Abstract
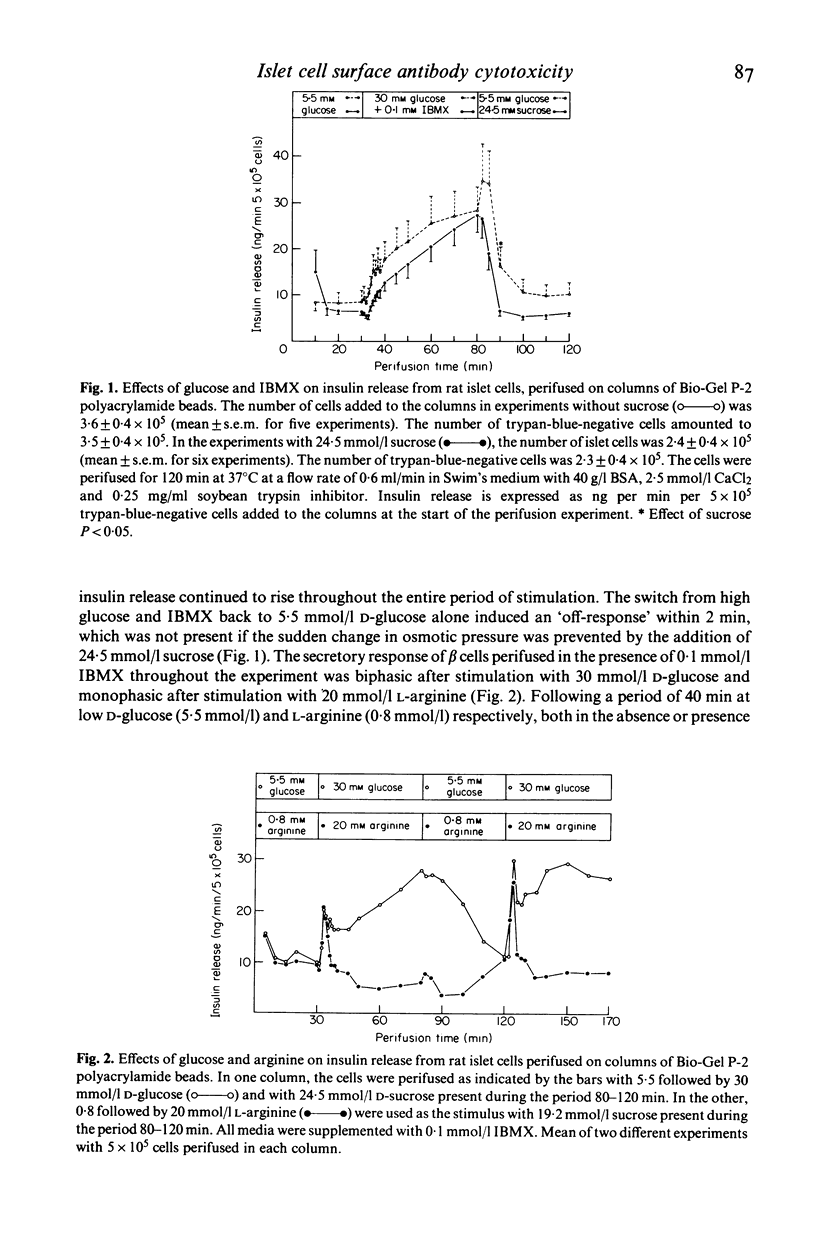
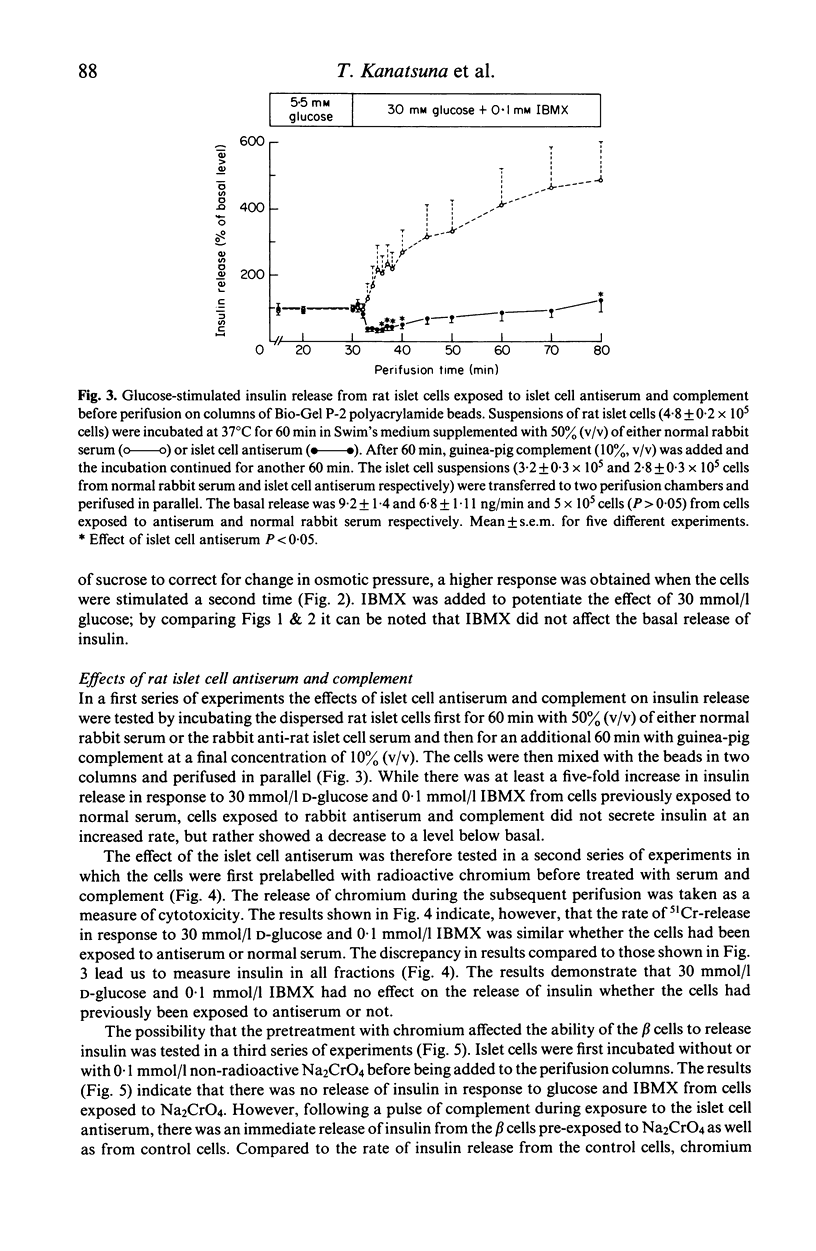
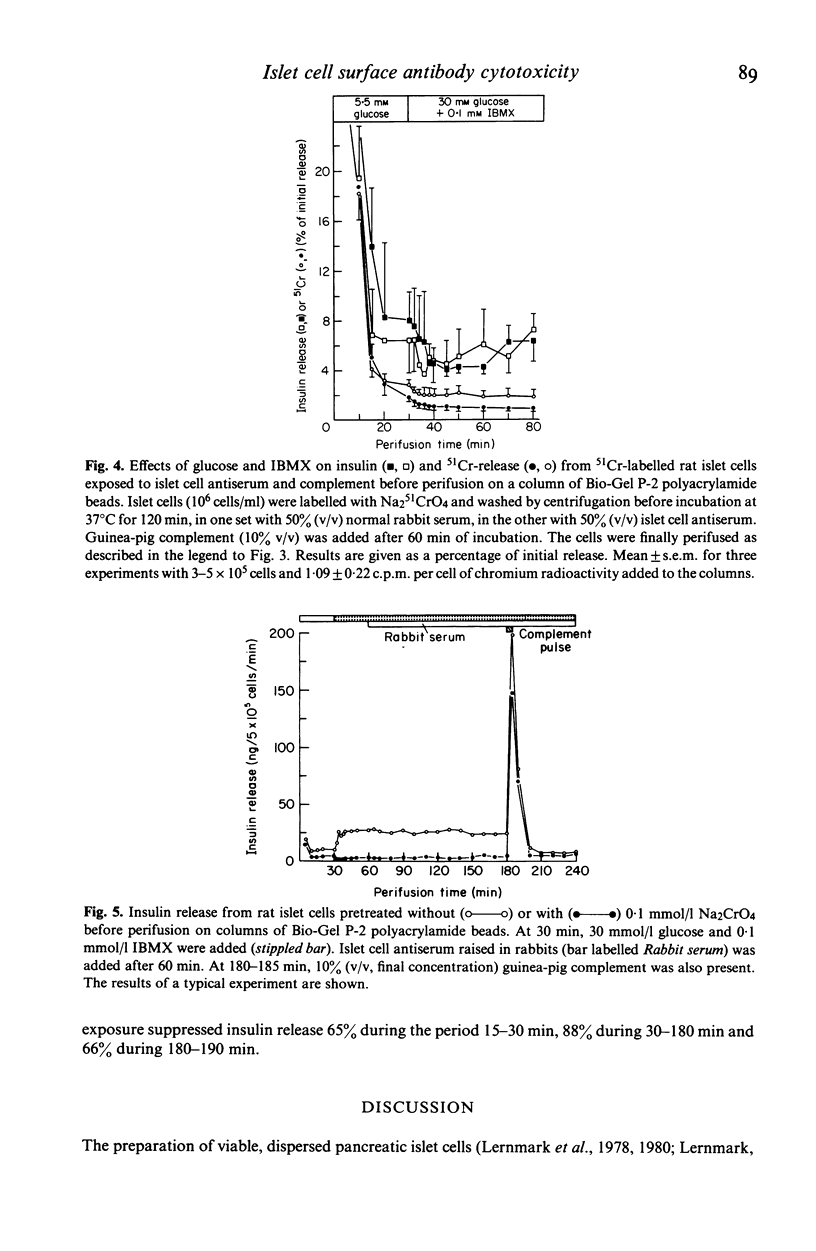
The dynamics of insulin and chromium release from prelabelled rat pancreatic islet cells were studied by perifusion of cells supported in a column of Bio-Gel P-2 polyacrylamide beads. The column-perifused β cells released insulin in a biphasic pattern in response to 30 mmol/l D-glucose and in a monophasic pattern to 20 mmol/l L-arginine. Rat islet cells, first exposed to a rabbit anti-rat islet cell surface serum and complement and then added to the column, were unable to release insulin in response to 30 mmol/l D-glucose and 0·1 mmol/l 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX). In order to study cytotoxicity by an additional approach, islet cells were prelabelled with radioactive chromium (Na251CrO4). These cells did not release either insulin or 51Cr in response to glucose. Furthermore, exposure of the cells to surface antiserum and complement before perifusion did not induce either chromium or insulin release. Similar results were obtained when glucose alone or combined with surface antiserum was added to the perifusate bathing rat islet cells incubated with 0·1 mmol/l non-radioactive Na2CrO4 before perifusion. However, a transient, dramatic release of insulin from these cells was induced by adding complement to the perifusion medium (containing surface antibodies). These results indicate that complement-dependent cytotoxicity of islet cell surface antibodies involves different phenomena. Firstly, the cytotoxic reaction results in a transient release of insulin whether the physiological release mechanisms were blocked by chromium or not. Secondly, in cells not treated with chromium the cytotoxic reactions renders the β cells unable to release insulin in response to glucose.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackard W. G., Kikuchi M., Rabinovitch A., Renold A. E. An effect of hyposmolarity on insulin release in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1975 Mar;228(3):706–713. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.3.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Christensen A., Doniach D. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1279–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G. F., Betterle C., Padovan D., Erle G., Toffolo A., Bersahi G. Incidence and significance of islet-cell autoantibodies in different types of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1977 Oct;26(10):909–915. