Abstract
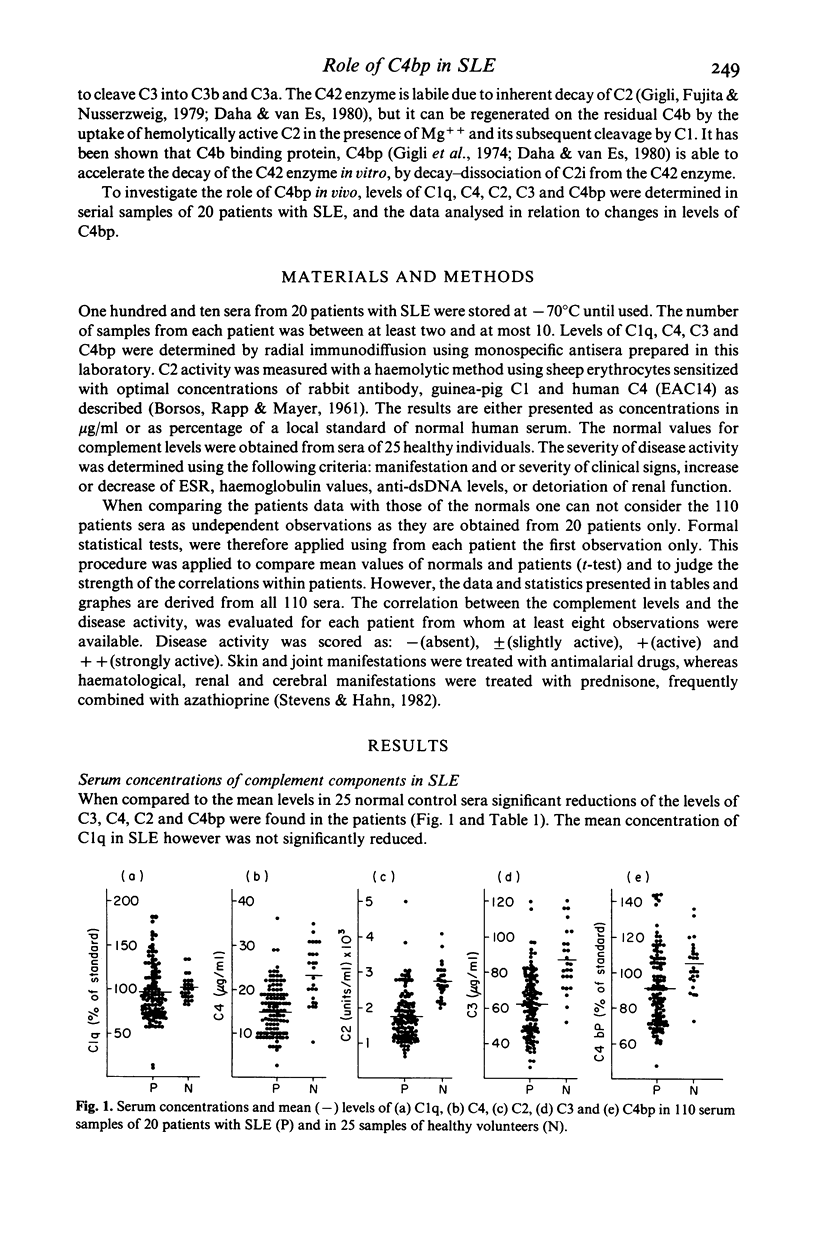
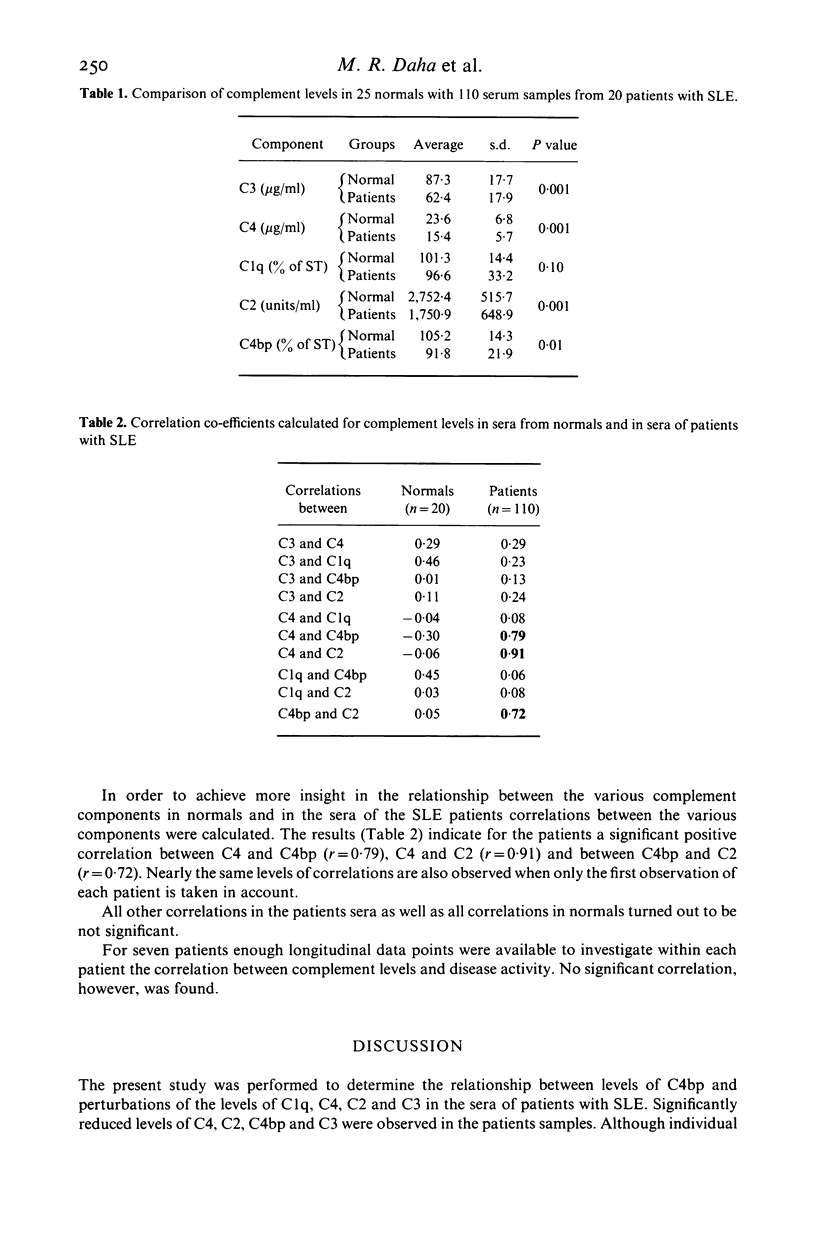
Serum concentrations of C1q, C4, C4 binding protein (C4bp), C3 and C2 haemolytic activity have been measured in 110 samples from 20 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Significant reductions in comparison to normal levels were found in the mean serum concentrations of C4, C3 and C4bp as well as C2 haemolytic activities. For patients serum concentrations of C4 correlated with C2 haemolytic activities (r = 0.91) and C4bp (r = 0.79); the C2 haemolytic levels correlated with the concentration of C4b (r = 0.72). It is concluded that serum concentrations of the complement components C4 and C2, which are the constituents of the classical pathway C3 convertase, are regulated by C4bp in vivo. Further metabolic studies are required to determine the causes of decreased serum concentrations of C4bp in patients with SLE.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daha M. R., van Es L. A. Relative resistance of the F-42-stabilized classical pathway C3 convertase to inactivation by C4-binding protein. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2051–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Pickering R. J., Naff G., Snyderman R., Mergenhagen S. E., Good R. A. Decreased properdin activity in acute glomerulonephritis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(6):592–598. doi: 10.1159/000230780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Fujita T., Nussenzweig V. Modulation of the classical pathway C3 convertase by plasma proteins C4 binding protein and C3b inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6596–6600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H., Merrill J. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Austen K. F. Metabolism of third complement component (C3) in nephritis. Involvement of the classic and alternate (properdin) pathways for complement activation. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 26;287(17):835–840. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210262871701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Agnello V., Carr R. I., Kunkel H. G. Variable patterns of immunoglobulin and complement deposition in the kidneys of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Pathol. 1969 Sep;56(3):305–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., NAFF G. B., TODD E. W., PENSKY J., HINZ C. F. Chromatographic resolution of the first component of human complement into three activities. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:983–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H. Serum complement component levels in human glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Oct;75(4):555–560. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. H., Michael A. F. Properdin anc C3 proactivator: alternate pathway components in human glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):634–644. doi: 10.1172/JCI107225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Stroud R. M. Cleavage of C2 by C1s into the antigenically distinct fragments C2a and C2b: demonstration of binding of C2b to C4b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2998–3001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polley M. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Enharncement of the hemolytic activity of the second component of human complement by oxidation. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1013–1025. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. B., Hahn B. H. Management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Bull Rheum Dis. 1982;32(4):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Schur P. H., Ruddy S. Relative importance of C3b inactivator and beta 1H globulin in the modulation of the properdin amplification loop in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jun;36(3):408–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Peters D. K., Fallows J., Petrie A., Kourilsky O., Morel-Maroger L., Cameron J. S. Studies of serum complement in the hypocomplementaemic nephritides. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):391–405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler J. B., Rosen F. S., Alper C. A., Grupe W., Lepow I. H. Metabolism of properdin in normal subjects and patients with renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):761–767. doi: 10.1172/JCI108147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


