Abstract
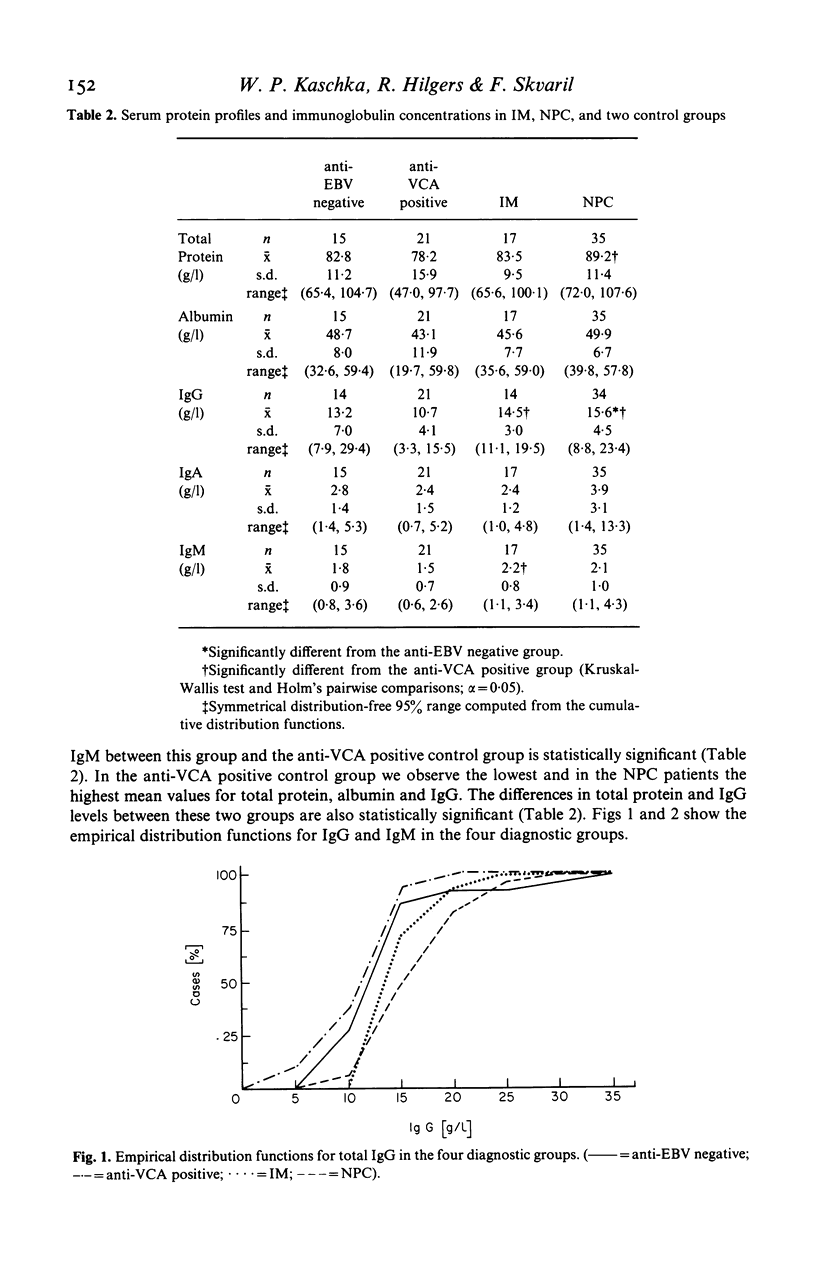
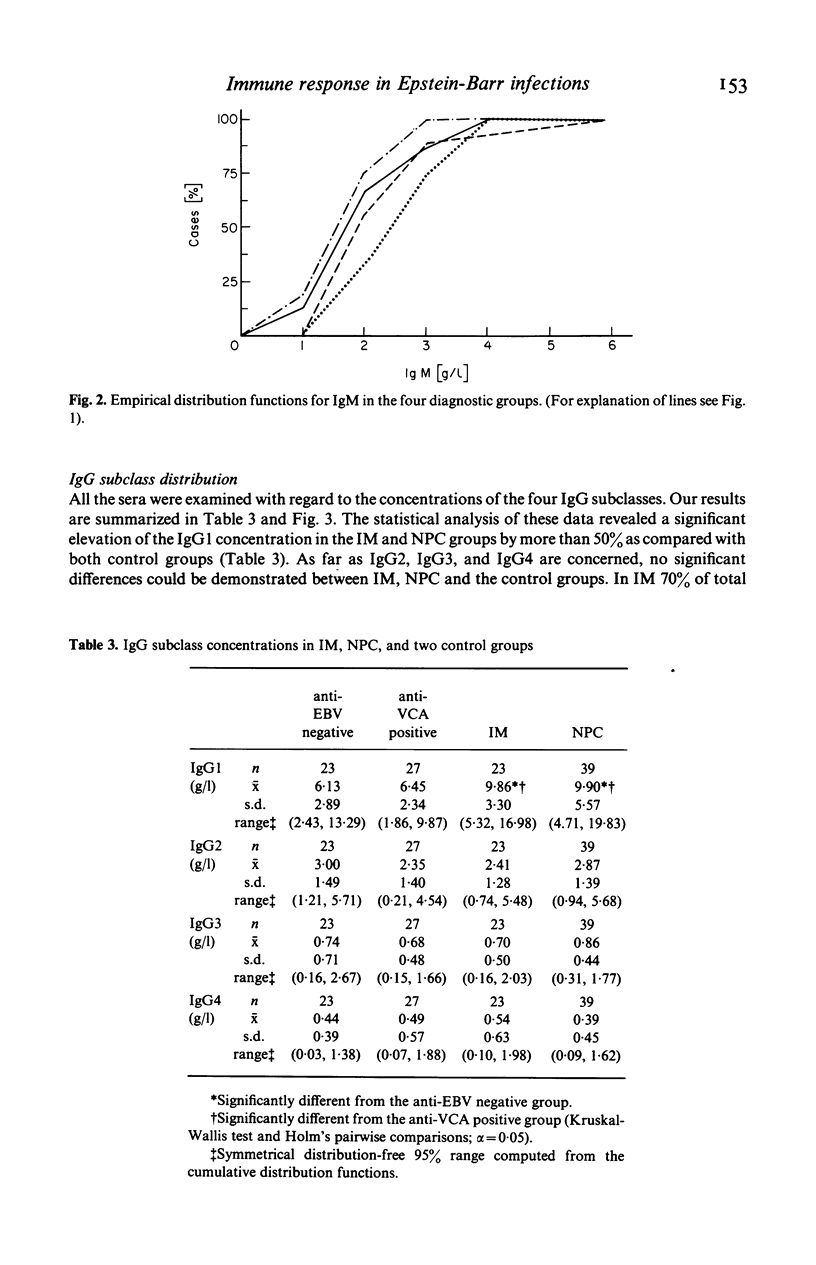
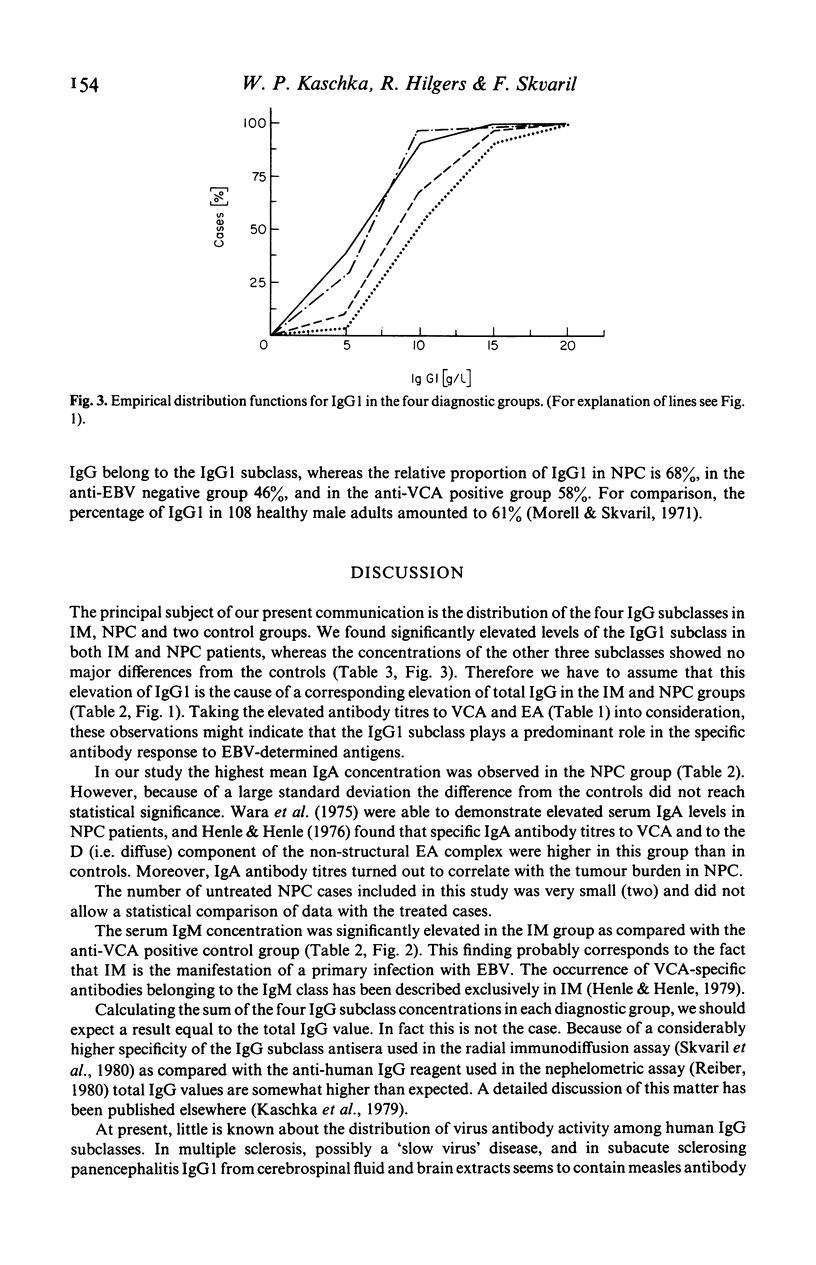
Using radial immunodiffusion we measured IgG subclass concentrations and studied their distribution in serum samples from patients with infectious mononucleosis (IM) and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), two Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated diseases, in comparison with two control groups [completely anti-EBV negative persons and subjects carrying antibodies to the viral capsid antigen (VCA)]. Antibody titres to VCA and to the early antigen (EA) were determined by indirect immunofluorescence and revealed characteristic patterns for the respective diagnostic groups. Nephelometric assays served for quantitating total protein, albumin, total IgG, IgA and IgM in all the sera. In the IM and NPC groups the concentration of IgG1 was significantly elevated by more than 50% whereas the other three subclasses remained unchanged as compared with the controls. Correspondingly, we found a significant increase of total IgG in IM and NPC. In IM, the only disease where VCA-specific IgM antibodies have been reported to occur, IgM levels were markedly elevated. Our data suggest that the IgG1 subclass plays an important role in the humoral immune response to EBV-determined antigens and that it is possibly involved in the control of virus infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck O. E. Distribution of virus antibody activity among human IgG subclasses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):626–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Klein E., Klein G., Clifford P., Singh S. Immunoglobulin and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase as markers of cellular origin in Burkitt lymphoma. J Exp Med. 1973 Jul 1;138(1):89–102. