Abstract
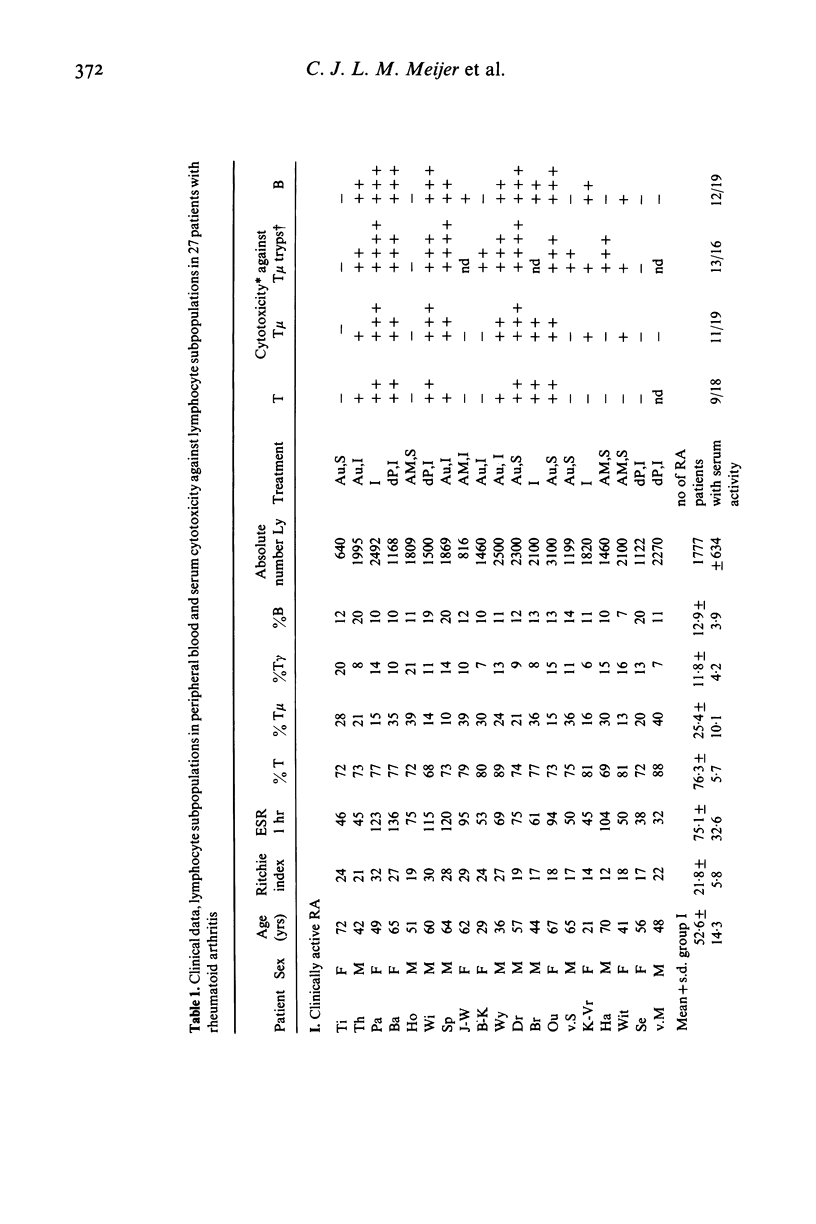
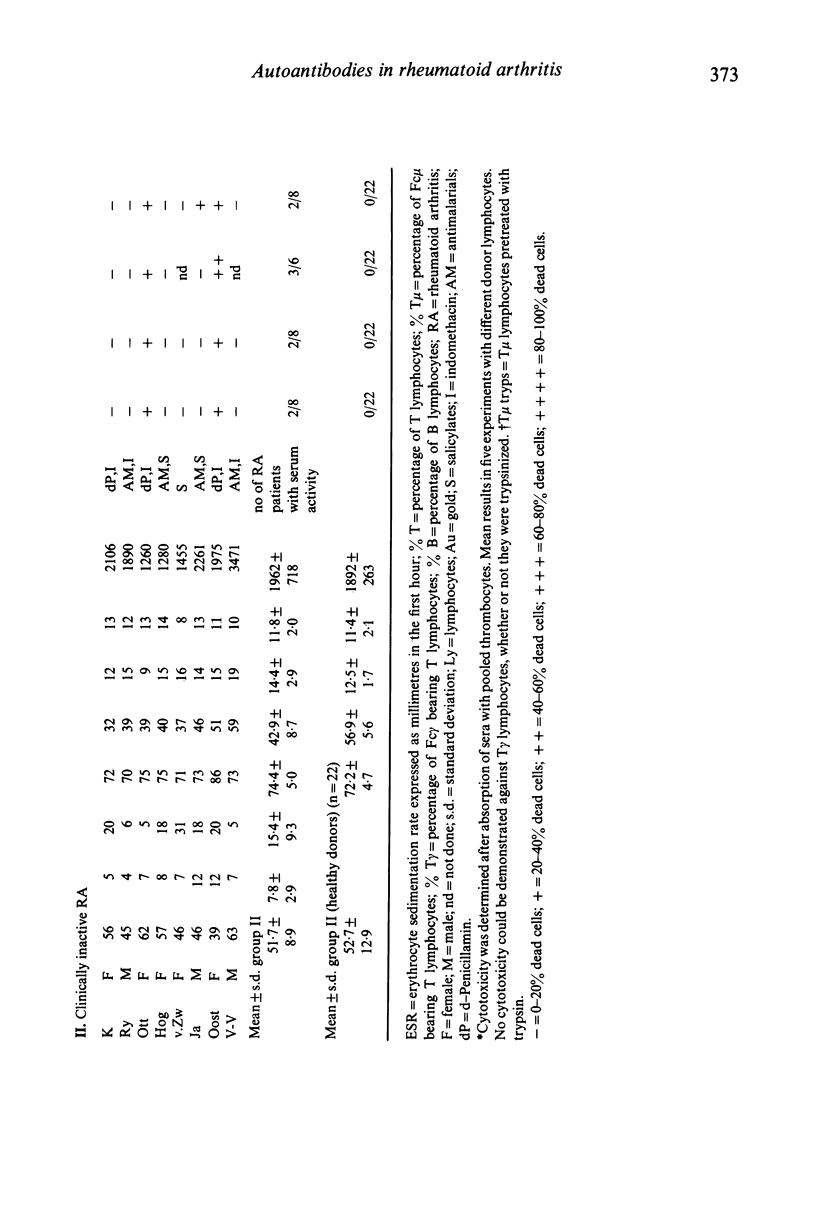
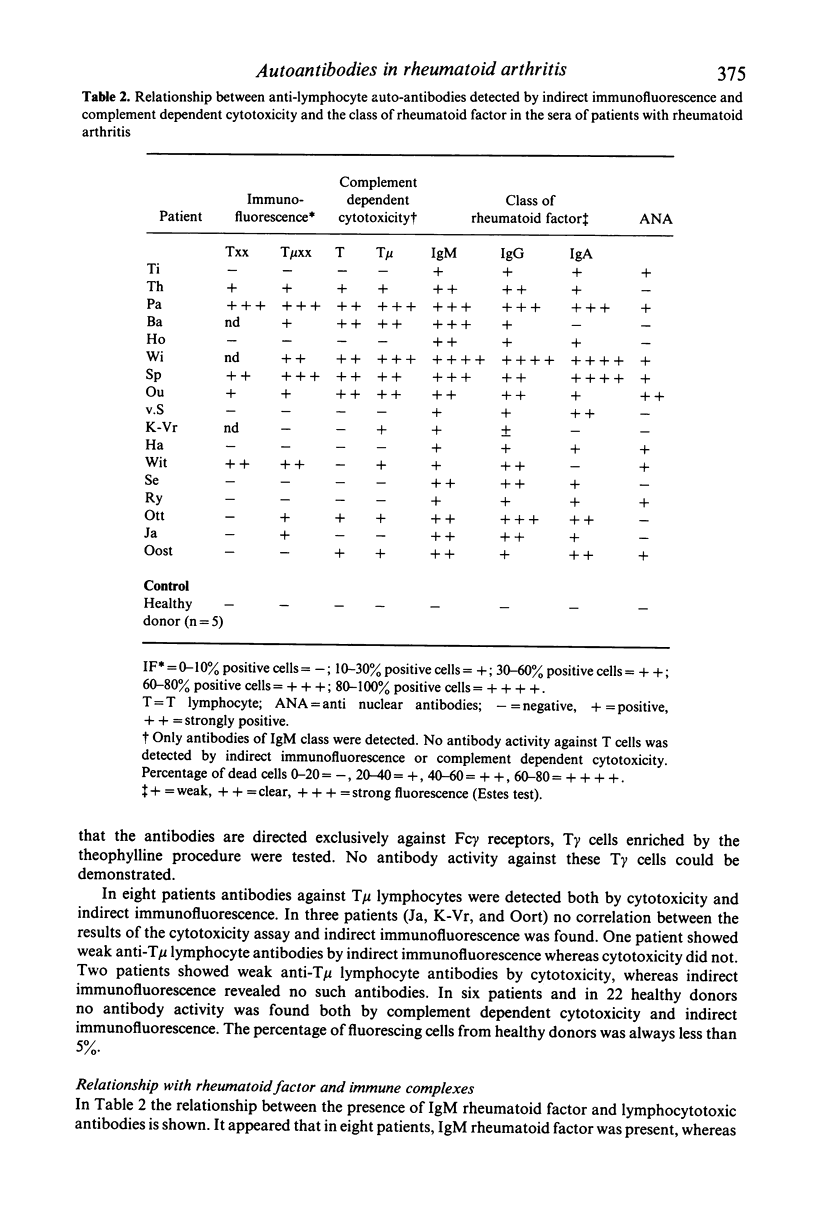
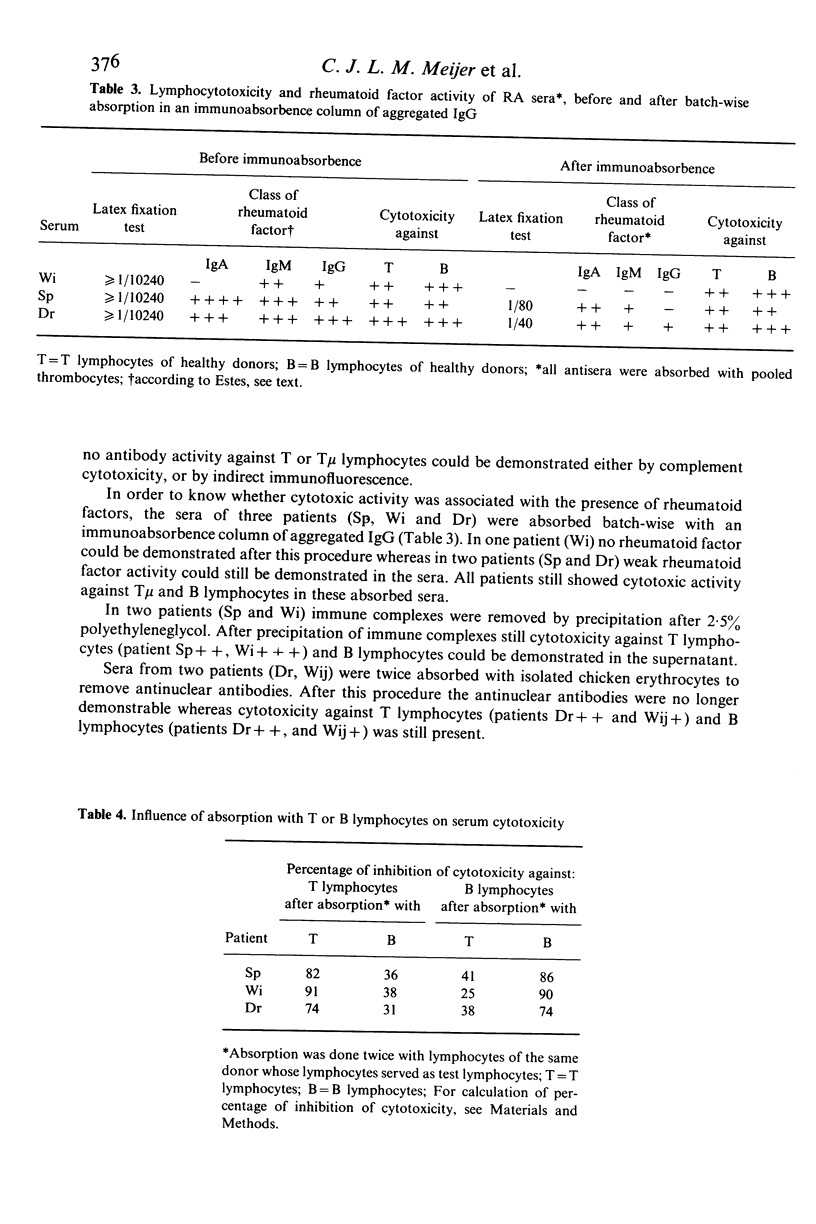
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis have decreased numbers of T mu lymphocytes in their peripheral blood. To find out whether these low number of T mu lymphocytes were associated with the presence of anti-lymphocyte antibodies, the sera of 27 patients with definite or classical rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were investigated for the presence of autoantibodies against subsets of lymphocytes. In addition the numbers of T, T mu, T gamma and B lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of these patients were investigated. Patients with active RA showed lower numbers of T mu lymphocytes in their peripheral blood than patients with inactive RA. However, both groups of RA patients had significantly decreased numbers of T mu lymphocytes in their peripheral blood as compared with 22 age matched healthy donors. Moreover, mainly in patients with active RA cold reactive antibodies were found directed against T mu and B lymphocytes, but never against T gamma lymphocytes of healthy donors. Similar results were found in the indirect immunofluorescence procedure when tested for reactivity against T-cell subsets. This serum reactivity was not caused by rheumatoid factors or antinuclear antibodies. Since RA sera after precipitation with 2.5% polyethyleneglycol, still showed cytotoxicity against T and B lymphocytes, it is suggested that this serum reactivity is not caused by immune complexes but by antibodies.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biberfeld G., Nilsson E., Biberfeld P. T lymphocyte subpopulations in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Sep;22(9):978–982. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cnossen J., Lafeber G. J., Damsteeg W. J., Meijer C. J. Mixed rosette assay for the detection of T mu and T gamma lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAGNOSTIC criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: 1958 revision by a committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Ann Rheum Dis. 1959 Mar;18(1):49–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P., Jayson M. I. Serological changes in progressive systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1976 Feb;15(1):45–50. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/15.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinski W., Gershwin M. E., Budman D. R., Steinberg A. D. Study of lymphocyte subpopulations in normal humans and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus by fractionation of peripheral blood lymphocytes on a discontinuous Ficoll gradient. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):228–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Malaviya A. N., Rajagopalan P., Good R. A. Subpopulations of human T lymphocytes. IX. Imbalance of T cell subpopulations in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Nov;38(2):342–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijnen C. J., UytdeHaag F., Ballieux R. E. In vitro antibody response of human lymphocytes. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980 May;3(1):63–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00199926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. W., Lattos D. B., Nelson D. B., Reeb K., Hong R. Antibody-associated lymphotoxin in acute infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1033–1040. doi: 10.1172/JCI107268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby G., Messner R. P. Detection of antilymphocyte antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus by indirect immunofluorescence on acetone-fixed lymphocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Feb;89(2):240–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J., Schuit H. R., van Zwet T. L., Meijer C. J., Hijmans W. Hairy-cell leukaemia: a B-lymphocytic disorder. Br J Haematol. 1979 May;42(1):21–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keystone E. C., Gladman D. D., Buchanan R., Cane D., Poplonski L. Impaired antigen-specific suppressor cell activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Nov;23(11):1246–1250. doi: 10.1002/art.1780231103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Winfield J. B., Craig A., Westervelt F. B., Jr Utility of protease-digested human peripheral blood lymphocytes for the detection of lymphocyte-reactive alloantibodies by indirect immunofluorescence. Transplantation. 