Abstract
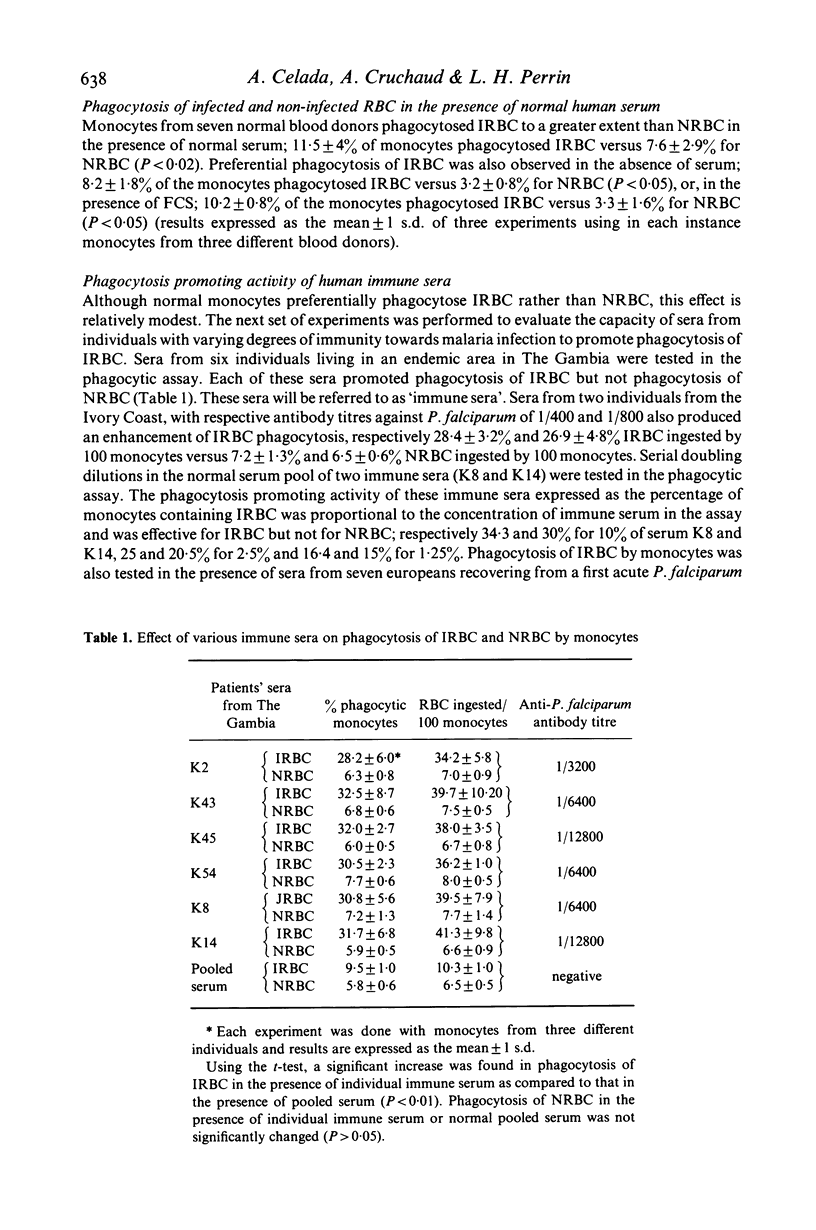
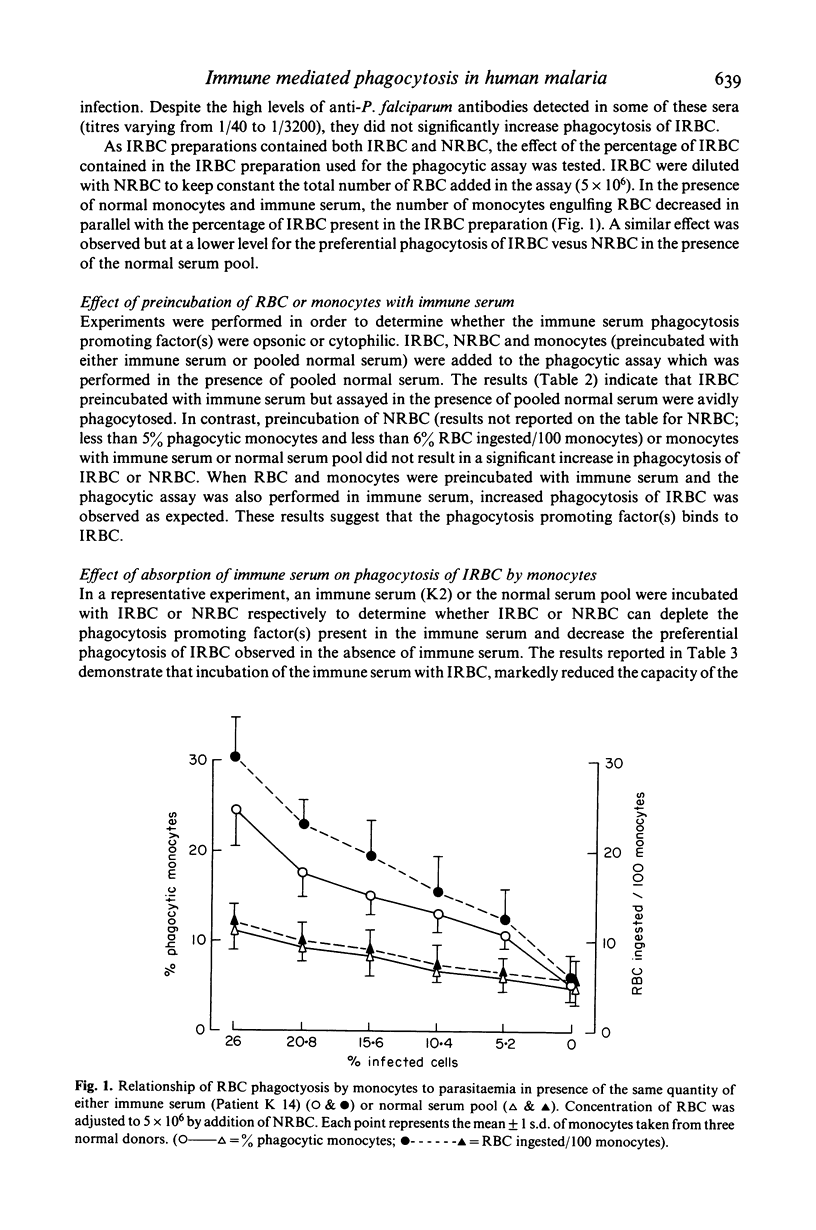
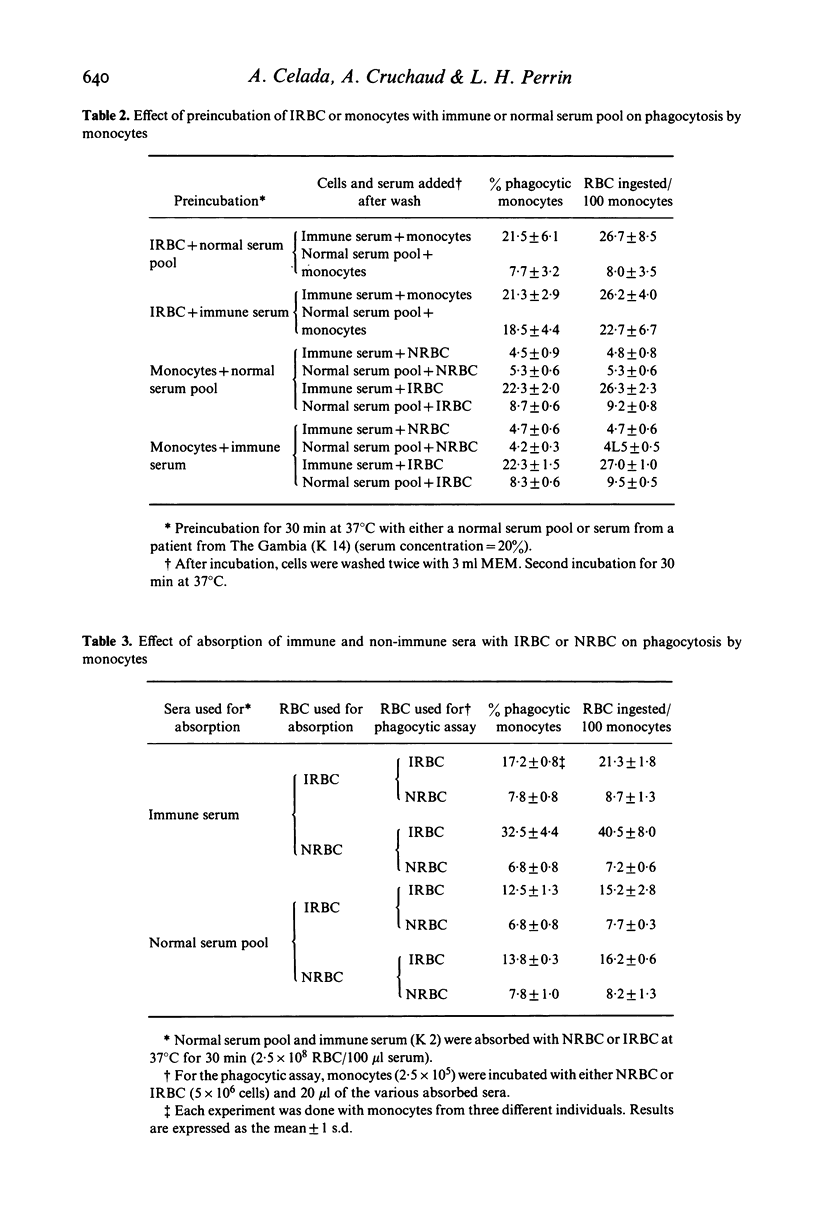
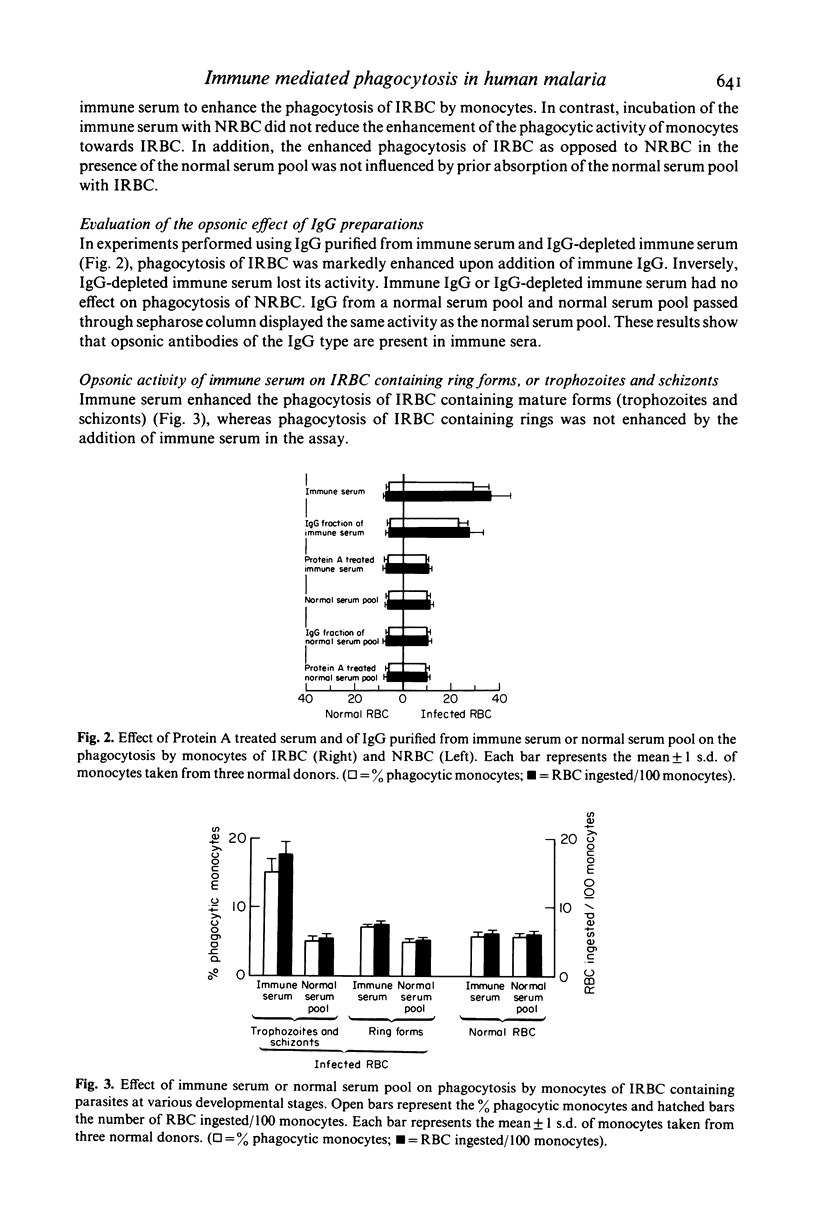
In vitro human monocytes from normal blood donors ingest red blood cells infected with Plasmodium falciparum more efficiently than normal red blood cells (NRBC). The phagocytic activity of human monocytes for infected red blood cells (IRBC) is greatly enhanced by the addition of immune sera obtained from individuals living in areas with endemic malaria. In contrast, the addition of sera obtained from individuals recovering from a first infection, or pooled normal sera, does not result in increased phagocytosis of IRBC. The phagocytosis enhancing activity of immune sera is associated with the IgG fraction and IgG depleted sera do not stimulate phagocytosis. Enhanced immune serum mediated phagocytosis occurs as a result of opsonization of IRBC. This was demonstrated by experiments in which monocytes or IRBC were preincubated with immune serum prior to the phagocytic assay. The opsonic activity could be absorbed by IRBC but not by NRBC. The opsonization of IRBC and subsequent phagocytosis were also dependent on the stage of development of the intracellular parasite. IRBC containing schizonts and trophozoites were preferentially phagocytosed as compared with ring forms. The role of malaria induced surface alterations and/or malaria surface antigens in the opsonization of IRBC by immune sera is discussed. These experiments suggest that phagocytosis of P. falciparum IRBC by monocytes may play a role in the immune elimination of malaria infection in humans.