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.10.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobersen M. J., Scharff J. E., Ginsberg-Fellner F., Notkins A. L. Cytotoxic autoantibodies to beta cells in the serum of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 25;303(26):1493–1498. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012253032601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Adamson U., Rundfeldt M., Andersson S., Cerasi E. Glucose memory of pancreatic B and A2 cells: evidence for common time-dependent actions of glucose on insulin and glucagon secretion in the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):700–707. doi: 10.1172/JCI109512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Curry D., Landahl H., Bennett L. [Further studies on the dynamic aspects of insulin release in vitro with evidence for a two-compartmental storage system]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1969 Sep;6 (Suppl 1):554–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., McCallum C. J., Gray R. S., Campbell C. J., Duncan L. J., Farquhar J. W., Vaughan H., Morris P. J. Pancreatic islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus correlated with the duration and type of diabetes, coexistent autoimmune disease, and HLA type. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):138–147. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanatsuna T., Lernmark A., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. Block in insulin release from column-perifused pancreatic beta-cells induced by islet cell surface antibodies and complement. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):231–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kromann H., Christy M., Egeberg J., Lernmark A., Nerup J., Richter-Olesen H. Direct streptozotocin toxicity on dispersed mouse islet cells determined by [51]Cr-release. Med Biol. 1980 Dec;58(6):322–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lendrum R., Walker G., Cudworth A. G., Theophanides C., Pyke D. A., Bloom A., Gamble D. R. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1976 Dec 11;2(7998):1273–1276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lendrum R., Walker G., Gamble D. R. Islet-cell antibodies in juvenile diabetes mellitus of recent onset. Lancet. 