erythrocytes. BSA-anti-BSA complement reacted IC bound to human erythrocytes and to SPA. Complexes generated by solubilization of immune precipitates showed greater immune adherence than complexes held in solution by complement, despite their similar size. Complexes held in solution in a factor D depleted human serum bound more efficiently to erythrocytes than complexes formed in normal serum. These experiments demonstrate that complement reacted IC cannot be regarded as biologically inert and that factors affecting complement function may have important effects on the properties of antigen-antibody complexes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaout M. A., Dana N., Melamed J., Medicus R., Colten H. R. Low ionic strength or chemical cross-linking of monomeric C3b increases its binding affinity to the human complement C3b receptor. Immunology. 1983 Feb;48(2):229–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Identification of the membrane glycoprotein that is the C3b receptor of the human erythrocyte, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, B lymphocyte, and monocyte. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):20–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällgren R., Wide L. Detection of circulating IgG aggregates and immune complexes using 125I protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):306–313. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Redecha P. B., Inman R. D., Christian C. L. Binding of immunoglobulin G aggregates and immune complexes in human sera to Staphylococci containing protein A. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):627–636. doi: 10.1172/JCI109345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Nussenzweig V. A new complement function: solubilization of antigen-antibody aggregates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):418–422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T., Anderson L. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXVIII. Dissection of complex antigenic mixtures using monoclonal antibodies and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 15;101(2):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharfstein J., Correa E. B., Gallo G. R., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. Association with immune complexes in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):437–442. doi: 10.1172/JCI109320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Bartolotti S. R., Peters D. K. Inhibition of immune precipitation by complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):387–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Peters D. K. Complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation. II. Analysis by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):563–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Woo P., Peters D. K. Complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation. I. Role of the classical and alternative pathways. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):555–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Hirose S. Solubilization of antigen-antibody complexes: a new function of complement as a regulator of immune reactions. Prog Allergy. 1980;27:134–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


