Abstract
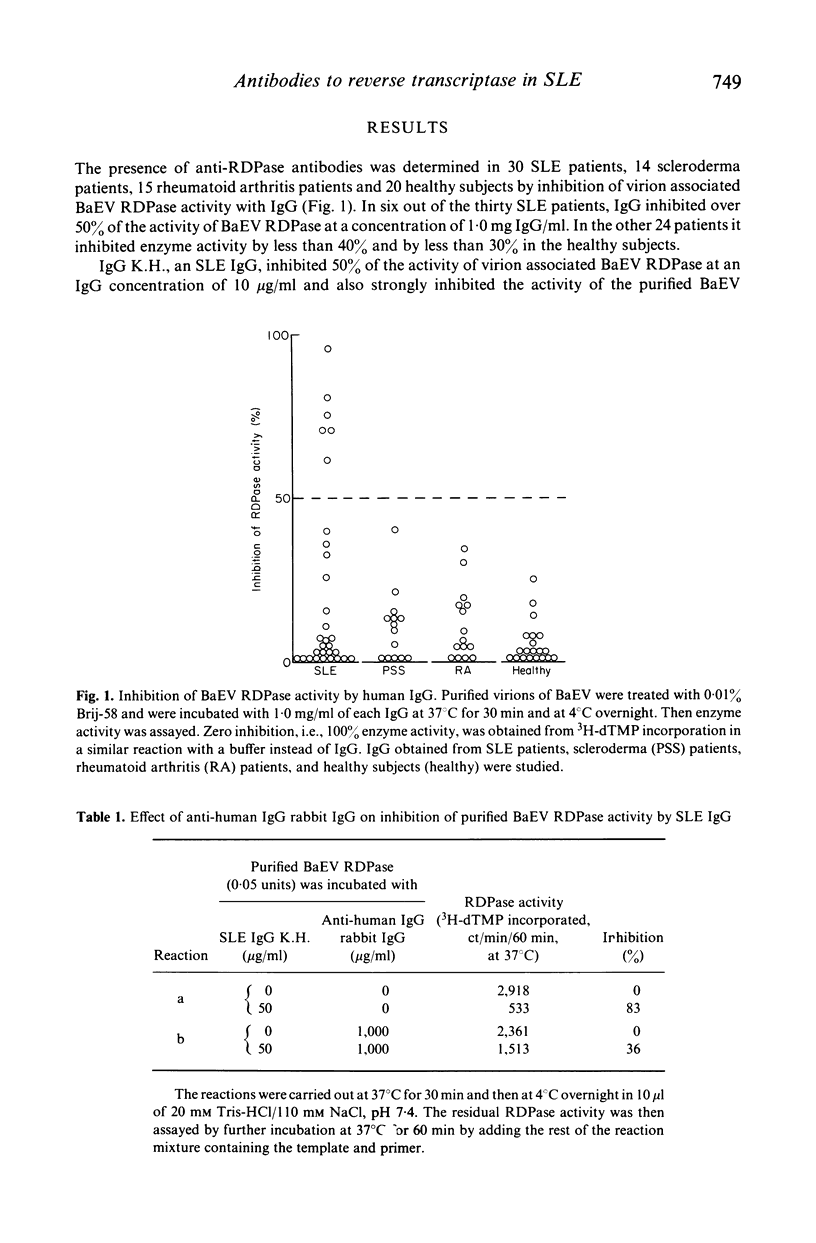
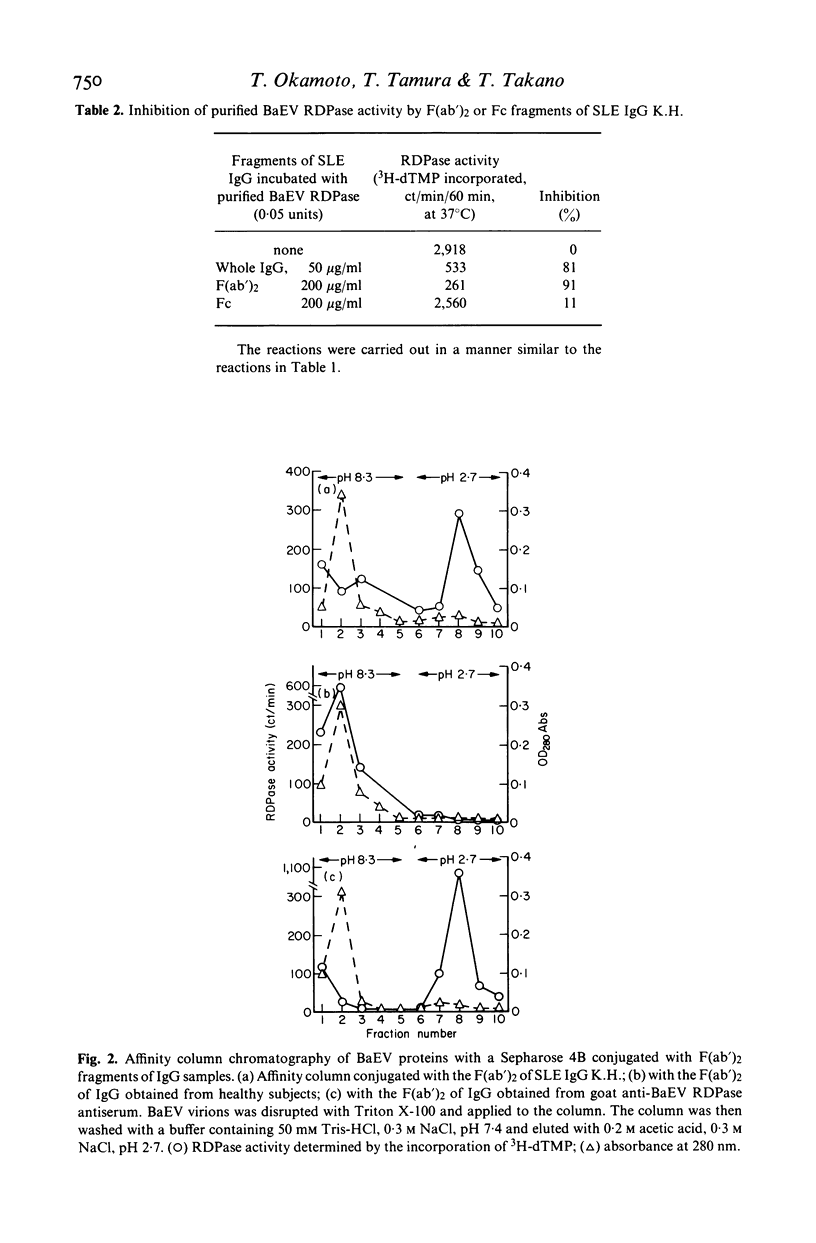
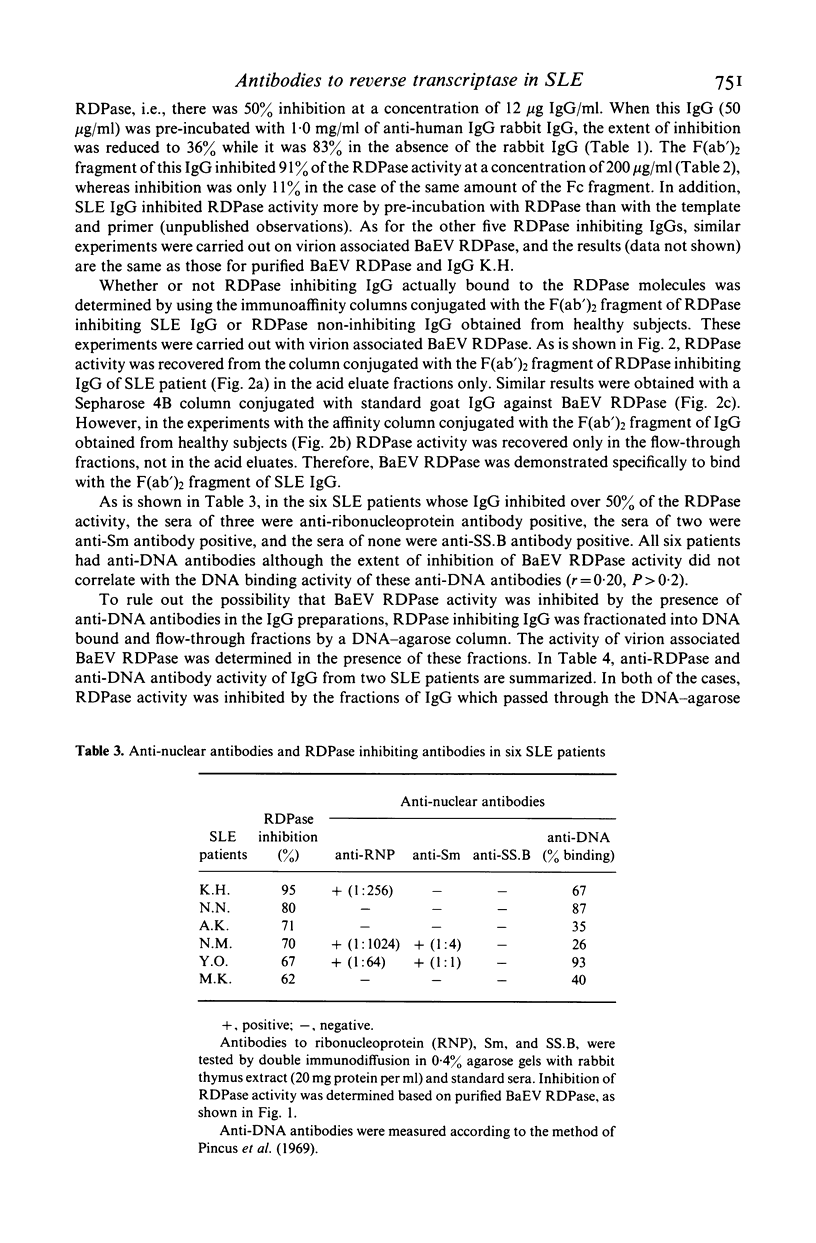
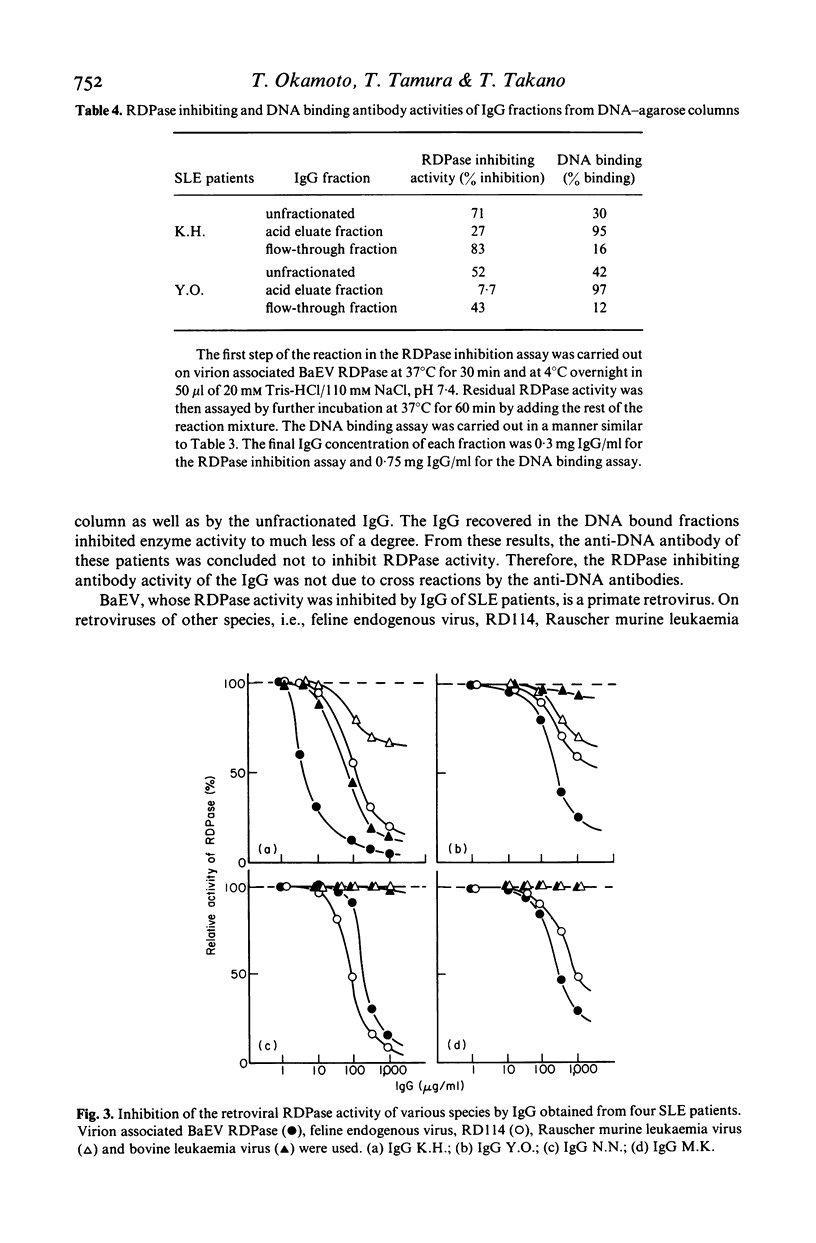
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) in six out of 30 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) strongly inhibited the activity of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (RDPase) of baboon endogenous virus, M7, while IgG obtained from scleroderma patients, rheumatoid arthritis patients and normal subjects was less reactive. Experiments with anti-human IgG and with IgG F (ab')2-bound immunoaffinity columns indicated that the inhibition of RDPase was antibody-mediated. The RDPase inhibiting activity of SLE IgG was considered not to be due to cross-reactions of anti-nuclear antibodies including anti-DNA, anti-ribonucleoprotein, anti-Sm and anti-SS.B antibodies. SLE IgG preferably inhibited the RDPase activity of baboon endogenous virus and a feline endogenous virus, RD114. These findings support the hypothesis that retrovirus(es) might be involved in SLE.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Bolognesi D., Aaronson S. A. Humans have antibodies capable of recognizing oncoviral glycoproteins: demonstration that these antibodies are formed in response to cellular modification of glycoproteins rather than as consequence of exposure to virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1617–1621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Lieber M. M., Livingston D. M., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J., Kalter S. S. Infectious C-type virus isolated from a baboon placenta. