Abstract
The association between periodontal disease in humans and serum and salivary antibody to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans strain Y4 was determined. An Elisa was used to examine anti-Y4 antibody of the IgM, IgG, IgA and IgE isotypes in serum from 127 individuals and IgA in parotid saliva. Patients diagnosed as having localized juvenile periodontitis (n = 37) had significantly higher levels and frequency of serum IgG antibodies to Y4 than all other groups. Serum and salivary IgA and serum IgE antibody levels were significantly increased in patients with both localized and generalized types of juvenile periodontitis (n = 48) when compared to all other patient groups. Specificity studies suggested that the antigenic determinants that were differentiating the group responses were unique to the Y4 organism. These results indicate that serum antibodies to Y4 may reflect an infectious process with this micro-organism and that these responses may provide some diagnostic value in delineating different types of periodontal diseases.
Full text
PDF

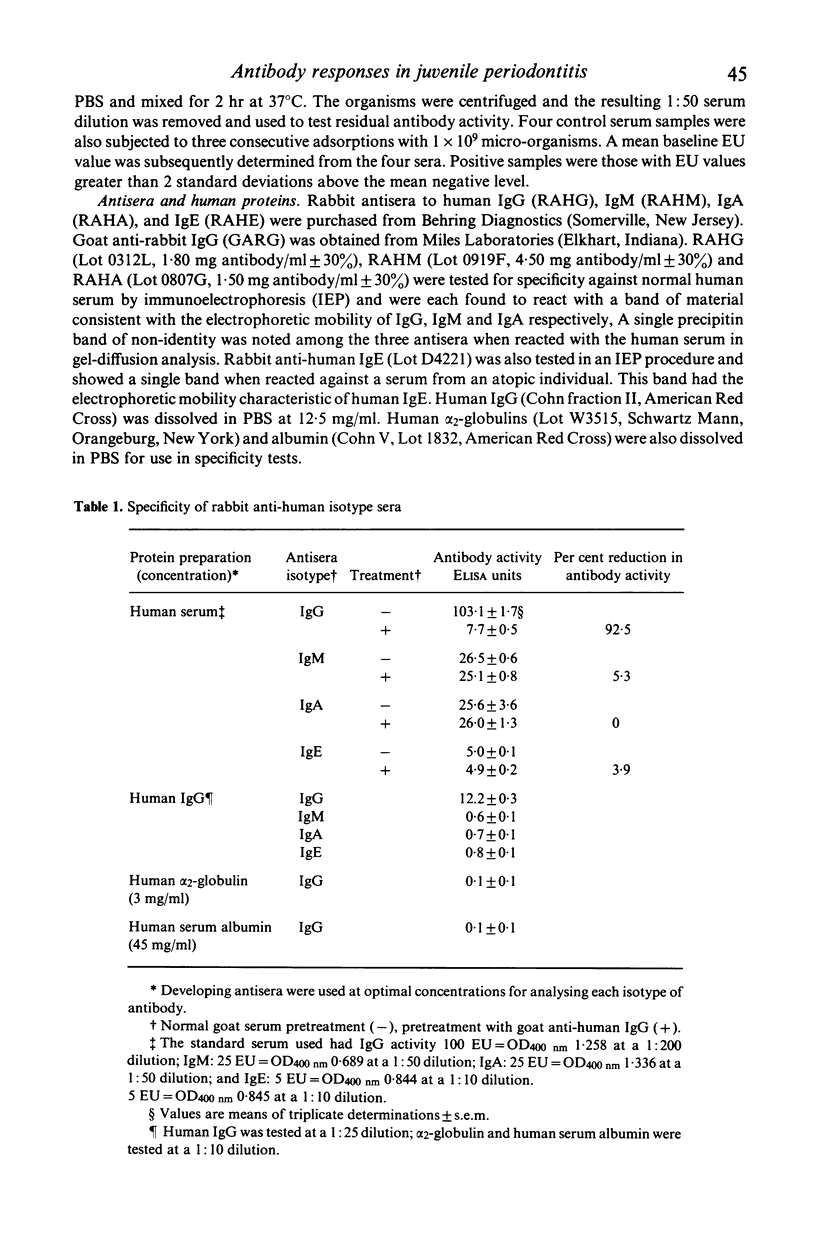
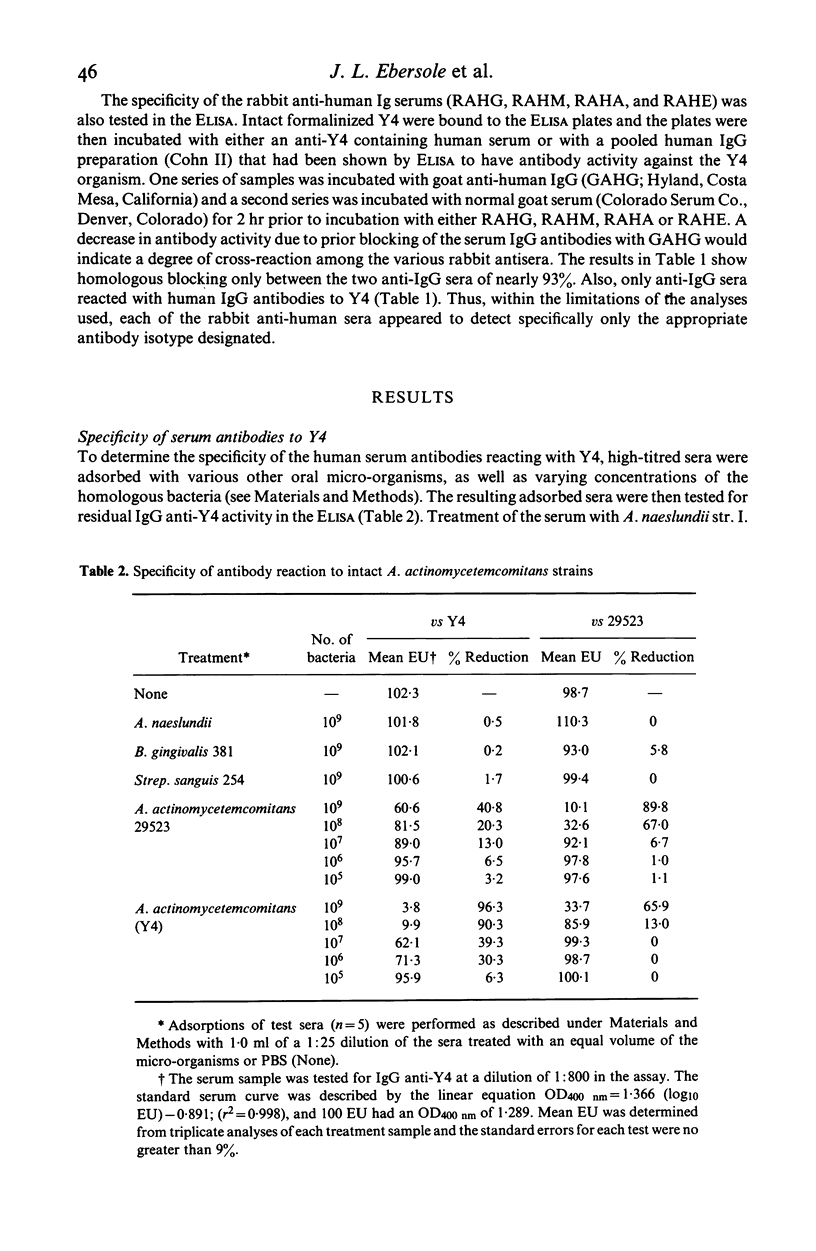

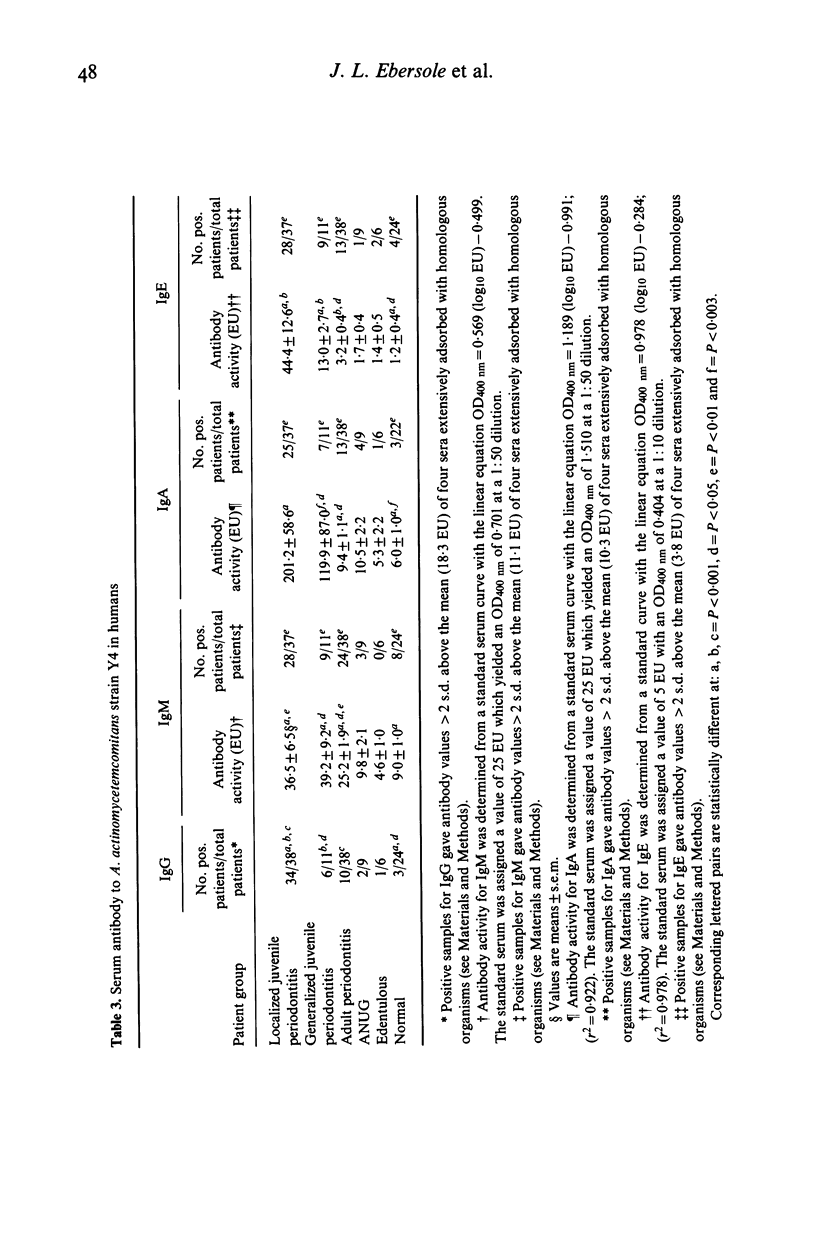




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer P. N. The case for periodontosis as a clinical entity. J Periodontol. 1971 Aug;42(8):516–520. doi: 10.1902/jop.1971.42.8.