Abstract
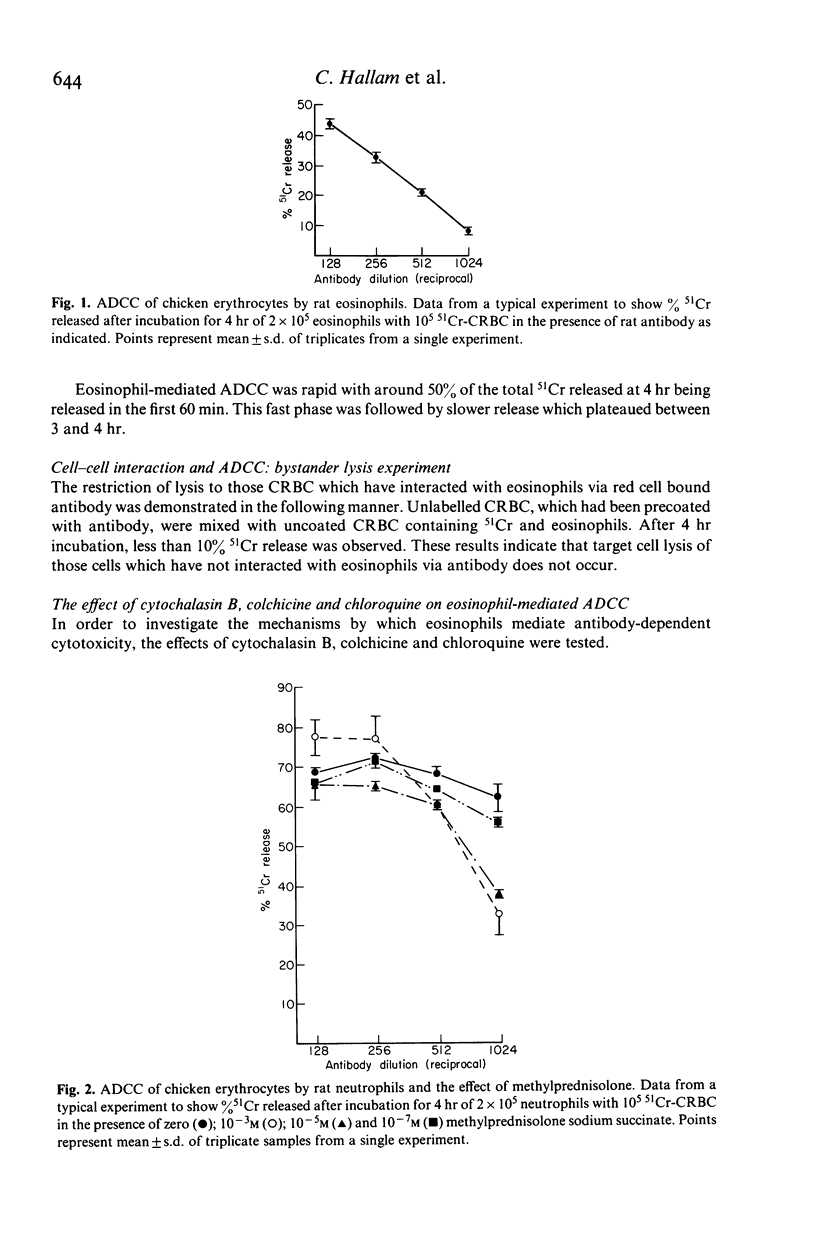
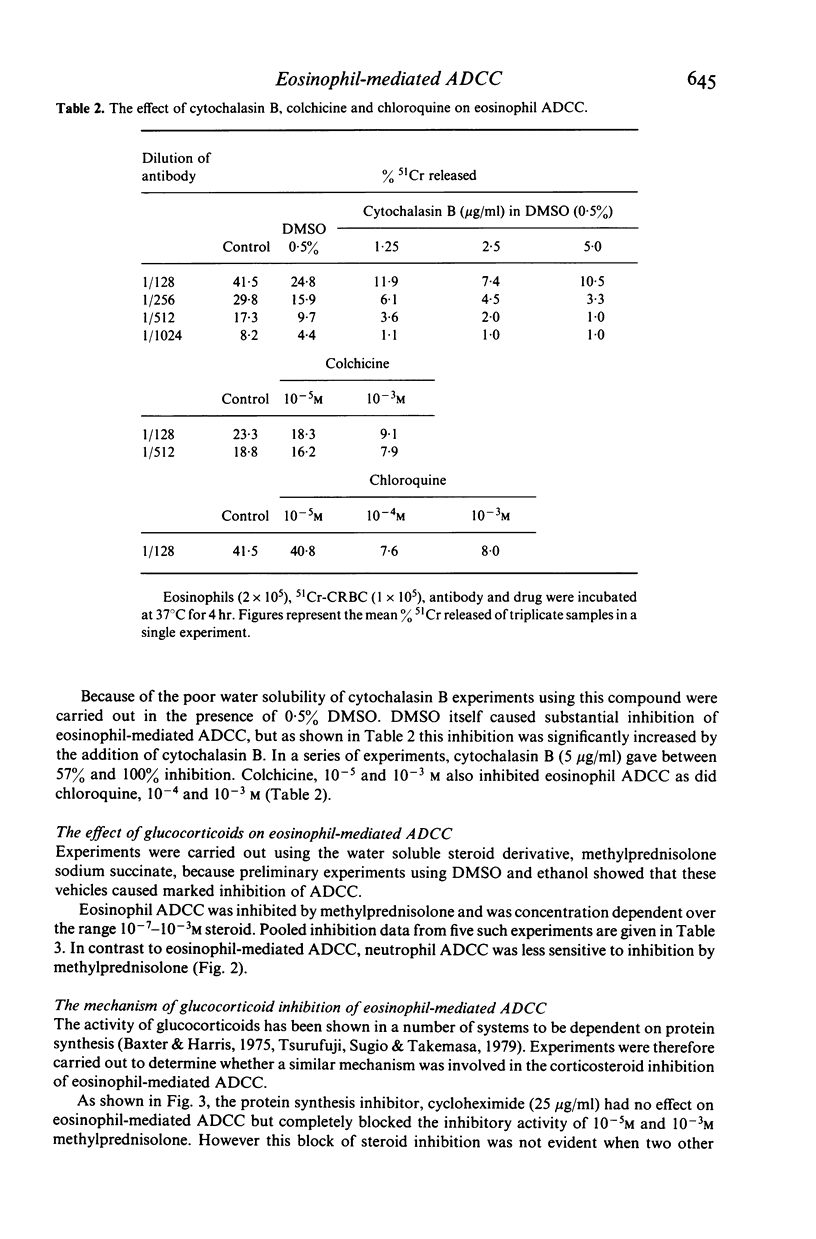
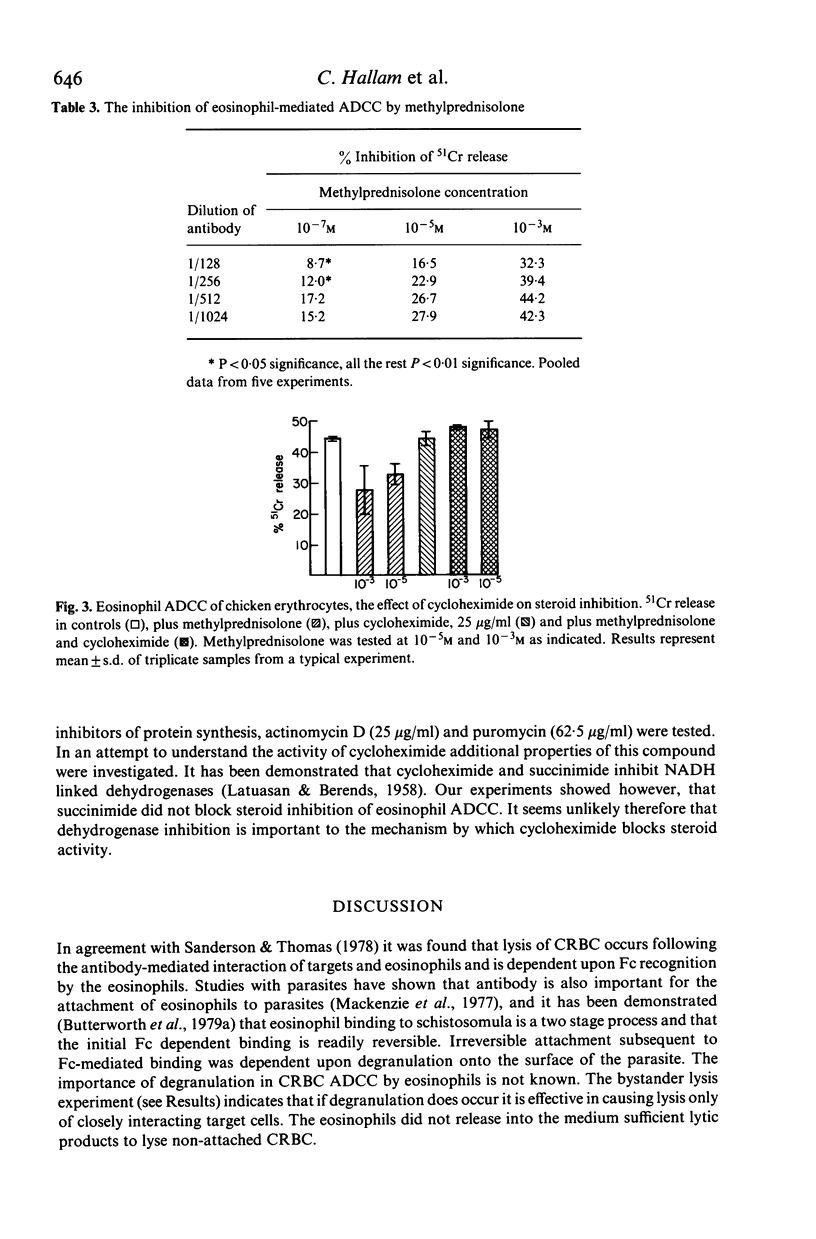
Purified eosinophils from the peritoneal washings of N. brasiliensis infected rats demonstrated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) for 51Cr-labelled chicken erythrocytes. The F(ab')2 fragment of the antibody did not support cytotoxicity thereby demonstrating the importance of the eosinophil Fc receptor to this activity. Bystander lysis of erythrocytes did not occur, indicating that the eosinophil does not release lytic agents free into the medium. Cytochalasin B (1.25-5 micrograms/ml) colchicine (10(-5)-10(-3) M) and chloroquine (10(-4)-10(-3) M) inhibited eosinophil ADCC. Inhibition was also demonstrated by methylprednisolone, 10(-7)-10(-3) M and this inhibition was blocked by the protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide (25 micrograms/ml). Cycloheximide alone had no effect. This block of steroid inhibition by cycloheximide suggests that the steroid effect on this system may be mediated by a newly synthesized protein and implies that the eosinophil may possess a glucocorticoid receptor.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. C., Hill J. S., Hairfield W. M., Mullarkey M. F. Effects of corticosteroids on eosinophil chemotaxis and adherence. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):28–36. doi: 10.1172/JCI110024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austen K. F., Orange R. P. Bronchial asthma: the possible role of the chemical mediators of immediate hypersensitivity in the pathogenesis of subacute chronic disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Sep;112(3):423–436. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.3.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Harris A. W. Mechanism of glucocorticoid action: general features, with reference to steroid-mediated immunosuppression. Transplant Proc. 1975 Mar;7(1):55–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V., Mahmoud A. A., Sher A., Rees P. H. Eosinophils as mediators of antibody-dependent damage to schistosomula. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):727–729. doi: 10.1038/256727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Vadas M. A., Wassom D. L., Dessein A., Hogan M., Sherry B., Gleich G. J., David J. R. Interactions between human eosinophils and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. II. The mechanism of irreversible eosinophil adherence. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1456–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Wassom D. L., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., David J. R. Damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni induced directly by eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):221–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Capron A., Torpier G., Bazin H., Bout D., Joseph M. Eosinophil-dependent cytotoxicity in rat schistosomiasis. Involvement of IgG2a antibody and role of mast cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Gallin J. I., Fauci A. S. Effects of in vivo prednisone on in vitro eosinophil and neutrophil adherence and chemotaxis. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):633–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R., Butterworth A. E., Remold H. G., David P. H., Houba V., Sturrock R. F. Antibody-dependent, eosinophil-mediated damage to 51Cr-labeled schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni: effect of metabolic inhibitors and other agents which alter cell function. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2221–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauderer C. A., Gleich G. J. Inhibition of eosinophilotaxis by chloroquine and corticosteroids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Jan;157(1):129–133. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins D. Neutrophilic leukocytes in immunologic reactions in vitro. 3. Pharmacologic modulation of lysosomal constituent release. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Jan;2(2):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins D. Neutrophilic leukocytes in immunologic reactions in vitro: effect of cytochalasin B. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):294–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubscher T. Immune and biochemical mechanisms in the allergic disease of the upper respiratory tract; role of antibodies, target cells, mediators and eosinophils. Ann Allergy. 1977 Feb;38(2):83–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. G., Kay A. B. Inhibition of eosinophil chemotaxis by the antagonist of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis--compound FPL 55712. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;26(11):917–918. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1974.tb09208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Simone C. B., Henkart P. A., Fauci A. S. Mechanisms of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity: the use of effector cells from chronic granulomatous disease patients as investigative probes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):55–63. doi: 10.1172/JCI109660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Gallin J. I. Inhibition of neutrophil Fc receptor function by cotricosteroids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Oct;34(1):137–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie C. D., Ramalho-Pinto F. J., McLaren D. J., Smithers S. R. Antibody-mediated adherence of rat eosinophils to schistosomula of Schistoma mansoni in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):97–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Fauci A. S. Human eosinophils. Purification and cytotoxic capability of eosinophils from patients with the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood. 1978 Mar;51(3):457–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Thomas J. A. A comparison of the cytotoxic activity of eosinophils and other cells by 51 chromium release and time lapse microcinematography. Immunology. 1978 Apr;34(4):771–780. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Dorrington K. J. The recombination of dimers of immunoglobulin peptide chains. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):703–712. doi: 10.1042/bj1180703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J. Enzymes altering the binding capacity of human blood eosinophils for IgG antibody-coated erythrocytes (EA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Apr;40(1):206–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurufuji S., Sugio K., Takemasa F. The role of glucocorticoid receptor and gene expression in the anti-inflammatory action of dexamethasone. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):408–410. doi: 10.1038/280408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wibo M., Poole B. Protein degradation in cultured cells. II. The uptake of chloroquine by rat fibroblasts and the inhibition of cellular protein degradation and cathepsin B1. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):430–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Colten H. R. Histaminase release from human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):540–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Cytochalasin B: effect on lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