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):17–20. doi: 10.1038/248017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian C. L. Editorial: Systemic lupus erythematosus and type C RNA viruses. N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 26;295(9):501–502. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608262950911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian C. L., Phillips P. E. Viruses and autoimmunity. Am J Med. 1973 May;54(5):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., HORBETT A. P. Human gamma globulin fractionation on anion exchange cellulose columns. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2645–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., Ferrer J. F. In vitro transmission and propagation of the bovine leukemia virus in monolayer cell cultures. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 1):4152–4159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin P. C., Saxinger C., Gallo R. C. Surface antibodies of human myelogenous leukaemia leukocytes reactive with specific type-C viral reverse transcriptases. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):230–236. doi: 10.1038/276230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E., Ziff M. Immunoglobulin synthesis by peripheral blood cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):219–228. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakower J. M., Barbacid M., Aaronson S. A. Radioimmunoassay for mammalian type C viral reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):331–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.331-339.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Autoimmunity and neoplasia. The possible role of C-type viruses. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Aug;62(2):258–280. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Bryan T., Rasheed S., Khan A. S. Identification and cloning of endogenous retroviral sequences present in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4892–4896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukage A., Bohn E. W., Wilson S. H. Multiple forms of DNA polymerase in mouse myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):578–582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. M., Nicolson M., Gardner M. B., Rongey R. W., Rasheed S., Sarma P. S., Huebner R. J., Hatanaka M., Oroszlan S., Gilden R. V. C-type virus released from cultured human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):3–6. doi: 10.1038/newbio235003a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C., Mellors J. W. Antigen related to mammalian type-C RNA viral p30 proteins is located in renal glomeruli in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):233–237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C., Mellors J. W. Type C RNA virus-specific antibody in human systemic lupus erythematosus demonstrated by enzymoimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2463–2467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., WISSLER F. C., LIPMAN L. N., WOERNLEY D. L. Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:230–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Kurihara M., Takano T. Retrovirus-related sequences in human DNA: detection and cloning of sequences which hybridize with the long terminal repeat of baboon endogenous virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2865–2878. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panem S., Ordóez N. G., Kirstein W. H., Katz A. I., Spargo B. H. C-type virus expression in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 26;295(9):470–475. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608262950903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P. E. Viruses and systemic lupus erythematosus. Bull Rheum Dis. 1977;28(7):954–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Schur P. H., Rose J. A., Decker J. L., Talal N. Measurement of serum DNA-binding activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 25;281(13):701–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909252811304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T. Studies regarding a possible function for viruses in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):847–856. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUSCHER F. J. A virus-induced disease of mice characterized by erythrocytopoiesis and lymphoid leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Sep;29:515–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin P. S., Friedman B., Gallo R. C. Purification and characterization of baboon endogenous virus DNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 16;479(2):198–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder H. W., Jr, Fleissner E. Specificity of human antibodies to oncovirus glycoproteins: recognition of antigen by natural antibodies directed against carbohydrate structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1622–1626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T. A., Takano T. The characteristics of the RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of baboon endogenous virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Mar;47(1):237–241. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-1-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