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Immunology of inflammatory periodontal lesions. Int Dent J. 1973 Sep;23(3):438–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Frey D. E., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J. An ELISA for measuring serum antibodies to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1980 Nov;15(6):621–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1980.tb00321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Protection against enteric bacterial infection by secretory IgA antibodies. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco R. J. Immunoglobulins and periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1970 Apr;41(4):196–201. doi: 10.1902/jop.1970.41.4.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving J. T., Socransky S. S., Heeley J. D. Histological changes in experimental periodontal disease in gnotobiotic rats and conventional hamsters. J Periodontal Res. 1974;9(2):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1974.tb00656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Schiott C. R. Haemophili and related bacteria in the human oral cavity. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Dec;20(12):791–796. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Wilton J. M., Ivanyi L., Manson J. D. Immunological aspects of juvenile periodontitis (periodontosis). J Periodontal Res. 1974;9(5):261–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1974.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson J. D., Lehner T. Clinical features of juvenile periodontitis (periodontosis). J Periodontol. 1974 Aug;45(8):636–640. doi: 10.1902/jop.1974.45.8.2.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S. Predominant cultivable microbiota in periodontosis. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Mar;12(2):120–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisengard R. Immediate hypersensitivity and periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1974 May;45(5):344–347. doi: 10.1902/jop.1974.45.5.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Subgingival microflora and periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):351–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable organisms in juvenile periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;84(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1976.tb00454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., McArthur W. P., Baehni P. C., Hammond B. F., Taichman N. S. Extraction and partial characterization of a leukotoxin from a plaque-derived Gram-negative microorganism. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):427–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.427-439.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. E., Horoszewicz H. U., Cianciola L. J., Genco R. J. Neutrophil chemotaxis dysfunction in human periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):124–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.124-132.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. B., Ratliff D., Muller D., Mandell R., Socransky S. S. Medium for selective isolation of Fusobacterium nucleatum from human periodontal pockets. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):844–849. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.844-849.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


