Abstract
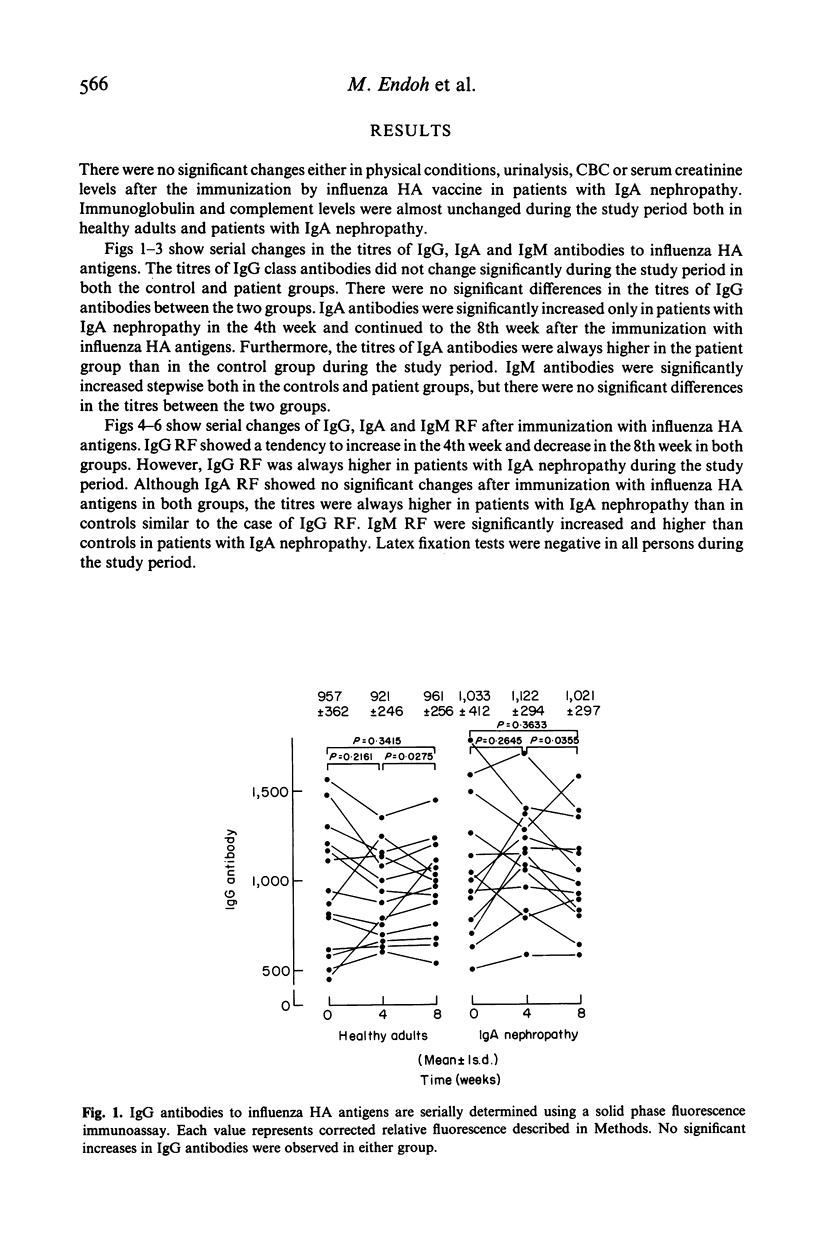
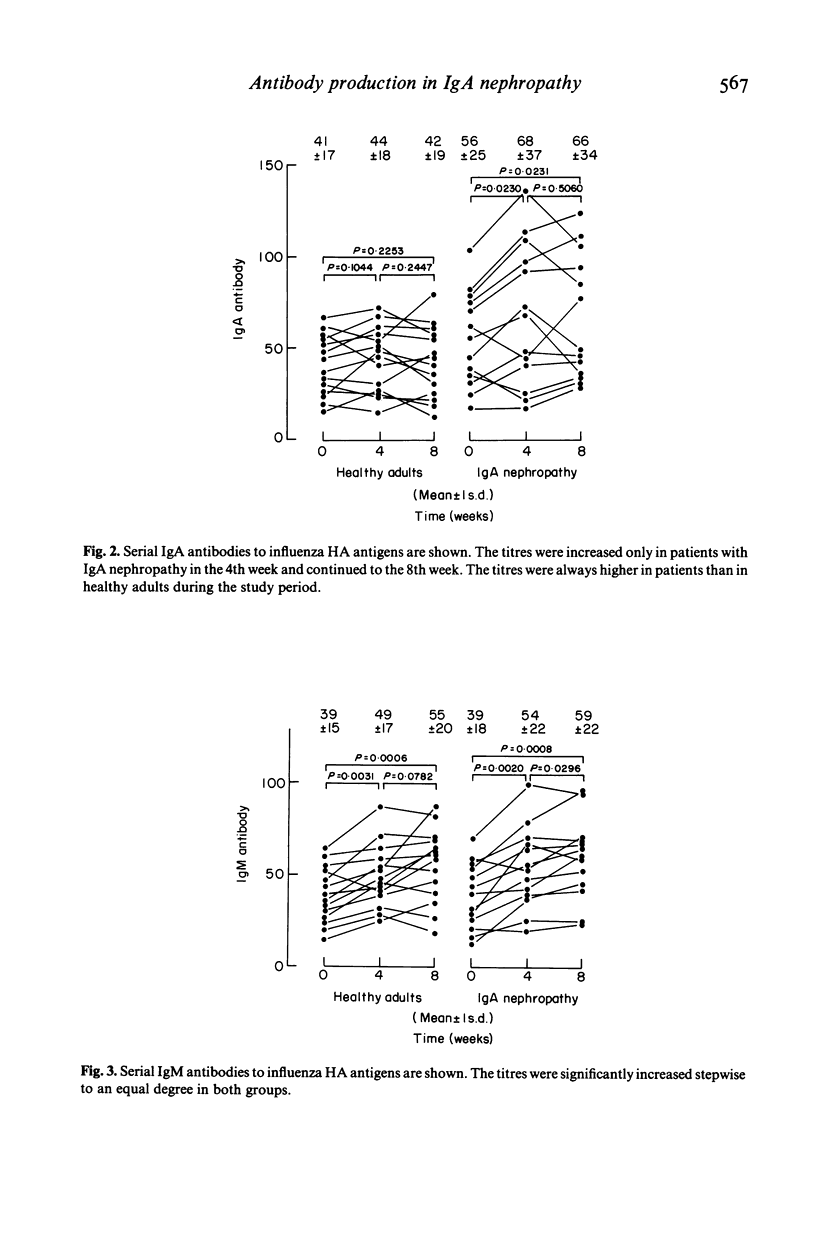
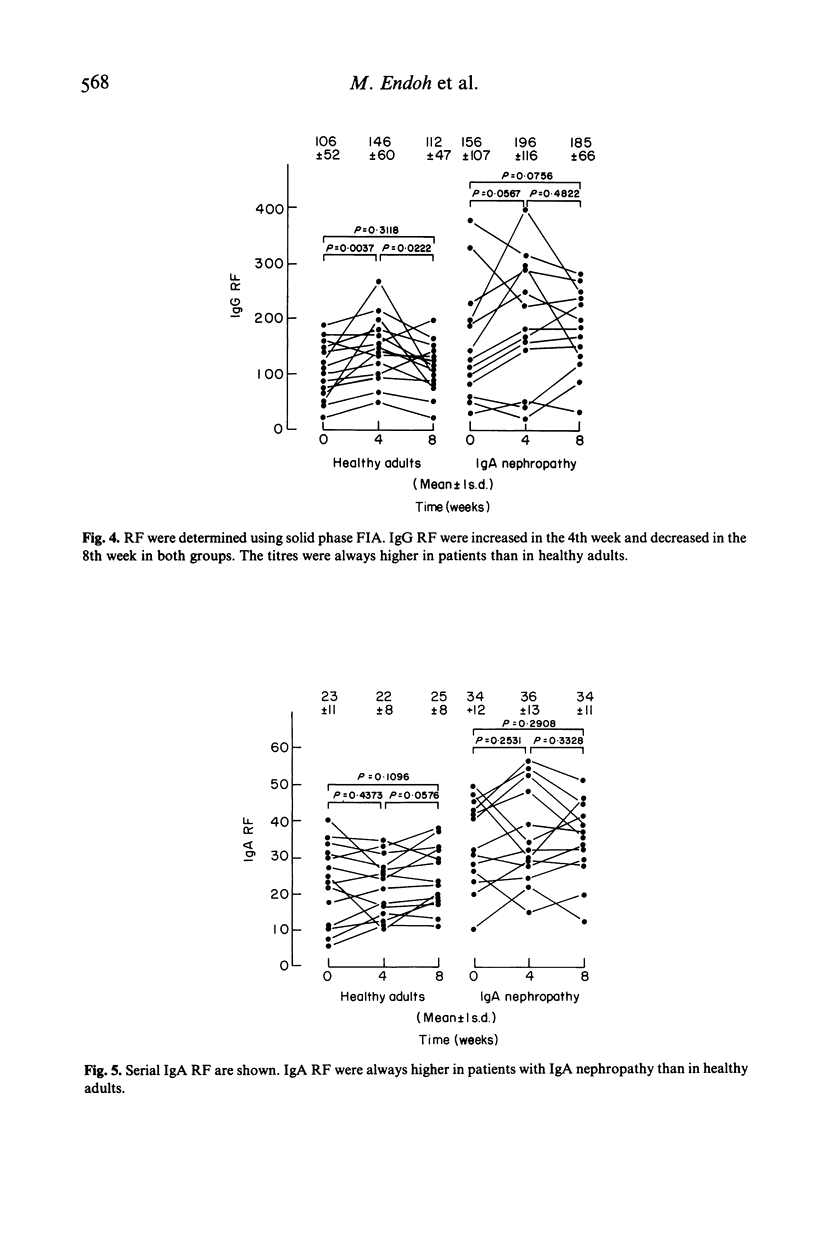
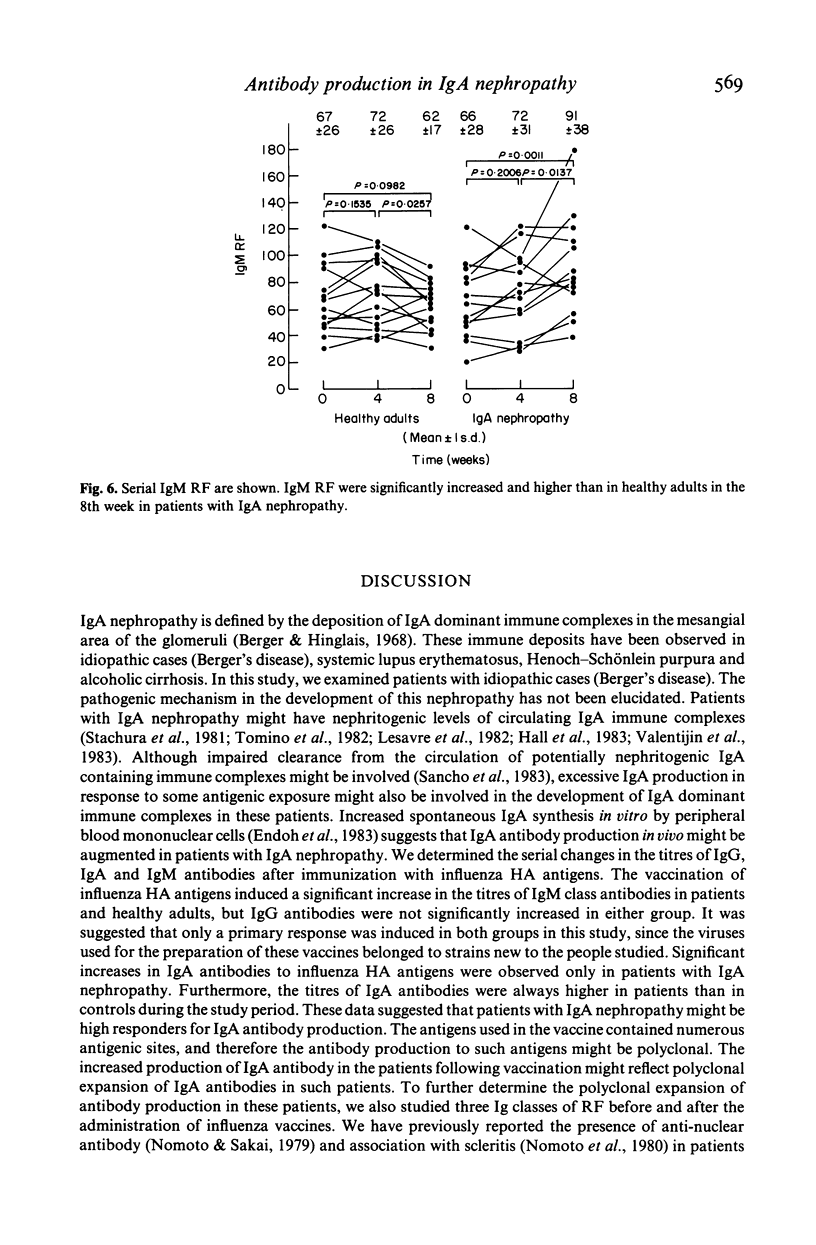
Augmentation of IgA production has been postulated for the development of IgA nephropathy. An influenza HA vaccine was administered to healthy adults and patients with IgA nephropathy to elucidate if there was any in vivo alteration of antibody production in response to antigenic stimulation in these patients. The vaccine was administered s.c. in a dose of 350 CCA units at an interval of 4 weeks. IgG, IgA and IgM class antibodies to influenza HA antigens and three classes of rheumatoid factors (RF) were determined using a solid phase fluorescence immunoassay. The titres of IgG class antibodies to influenza HA antigens did not change significantly in either group after the vaccination. No significant differences were observed in the titres of IgG antibodies between the two groups. IgA antibodies were significantly increased only in patients in the 4th week and continued to the 8th week. The titres of IgA antibodies were always higher in patients than in controls during the study period. IgM antibodies were significantly increased stepwise in both groups to an equal degree. IgG and IgA RF were always higher in patients than in controls. IgM RF were significantly increased and higher than in controls in the 8th week in patients. It is concluded that patients with IgA nephropathy might be high responders for IgA antibody