Abstract
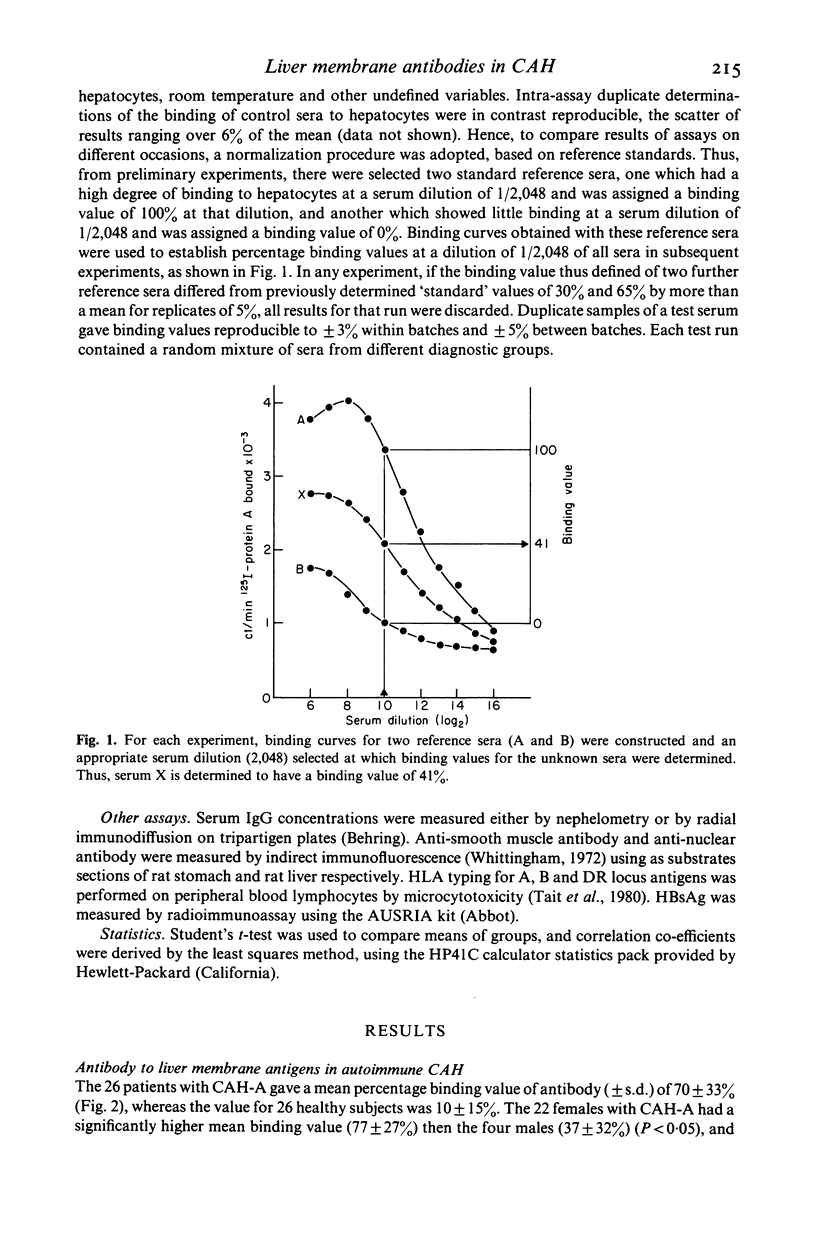
An immunoradiometric assay for IgG class autoantibody to liver membrane antigens, based on serum binding to glutaraldehyde treated monkey hepatocytes, was used to examine sera from patients with chronic active hepatitis (CAH) and other acute and chronic liver diseases. All sera from normals and patients showed binding, up to a titre of 1/2,048. For comparison of assays, results were normalized by selecting two reference sera, one with a high degree of binding, and one from a healthy subject with a low degree of binding: at a dilution of 1/2,048, these sera were given binding values of 100% and 0%. The values for the binding of unknown sera at the same dilution were calculated from these two reference values. For 26 patients with autoimmune CAH, the mean (+/- s.d.) percentage binding value (70 +/- 33%) was significantly higher than the mean value for 26 healthy subjects (10 +/- 15%), and high binding values were significantly associated with biochemically active hepatitis. The mean percentage binding value was moderately increased for eight patients with HBsAg associated CAH (42 +/- 12%), 13 patients with alcoholic hepatitis with cirrhosis (37 +/- 25%) and 45 patients with acute viral hepatitis A (40 +/- 27%) or B (52 +/- 37%). At a cut-off binding value of 65%, the assay as a single diagnostic procedure was shown to have a 70% sensitivity and a 95% specificity for the diagnosis of autoimmune CAH. Better understanding of the pathogenetic significance of antibodies to liver membrane antigens in CAH and other liver diseases will depend upon biochemical analysis of the presumably multiple antigenic determinants on the hepatocyte membrane.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomaeus W. N., Reed W. D., Joske R. A., Shilkin K. B. Autoantibody responses to liver-specific lipoprotein in mice. Immunology. 1981 Jun;43(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fabre J. W. Organ-specific IgM autoantibodies to liver, heart and brain in man: generalized occurrence and possible functional significance in normal individuals, and studies in patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jul;45(1):37–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feighery C., McDonald G. S., Greally J. F., Weir D. G. Histological and immunological investigation of liver-specific protein (LSP) immunized rabbits compared with patients with liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jul;45(1):143–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Arnold W. Detection of a liver-membrane autoantibody in HBsAg-negative chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Mar 11;294(11):578–582. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603112941103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen D. M., McFarlane I. G., Portmann B. S., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Detection of antibodies directed against a liver-specific membrane lipoprotein in patients with acute and chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jul 6;299(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197807062990101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakumu S., Arakawa Y., Goji H., Kashio T., Yata K. Occurrence and significance of antibody to liver-specific membrane lipoprotein by double-antibody immunoprecipitation method in sera of patients with acute and chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 1979 Apr;76(4):665–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronborg I. J., Frazer I. H., Mackay I. R. Autoantibodies to liver antigens in chronic liver disease. I. A radioimmunoassay for antibody to liver membrane antigens. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1982 Dec;9(3):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Baekkeskov S. Islet cell antibodies-theoretical and practical implications. Diabetologia. 1981 Nov;21(5):431–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00257781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane I. G., Wojcicka B. M., Zucker G. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Purification and characterization of human liver-specific membrane lipoprotein (LSP). Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):381–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meliconi R., Perperas A., Jensen D., Alberti A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Anti-LSP antibodies in acute liver disease. Gut. 1982 Jul;23(7):603–607. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.7.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Manns M., Hütteroth T. H., Hopf U., Arnold W. LM-Ag and LSP--two different target antigens involved in the immunopathogenesis of chronic active hepatitis? Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Aug;37(2):205–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Knolle J., Berger J. Celluläre Immunreaktionen gegenüber homologen leberspezifischen Antigenen (HLP) bei chronischen Leberentzündungen. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Mar 1;52(5):246–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01468598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


