Abstract
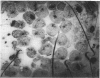
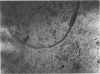
During routine immunofluorescence studies of the serum of a patient with Sjögren's syndrome and lymphoma we detected antibodies giving a cytoplasmic pattern which did not correspond to previously described patterns found for autoantibodies. Using different cells and tissues as substrates for indirect immunofluorescence, including rat liver, rat small bowel, rat testicle, human thyroid, guinea-pig plasma cells and cultured human fibroblasts, the cytoplasmic structure to which these autoantibodies are directed seems to be the golgi complex, a conclusion supported by histochemical studies. Furthermore, these antibodies were absorbed by isolated golgi vesicles. The autoantibodies are of IgG and IgA classes, and the antigen(s) with which they react is(are) resistant to treatment with DNAse and RNAse. None of the sera from 50 normal individuals, seven patients with Sjögren's syndrome (five of them primary and two associated with rheumatoid arthritis; none of them with lymphoma), 25 patients with mixed connective tissue disease, 10 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and five patients with progressive systemic sclerosis, had antibodies directed against this cytoplasmic specificity, as determined by indirect immunofluorescence. This is the first time that autoantibodies directed to the golgi complex are reported. The significance of this finding awaits further descriptions in patients with a clinical picture similar to the one reported here.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcon-Segovia D., Ruiz-Arguelles A., Fishbein E. Antibody to nuclear ribonucleoprotein penetrates live human mononuclear cells through Fc receptors. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):67–69. doi: 10.1038/271067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker J. L., Steinberg A. D., Reinertsen J. L., Plotz P. H., Balow J. E., Klippel J. H. NIH conference. Systemic lupus erythematosus: evolving concepts. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Oct;91(4):587–604. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-4-587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digeon M., Laver M., Riza J., Bach J. F. Detection of circulating immune complexes in human sera by simplified assays with polyethylene glycol. J Immunol Methods. 1977;16(2):165–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassan S. S., Thomas T. L., Moutsopoulos H. M., Hoover R., Kimberly R. P., Budman D. R., Costa J., Decker J. L., Chused T. M. Increased risk of lymphoma in sicca syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Dec;89(6):888–892. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-6-888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem K. L., ten Veen J. H., Lie K. I., Feltkamp T. E., Durrer D. Incidence and significance of heartmuscle antibodies in patients with acute myocardial infarction and unstable angina. Acta Med Scand. 1979;206(6):473–475. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb13549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Queally S. A. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes Golgi-associated protein of cultured fibroblast cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):108–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Abdou N. I., Zweiman B., Zmijewski C., Penn A. S. Aspects of lymphocyte function in myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:402–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Reggio H., Warren G. Antibodies to the Golgi complex and the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):92–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli M., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of RNA protein antigens reactive with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Description of a cytoplasmic nonribosomal antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jul-Aug;17(4):421–429. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. M., Cowin P., Whitehouse J. M. Antitubulin antibody in healthy adults and patients with infectious mononucleosis and its relationship to smooth muscle antibody (SMA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):328–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki S., Kohmoto K., Kurata N., Ofuji T. Identification and characterization of two new soluble nuclear antigens reactive with sera of patients with connective tissue diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Sep-Oct;21(7):803–810. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Abe T., Homma M., Schlossman S. F. Characteristics of anti-T-cell antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for selective reactivity with normal suppressor cells defined by monoclonal antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Aug;16(4):474–484. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutsopoulos H. M., Chused T. M., Mann D. L., Klippel J. H., Fauci A. S., Frank M. M., Lawley T. J., Hamburger M. I. Sjögren's syndrome (Sicca syndrome): current issues. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):212–226. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Immunglobulin classes, subclasses and complexes of IgG rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid plasma cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):55–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., Tan E. M., Gould R. G., Holman H. R. Mixed connective tissue disease--an apparently distinct rheumatic disease syndrome associated with a specific antibody to an extractable nuclear antigen (ENA). Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):148–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALAL N., BUNIM J. J. THE DEVELOPMENT OF MALIGNANT LYMPHOMA IN THE COURSE OF SJOEGREN'S SYNDROME. Am J Med. 1964 Apr;36:529–540. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergani D., Mieli-Vergani G., Alberti A., Neuberger J., Eddleston A. L., Davis M., Williams R. Antibodies to the surface of halothane-altered rabbit hepatocytes in patients with severe halothane-associated hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 10;303(2):66–71. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007103030202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. S., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Enhanced binding of neuraminidase-treated sheep erythrocytes to human T lymphocytes. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):939–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenburger D., Armitage J., Dick F. Immunoblastic lymphadenopathy with pulmonary infiltrates, hypocomplementemia and vasculitis. A hyperimmune syndrome. Am J Med. 1977 Dec;63(6):849–854. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90535-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Fudenberg H. H. Thymus-derived rosette-forming cells in various human disease states: cancer, lymphoma, bacterial and viral infections, and other diseases. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1026–1032. doi: 10.1172/JCI107267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zulman J., Jaffe R., Talal N. Evidence that the malignant lymphoma of Sjögren's syndrome is a monoclonal B-cell neoplasm. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 30;299(22):1215–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811302992204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]