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown K. N., Hills L. A. Macrophage "activation" and the action of opsonizing antibodies in malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65(1):6–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow J. S., Kreier J. P. Plasmodium berghei: adherence and phagocytosis by rat macrophages in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1972 Feb;31(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(72)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Butcher G. A., Crandall R. B. Action of malarial antibody in vitro. Nature. 1969 Jul 26;223(5204):368–371. doi: 10.1038/223368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criswell B. S., Butler W. T., Rossen R. D., Knight V. Murine malaria: the role of humoral factors and macrophages in destruction of parasitized erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):212–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. J., Kreier J. P. Demonstration of the role of cytophilic antibody in resistance to malaria parasites (Plasmodium berghei) in rats. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):138–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.138-145.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter K. W., Jr, Winkelstein J. A., Simpson T. W. Serum opsonic activity in rodent malaria: functional and immunochemical characteristics in vitro. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2582–2587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Stage-specific proteins and glycoproteins of plasmodium falciparum: identification of antigens unique to schizonts and merozoites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3695–3699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Reese R. T. Antigenicity of the infected-erythrocyte and merozoite surfaces in Falciparum malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1241–1254. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse S. A., Miller L. H. Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ultrastructure of parasitized erythrocytes in cardiac vessels. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Sep;20(5):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor I. A., Williams K. Value of the gel-precipitation test in monitoring the endemicity of malaria in a rural African village. Isr J Med Sci. 1978 Jun;14(6):697–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Powers K. G., Shiroishi T. Plasmodium knowlesi: functional immunity and antimerozoite antibodies in rhesus monkeys after repeated infection. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Feb;41(1):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neva F. A., Sheagren J. N., Shulman N. R., Canfield C. J. Malaria: host-defense mechanisms and complications. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Aug;73(2):295–306. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill P., Johnson G. D. Multispot immunofluorescence: a simple semi-automatic method of processing large numbers of tests. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Mar;23(2):185–187. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Dayal R., Rieder H. Characterization of antigens from erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum reacting with human immune sera. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1981;75(1):163–165. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(81)90055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Ramirez E., Er-Hsiang L., Lambert P. H. Plasmodium falciparum: characterization of defined antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jul;41(1):91–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Wyler D. J. Intravascular clearance of parasitized erythrocytes in rodent malaria. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1187–1194. doi: 10.1172/JCI109413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Wyler D. J. Resolution of acute malaria (Plasmodium berghei in the rat): reversibility and spleen dependence. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jan;29(1):1–4. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese R. T., Langreth S. G., Trager W. Isolation of stages of the human parasite Plasmodium falciparum from culture and from animal blood. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):53–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheagren J. N., Tobie J. E., Fox L. M., Wolff S. M. Reticuloendothelial system phagocytic function in naturally acquired human malaria. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Mar;75(3):481–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear H. L., Nussenzweig R. S., Bianco C. Immune phagocytosis in murine malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1288–1298. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON D. B., GARNHAM P. C. C., SWELLENGREBEL N. H. A review of hyperendemic malaria. Trop Dis Bull. 1950 Aug;47(8):677–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Phillips R. S. Method to test inhibitory antibodies in human sera to wild populations of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):132–134. doi: 10.1038/263132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