1977 Jan;23(1):16–21. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197701000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunney J. K., Mann D. L., Sachs D. H. Sharing Ia antigens between species. III. Ia specificities shared between mice and human beings. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(5):403–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydyard P. M., Fanger M. W. Receptors for IgM on human lymphocytes. II. Mitogen-induced modulation of receptor expression. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Sep;37(3):486–494. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan S. A., Haire M., Middleton D. Antibodies to lymphocytes and smooth muscle in the sera of patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Jul;16(3):374–385. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer C. J., Lindeman J. A modified method for tissue localization of cells bearing a complement receptor. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Nov;9(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Mingari M. C., Santoli D., Perlmann P., Moretta L. Human T-lymphocyte subpopulations: alterations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(3):223–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Abe T., Toguchi T., Kiyotaki M., Homma M. Studies of anti-lymphocyte antibody in patients with active SLE. II. Effect of anti-lymphocyte antibody on autoreactive cell clones. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(5):479–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Borel Y., Mantzouranis E., Steinberg A. D., Schlossman S. F. Autoantibody to an immunoregulatory inducer population in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):753–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI110092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Current concepts in immunology: Regulation of the immune response--inducer and suppressor T-lymphocyte subsets in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 14;303(7):370–373. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008143030704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revillard J. P., Rivera S., Robert M. Auto-antibodies specific for lymphocyte surface antigens--a review. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1980;3(3):261–275. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(80)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich R. R., Johnson J. S. Salicylate hepatotoxicity in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Jan-Feb;16(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuit H. R., Hijmans W., Asma G. E. Identification of mononuclear cells in human blood. I. Qualitative and quantitative data on surface markers after formaldehyde fixation of the cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles R. P., Messner R. P., Bankhurst A. D. Cross--reactivity of antilymphocyte and antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Nov;14(3):292–299. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore A., Dosch H., Gelfand E. W. Induction and separation of antigen-dependent T helper and T suppressor cells in man. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):586–587. doi: 10.1038/274586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Winfield J. B., Siegal F., Wernet P., Bentwich Z., Kunkel H. G. Analyses of lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence of interfering cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1082–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI107852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Association of cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies with lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):587–594. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Winchester R. J., Wernet P., Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G. Nature of cold-reactive antibodies to lymphocyte surface determinants in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jan-Feb;18(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Loo E. M., Cnossen J., Meijer C. J. Morphological aspects of T cell subpopulations in human blood: characterization of the cerebriform mononuclear cells in healthy individuals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):506–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


