Abstract
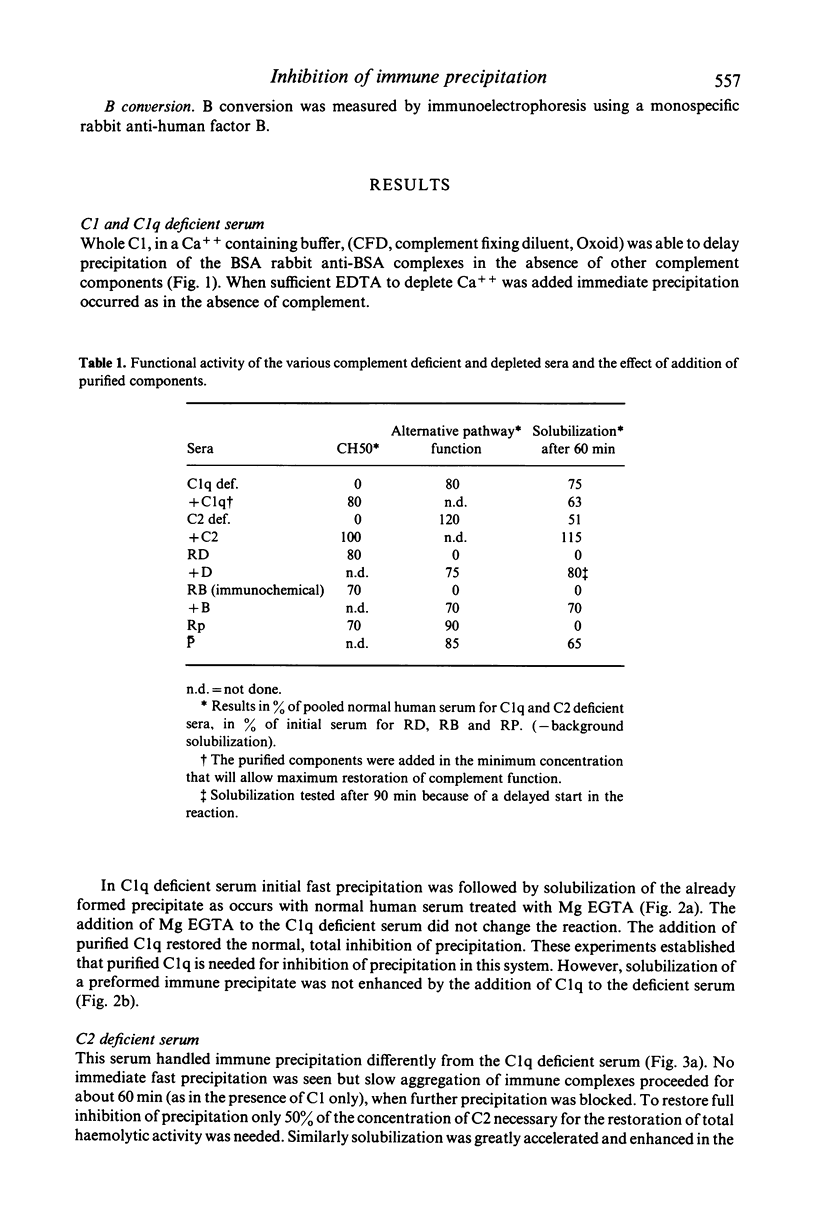
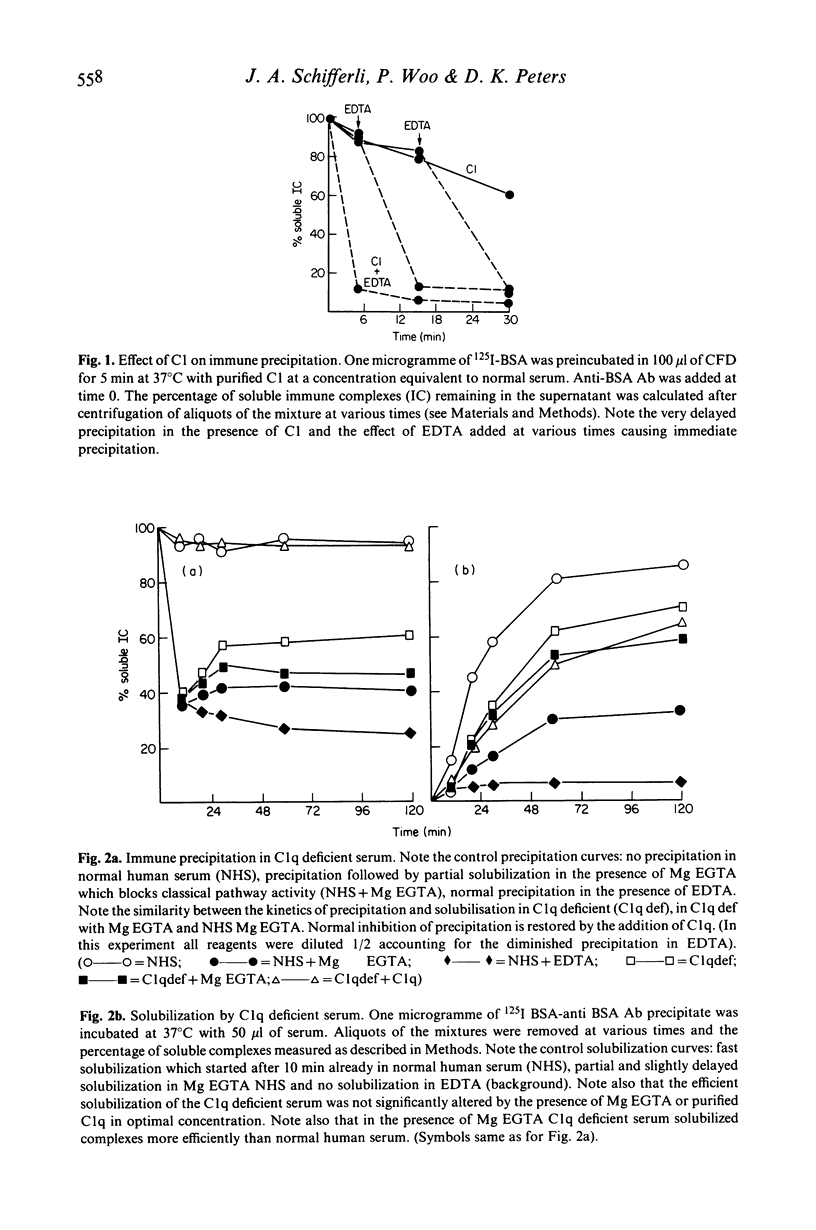
This study has examined the mechanisms involved in complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation using radiolabelled BSA and rabbit anti-BSA. Purified proenzyme C1 was capable of maintaining the complexes in soluble form during the first few minutes of reaction whereas immune precipitation was immediate in the presence of purified C1q or C1 + EDTA (ethylenediamine tetra-acetate). In C1q deficient serum, initial immune aggregation was followed by partial solubilization of the formed precipitate similar to that obtained with normal human serum in the presence of Mg EGTA. In C2 deficient serum precipitation occurred at a slow rate. Repletion of the deficient component (C1q or C2 respectively) restored fully inhibition of precipitation. These experiments establish a critical role for the classical pathway, in this phenomenon. By contrast the role of the alternative pathway in maintaining complexes in solution was less important; only partial and delayed precipitation occurred in sera depleted of factor D (RD) or factor B (RB). B and D restored normal complement activity to depleted sera. No precipitation was detected in a reagent depleted of properdin (RP). The mechanisms of inhibition of precipitation are therefore distinct from those responsible for solubilization of an immune precipitate, which is largely dependent on the alternative pathway.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Precipitin reactions of the C1q component of complement with aggregated gamma-globulin and immune complexes in gel diffusion. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):909–919. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J., Nussenzweig V. Studies on the mechanism of solubilization of immune precipitates by serum. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):615–630. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Porter R. R., Sim R. B. The unactivated form of the first component of human complement, C1. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1570541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällgren R. Human serum inhibits the interaction between C1q or rheumatoid factor and IgG-coated latex particles. Reduction of these C1-dependent properties after complement activation in vitro and in vivo. Immunology. 1979 Nov;38(3):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällgren R., Stålenheim G., Venge P. Kinetics of the agglutination of IgG-coated latex particles by C1q: the influence of heat-labile serum components. Scand J Immunol. 1979;9(4):365–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb03175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Effects of C-1 on the size of soluble immune aggregates and on their processing by macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):640–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J. The purification of specific antibody as F(ab')2 by the pepsin digestion of antigen-antibody precipitates, and its application to immunoglobulin and complement antigens. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jan;8(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90423-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Nussenzweig V. A new complement function: solubilization of antigen-antibody aggregates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):418–422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller N. P., Steensgaard J. Fc-mediated immune precipitation. II. Analysis of precipitating immune complexes by rate-zonal ultracentrifugation. Immunology. 1979 Nov;38(3):641–648. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Schreiber R. D. Molecular biology and chemistry of the alternative pathway of complement. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pussell B. A., Lockwood C. M., Scott D. M., Pinching A. J., Peters D. K. Value of immune-complex assays in diagnosis and management. Lancet. 1978 Aug 12;2(8085):359–364. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92954-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajnavölgyi E., Füst G., Ember J., Medgyeshi G. A., Gergely J. Evidences proving the intercalation hypothesis of the C-mediated complex release activity (CRA). Immunochemistry. 1978 May;15(5):335–337. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell J. D., Lih-Heng-Tang, Schumaker V. N. Antigen valence and Fc-localized secondary forces in antibody precipitation. Mol Immunol. 1980 Dec;17(12):1591–1597. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Bartolotti S. R., Peters D. K. Inhibition of immune precipitation by complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):387–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD E. W., PILLEMER L., LEPOW I. H. The properdin system and immunity. IX. Studies on the purification of human properdin. J Immunol. 1959 Oct;83:418–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tack B. F., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement: assembly of a factor B-dependent C3-convertase on the immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):86–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Brade V., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement. The role of the classical pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):349–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI109135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Haeney M., Reid K. B., Davies J. G., White R. H., Cameron A. H. A genetic defect of the C1q subcomponent of complement associated with childhood (immune complex) nephritis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 3;303(1):22–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007033030107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Nydegger U., Perrin L. H., Fehr K., McCormick J., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating and intra-articular immune complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of 125I-Clq binding activity with clinical and biological features of the disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1308–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI108399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


