Abstract
Thymic tissue obtained at autopsy from 123 victims of sudden death, ranging from neonates to individuals older than 80 years and predominantly male, was studied with histometric techniques, i.e. a combination of test point analysis and planimetry on unit optical fields. The pattern of 'natural' age-dependent involution of the thymic cortex was examined using computerized mathematical models. The range of variations of results was greatest in children and young adults, followed by the very old, then the middle age group. In a first approximation, regression for thymic cortical volume in individuals older than 15 years corresponded better to a negative exponential than to a negative linear function of age. Best fits for the data suggest at least a two-component negative exponential function of age, with a steeper slope of the regression for individuals beyond the age of 30 years. Extrapolation on a log-normal plot of regression lines for thymic cortical involution points to near-zero values at an age range below the estimated maximum human life span, corresponding to the steepest slope of survival curves in Western Europe.
Full text
PDF

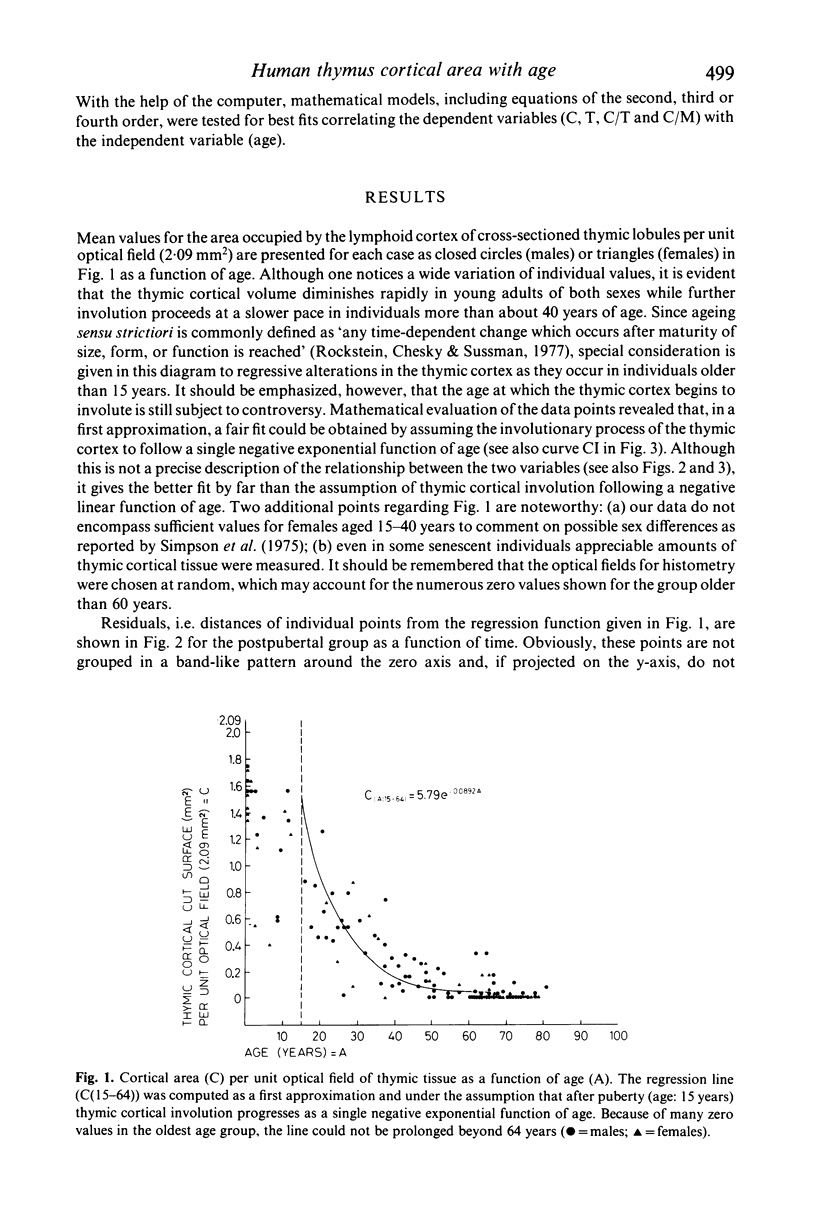
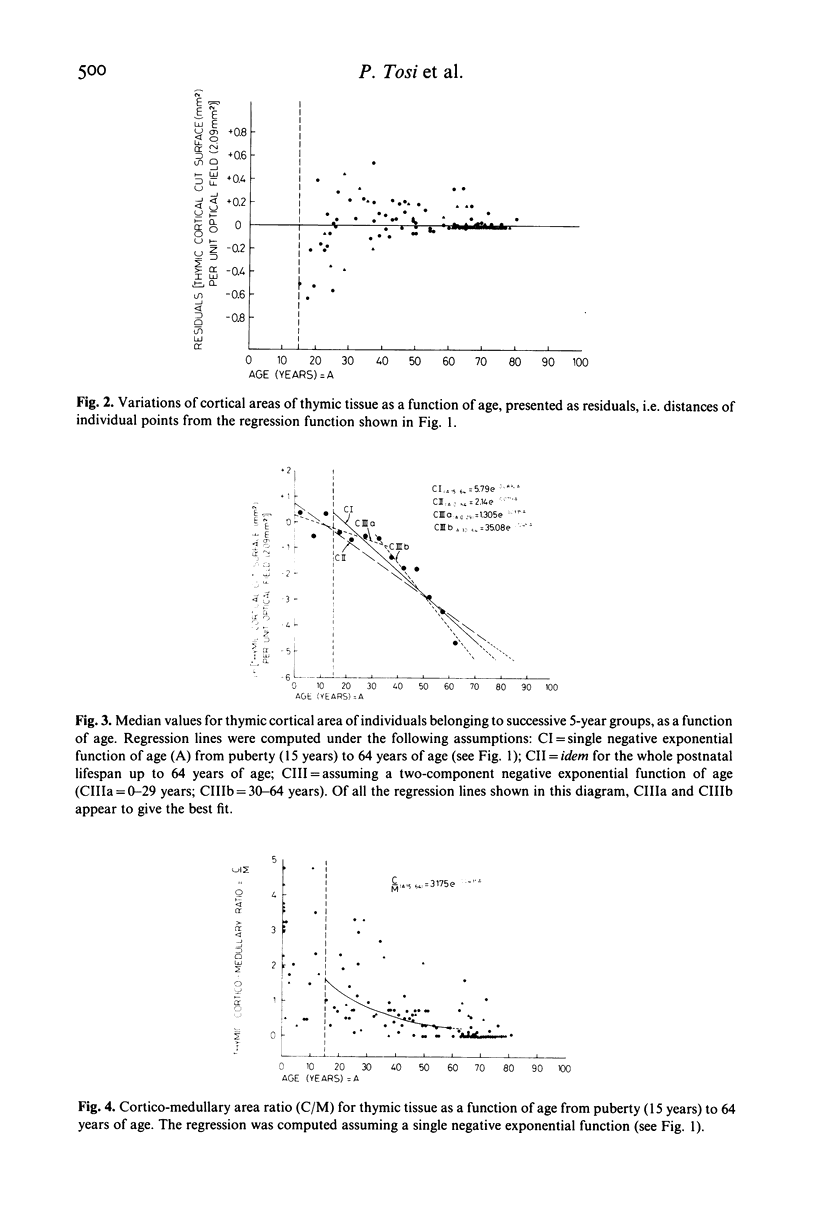




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belyaev D. K., Gruntenko E. V. Strain differences in thymus weight in mice with different predispositions to spontaneous mammary cancer. Nature. 1972 Jun 16;237(5355):401–402. doi: 10.1038/237401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss G. R., Thompson L. F., Spiegelberg H. L., Pichler W. J., Seegmiller J. E. Age-dependency of lymphocyte ecto-5'-nucleotidase activity. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):679–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottier H., Hess M. W., Keller H. U. Structural basis for lymphoid tissue functions: established and disputable sites of antigen-cell and cell-to-cell interactions in vivo. Monogr Allergy. 1980;16:50–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freire M., Hannappel E., Rey M., Freire J. M., Kido H., Horecker B. L. Purification of thymus mRNA coding for a 16,000-dalton polypeptide containing the thymosin alpha 1 sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):192–195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefton J. M., Darlington G. J., Casazza B. A., Weksler M. E. Immunologic studies of aging. V. Impaired proliferation of PHA responsive human lymphocytes in culture. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1007–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry L. "Accidental" involution of the human thymus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(2):337–343. doi: 10.1002/path.1700960211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinsull S. M., Bellamy D., Franklin A. A quantitative histological assessment of cellular death, in relation to mitosis, in rat thymus during growth and age involution. Age Ageing. 1977 May;6(2):77–84. doi: 10.1093/ageing/6.2.