production, and that polyclonal activation might be associated with increased IgA production following in vivo antigenic stimulation in these patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger J., Hinglais N. Les ddpôts intercapillaires d'IgA-IgG. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 1968 Sep;74(9):694–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Kaneshige H., Tomino Y., Nomoto Y., Sakai H., Arimori S., Shinbo T., Ishihara T. IgA nephropathy associated with myasthenia gravis and scleritis. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1981 Oct;6(4):421–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Sakai H., Nomoto Y., Tomino Y., Kaneshige H. IgA-specific helper activity of T alpha cells in human peripheral blood. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2612–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. P., Stachura I., Cason J., Whiteside T. L., Lawley T. J. IgA-containing circulating immune complexes in patients with igA nephropathy. Am J Med. 1983 Jan;74(1):56–63. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurault de Ligny B., Sirbat D., Bene M. C., Faure G., Kessler M. Scleritis associated with glomerulonephritis. Nephron. 1983;35(3):207–207. doi: 10.1159/000183077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai H., Nakamoto Y., Miki K., Miyakuni T., Miura A. B. Pseudothrombocytopenia and IgA-related platelet agglutinin in a patient with IgA nephritis. Nephron. 1983;34(3):154–158. doi: 10.1159/000183001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennette J. C., Ferguson A. L., Moore M. A., Freeman D. G. IgA nephropathy associated with seronegative spondylarthropathies. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Feb;25(2):144–149. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustonen J., Pasternack A., Helin H., Rilva A., Penttinen K., Wager O., Harmoinen A. Circulating immune complexes, the concentration of serum IgA and the distribution of HLA antigens in IgA nephropathy. Nephron. 1981;29(3-4):170–175. doi: 10.1159/000182350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto Y., Sakai H., Arimori S. Increase of IgA-bearing lymphocytes in peripheral blood from patients with IgA nephropathy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Feb;71(2):158–160. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto Y., Sakai H. Cold-reacting antinuclear factor in sera from patients with IgA nephropathy. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jul;94(1):76–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai H., Endoh M., Tomino Y., Nomoto Y. Increase of IgA specific helper T alpha cells in patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):77–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai H., Nomoto Y., Arimori S. Decrease of IgA-specific suppressor T cell activity in patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Nov;38(2):243–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Egido J., Rivera F., Hernando L. Immune complexes in IgA nephropathy: presence of antibodies against diet antigens and delayed clearance of specific polymeric IgA immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):194–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spichtin H. P., Truniger B., Mihatsch M. J., Bucher U., Gudat F., Zollinger H. U. Immunothrombocytopenia and IgA nephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1980 Dec;14(6):304–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachura I., Singh G., Whiteside T. L. Immune abnormalities in IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Sep;20(3):373–388. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomino Y., Sakai H., Endoh M., Kaneshige H., Nomoto Y. Detection of immune complexes in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by double immunofluorescence in patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jul;24(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentijn R. M., Kauffmann R. H., de la Rivière G. B., Daha M. R., Van ES L. A. Presence of circulating macromolecular IgA in patients with hematuria due to primary IgA nephropathy. Am J Med. 1983 Mar;74(3):375–381. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90954-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe A. J., Gormly A. A., McKenzie P. E., Wootton A. M., Thompson A. J., Seymour A. E., Clarkson A. R. Immunologic studies in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1980 Sep;18(3):366–374. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


