Abstract
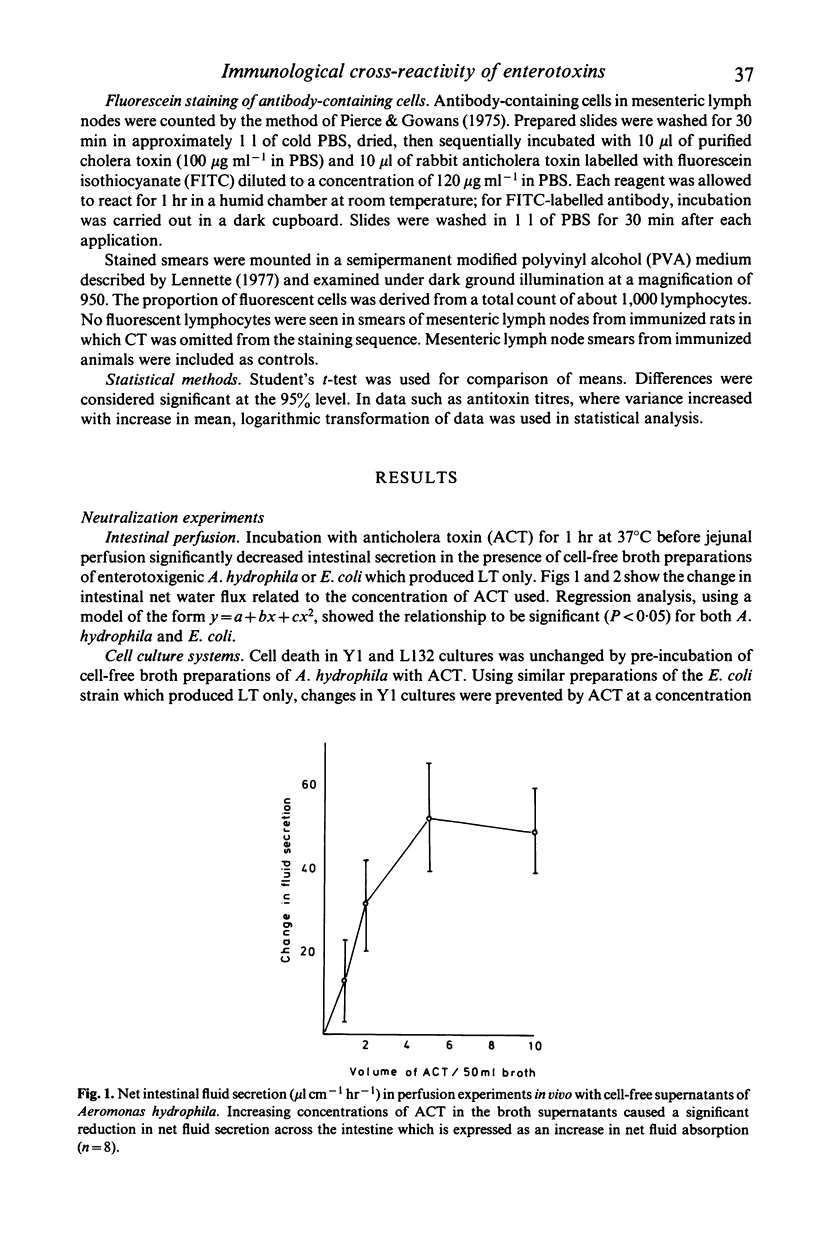
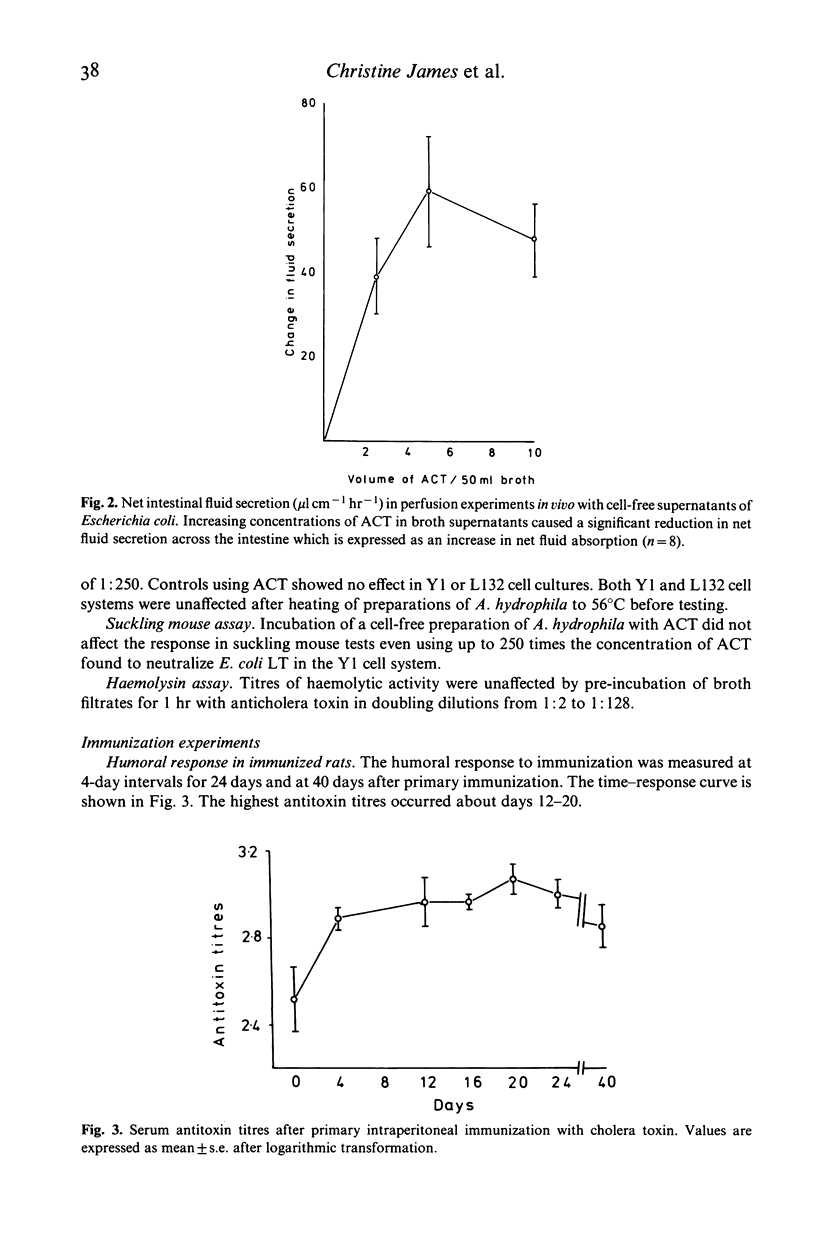
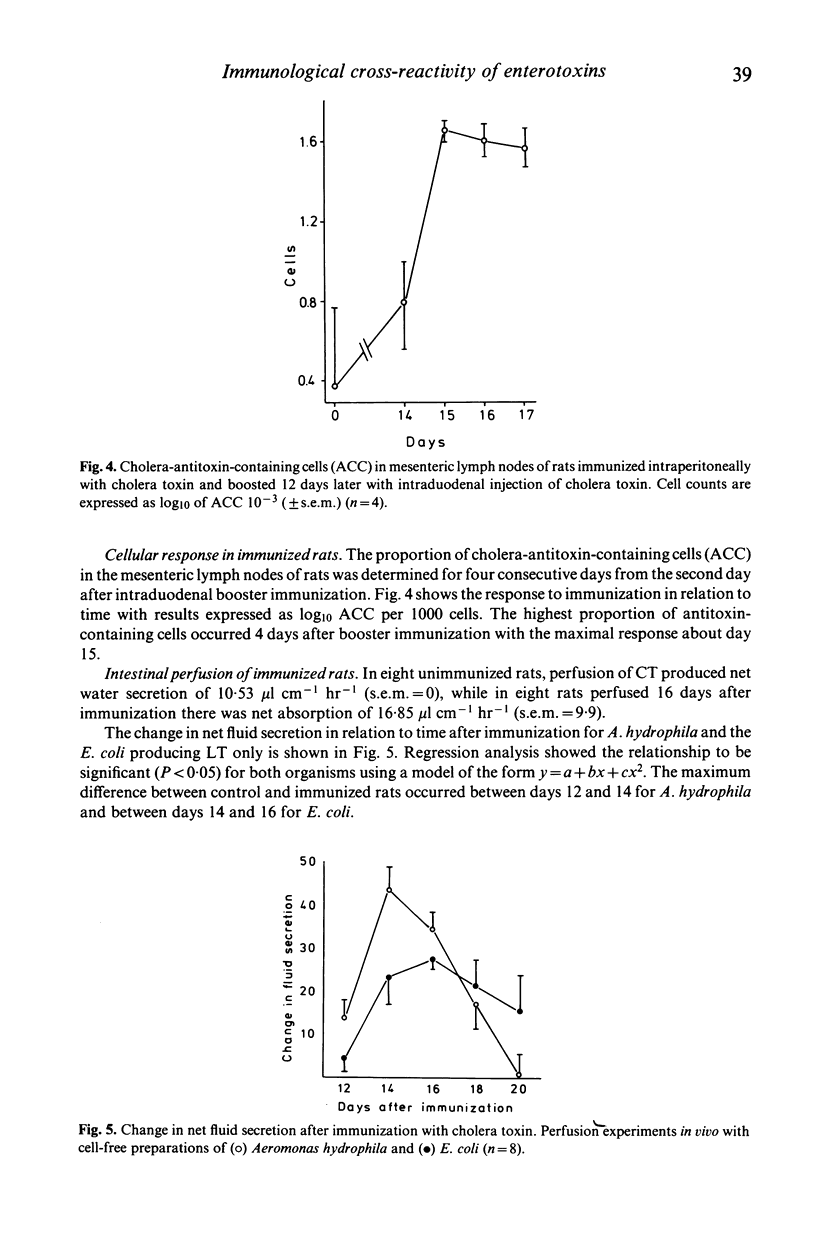
Pre-incubation with anticholera toxin (ACT) significantly reduced intestinal secretion induced by cell-free broth preparations of heat-labile toxins (LT) of Escherichia coli and Aeromonas hydrophila in jejunal perfusion experiments in rats in vivo. Pre-incubation with ACT also prevented cytotoxicity by E. coli LT in the Y1 cell culture system. Pre-incubation had no effect on cytotoxicity in Y1 and L132 cell lines or on haemolytic activity with cell-free preparations of A. hydrophila. In another series of experiments rats were immunized with cholera toxin given as an intraperitoneal priming dose followed 12 days later by intraduodenal boosting. Immunization significantly protected against net intestinal fluid secretion induced by enterotoxigenic E. coli and A. hydrophila and by cholera toxin.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulanger Y., Lallier R., Cousineau G. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1161–1164. doi: 10.1139/m77-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrescu L. Enterotoxigenic Aeromonas hydrophila from a case of piglet diarrhoea. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1978 Nov;25(9):713–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1978.tb01066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Haddow A. D. Cytotoxic activity of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):989–993. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.989-993.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Gorbach S. L. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and serum antitoxin activity by the vascular permeability factor assay. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):731–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.731-735.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Immunological study of the heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.564-570.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Söderlind O., Wadström T. Cross-reactivity between heat labile enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in neutralization tests in rabbit ileum and skin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):757–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Immunological interrelationships between cholera toxin and the heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of coliform bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):110–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.110-117.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennette D. A. An improved mounting medium for immunofluorescence microscopy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;69(6):647–648. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Gowans J. L. Cellular kinetics of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1550–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Koster F. T. Priming and suppression of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid/toxin by parenteral toxoid in rats. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):307–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Huda S., Neogi P. K., Daniel R. R., Spira W. M. Microtiter ganglioside enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for vibrio and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins and antitoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.35-40.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Neutralization of Salmonella toxin-induced elongation of Chinese hamster ovary cells by cholera antitoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):988–992. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.988-992.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen P., Burke V., Gracey M. Effects of intestinal micro-organisms on fluid and electrolyte transport in the jejunum of the rat. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):463–470. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trust T. J., Chipman D. C. Clinical involvement of Aeromonas hydrophila. Can Med Assoc J. 1979 Apr 21;120(8):942–946. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Ljungh A., Wretlind B. Enterotoxin, haemolysin and cytotoxic protein in Aeromonas hydrophila from human infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Apr;84(2):112–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


