Abstract
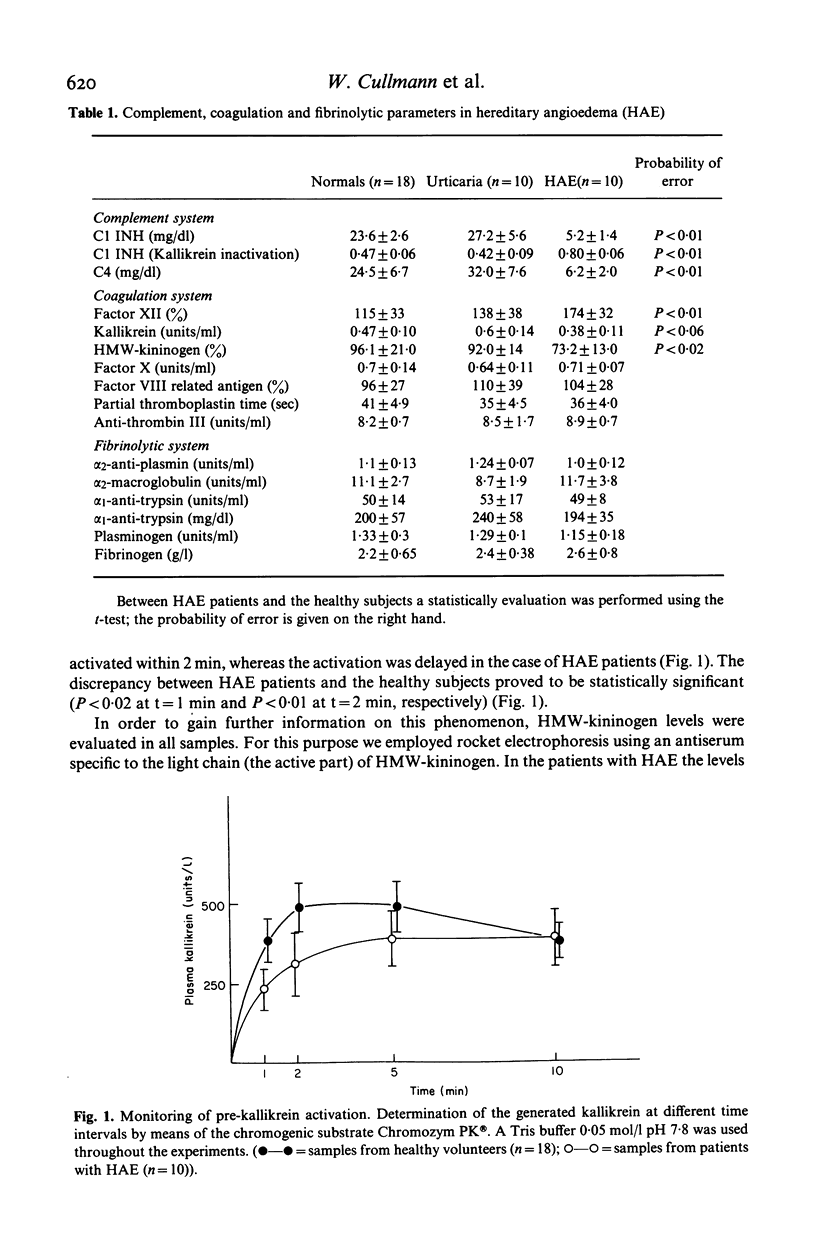
The intrinsic clotting, the kinin generating and the fibrinolytic systems were investigated in 10 patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE), 10 patients with chronic urticaria and 18 healthy volunteers. In spite of the fact that patients suffering from HAE severely lack C1 INH, neither the intrinsic coagulation nor the fibrinolytic systems are impaired. There was a slight decrease of plasma kallikrein--as already known--and moreover a greater decrease in HMW-kininogen, and increase in Factor XII levels. Furthermore, activation of pre-kallikrein was delayed in these patients. These findings make it apparent that lowered HMW-kininogen levels compensate the lack of C1 INH, thus preventing an enhanced activation of the intrinsic clotting and the fibrinolytic systems.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurell L., Friberger P., Karlsson G., Claeson G. A new sensitive and highly specific chromogenic peptide substrate for factor Xa. Thromb Res. 1977 Nov;11(5):595–609. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSS A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haematol. 1957 Apr;17(4):237–246. doi: 10.1159/000205234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullmann W., Dick W. A chromogenic assay for evaluation of alpha 2-macroglobulin level in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1981 May;19(5):287–290. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1981.19.5.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullmann W., Kövary P. M., Dick W., Czarnetzki B., Echternach-Happle K. A rapid method for functional determination of C1 esterase inhibitor in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Mar 12;119(3):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick W., Cullmann W. An amidolytic assay for determination of alpha 1-antitrypsin in serum and in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1982 Feb;20(2):57–60. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1982.20.2.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Mason J. W., Colman R. W., Austen K. F. Interaction of plasma kallikrein with the C1 inhibitor. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):574–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin. An inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):329–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDERMAN N. S., WEBSTER M. E., BECKER E. L., RATCLIFFE H. E. Hereditary angioneurotic edema. II. Deficiency of inhibitor for serum globulin permeability factor and/or plasma kallikrein. J Allergy. 1962 Jul-Aug;33:330–341. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(62)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY D. A., POTTER D. E., NICOLAIDES E. D. AN IN VIVO ESTIMATION OF THE POTENCIES AND HALF-LIVES OF SYNTHETIC BRADYKININ AND KALLIDIN. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Apr;148:117–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell D. J. Inhibitors of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1611–1623. doi: 10.1172/JCI106962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier H. L., Pierce J. V., Colman R. W., Kaplan A. P. Activation and function of human Hageman factor. The role of high molecular weight kininogen and prekallikrein. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):18–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI108754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., COLOPY J. E. A familial hemorrhagic trait associated with a deficiency of a clot-promoting fraction of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):602–613. doi: 10.1172/JCI103109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODMAN N. F., Jr, BARROW E. M., GRAHAM J. B. Diagnosis and control of the hemophilioid states with the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Jun;29(6):525–538. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/29.6.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Protection of human plasma kallikrein from inactivation by C1 inhibitor and other protease inhibitors. The role of high molecular weight kininogen. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2738–2743. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. Inhibition by C1INH of Hagemann factor fragment activation of coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1402–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI107313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria J., Soria C., Samama M. Dosage du plasminogène à l'aide d'un substrat chromogène tripeptidique. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1976 Dec;24(10):725–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormorken H., Baklund A., Gallimore M., Ritland S. Chromogenic substrate assay of plasma prekallikrein. With a note on its site of biosynthesis. Haemostasis. 1978;7(2-3):69–75. doi: 10.1159/000214237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teger-Nilsson A. C., Friberger P., Gyzander E. Determination of a new rapid plasmin inhibitor in human blood by means of a plasmin specific tripeptide substrate. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneröd A. M., Laake K., Solberg A. K., Strömland S. Inactivation and binding of human plasma kallikrein by antithrombin III and heparin. Thromb Res. 1976 Nov;9(5):457–466. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