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunvén P., Klein G., Klein E., Norin T., Singh S. Surface immunoglobulins on Burkitt's lymphoma biopsy cells from 91 patients. Int J Cancer. 1980 Jun 15;25(6):711–719. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Diehl V. Relation of Burkitt's tumor-associated herpes-ytpe virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):94–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaschka W. P., Theilkaes L., Eickhoff K., Skvaril F. Disproportionate elevation of the immunoglobulin G1 concentration in cerebrospinal fluids of patients with multiple sclerosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):933–941. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.933-941.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer G. E., Widdowson J. P. Predominance of immunoglobulin G sub-class 3 among the complement-fixing antibodies to streptococcal M-associated protein. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Aug;37(2):247–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Smith R. W., Gerber P. B-cell characteristics of human peripheral and cord blood lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1081–1086. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiber H. Eine schnelle und einfache nephelometrische Bestimmungsmethode für Protein im Liquor cerebrospinalis. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1980 Feb;18(2):123–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesen W. F., Skvaril F., Braun D. G. Natural infection of man with group A streptococci. Levels; restriction in class, subclass, and type; and clonal appearance of polysaccharide-group-specific antibodies. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):383–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosén A., Gergely P., Jondal M., Klein G., Britton S. Polyclonal Ig production after Epstein-Barr virus infection of human lymphocytes in vitro. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):52–54. doi: 10.1038/267052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Schur P. H., Aisenberg A. C., Weitzman S. A., Schiffman G. Correlation between serum IgG-2 concentrations and the antibody response to bacterial polysaccharide antigens. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 24;303(4):178–182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007243030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F., Roth-Wicky B., Barandun S. IgG subclasses in human gamma-globulin preparations for intravenous use and their reactivity with staphylococcus protein A. Vox Sang. 1980;38(3):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1980.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg J. C. A rate nephelometer for measuring specific proteins by immunoprecipitin reactions. Clin Chem. 1977 Aug;23(8):1456–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandvik B., Natvig J. B., Wiger D. IgG1 subclass restriction of oligoclonal IgG from cerebrospinal fluids and brain extracts in patients with multiple sclerosis and subacute encephalitides. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):427–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wara W. M., Wara D. W., Phillips T. L., Ammann A. J. Elevated IGA in carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Cancer. 1975 May;35(5):1313–1315. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197505)35:5<1313::aid-cncr2820350510>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., O'Neill F. J., Freese U. K., Hecker E. Persisting oncogenic herpesvirus induced by the tumour promotor TPA. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):373–375. doi: 10.1038/272373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G., Clifford P., Santesson L. EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/2281056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