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Makinodan T. Immunobiology of aging: evaluation of current status. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Nov;6(3):394–413. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennes B., Hubert C., Brohee D., Neve P. Early biochemical events associated with lymphocyte activation in ageing. I. Evidence that Ca2+ dependent processes induced by PHA are impaired. Immunology. 1981 Jan;42(1):119–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrecque P. G., Souadjian J. V., Titus J. L. Etude morphologique quantitative du thymus humain dans une série d'autopsies. Union Med Can. 1972 Apr;101(4):695–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscieti P., Hubschmid T., Cottier H., Hess M. W., Sobin L. H. Human lymph node morphology as a function of age and site. J Clin Pathol. 1980 May;33(5):454–461. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.5.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierpaoli W., Fabris N., Sorkin E. Developmental hormones and immunological maturation. Ciba Found Study Group. 1970;36:126–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruchti C., Cottier H., Cronkite E. P., Jansen C. R., Rai K. R. Studies on lymphocytes. XVII. Differential lymphocyte depletion in lymphoreticular organs of the calf during continuous extracorporeal x-irradiation of the circulating blood. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1970 Jul;3(3):301–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulof R. S., Garofalo J. A., Good R. A., Gupta S. Concanavalin A-induced suppressor cell activity for T-cell proliferative responses: autologous and allogeneic suppression in aging humans. Cell Immunol. 1980 Nov;56(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. G., Gray E. S., Beck J. S. Age involution in the normal human adult thymus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Feb;19(2):261–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J., Singh A. K. Age-related changes in human thymus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Sep;37(3):507–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman O., Good R. A. Duration of thymic function. Ser Haematol. 1974;7(4):505–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczuk M. R., DeKruyff R. H., Goidl E. A., Weksler M. E., Siskind G. W. Ontogeny of B lymphocyte function. VIII. Failure of thymus cells from aged donors to induce the functional maturation of B lymphocytes from immature donors. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Dec;10(12):918–923. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam C. F., Walford R. L. Alterations in cyclic nucleotides and cyclase-specific activities in T lymphocytes of aging normal humans and patients with Down's syndrome. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1665–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walford R. L. Immunology and aging Philip Levine Award. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Sep;74(3):247–253. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