1975 Apr 19;1(7912):880–882. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Freedman Z. R., Hofmann C., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F., Jackson R. L., Winter R. J., Traisman H. S. Islet-cell-surface antibodies in juvenile diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 24;299(8):375–380. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808242990802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Hägglöf B., Freedman Z., Irvine J., Ludvigsson J., Holmgren G. A prospective analysis of antibodies reacting with pancreatic islet cells in insulin-dependent diabetic children. Diabetologia. 1981 Apr;20(4):471–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00253410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Kanatsuna T., Patzelt C., Diakoumis K., Carroll R., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. Antibodies direct against the pancreatic islet cell plasma membrane. Detection and specificity. Diabetologia. 1980 Nov;19(5):445–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00281824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. The preparation of, and studies on, free cell suspensions from mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1974 Oct;10(5):431–438. doi: 10.1007/BF01221634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. [Isolated mouse islets as a model for studying insulin release]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1971 Jul-Aug;8(4):649–679. doi: 10.1007/BF01550894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCuish A. C., Irvine W. J., Barnes E. W., Duncan L. J. Antibodies to pancreatic islet cells in insulin-dependent diabetics with coexistent autoimmune disease. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1529–1531. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pek S., Santiago J. C., Tai T. Y. L-Leucine-induced secretion of glucagon and insulin, and the "off-response" to L-leucine in vitro. I. Characterization of the dynamics of secretion. Endocrinology. 1978 Oct;103(4):1208–1218. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-4-1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGZELL H. QUANTITATIVE TITRATIONS OF MOUSE H-2 ANTIBODIES USING CR-51-LABELLED TARGET CELLS. Transplantation. 1965 May;3:423–431. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196505000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


