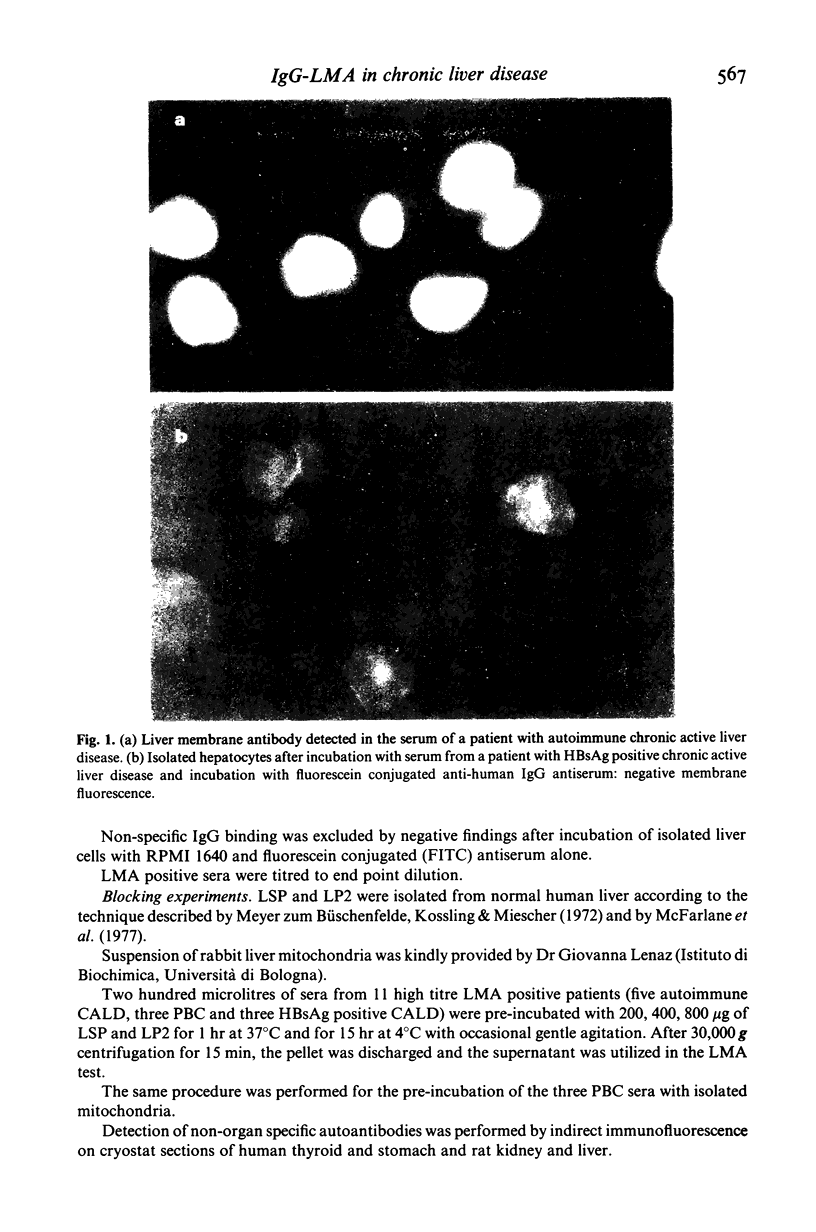
Abstract
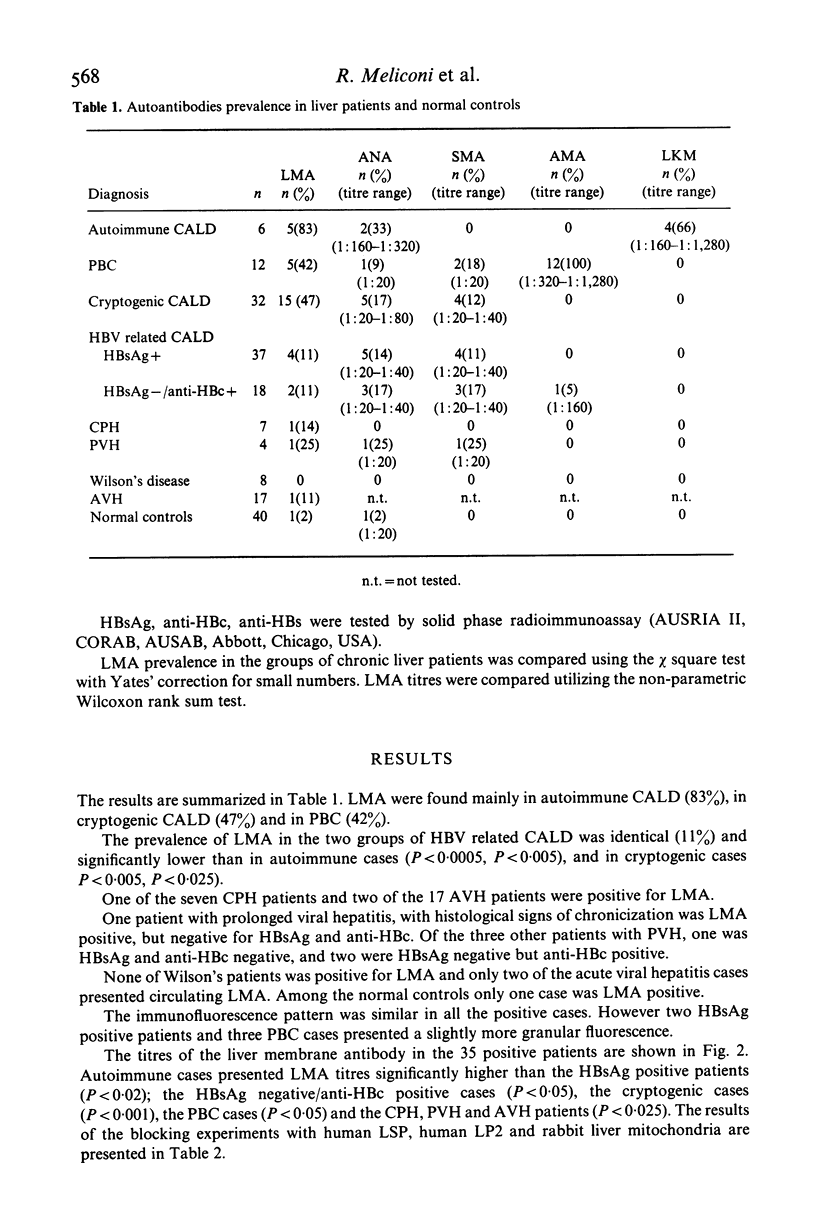
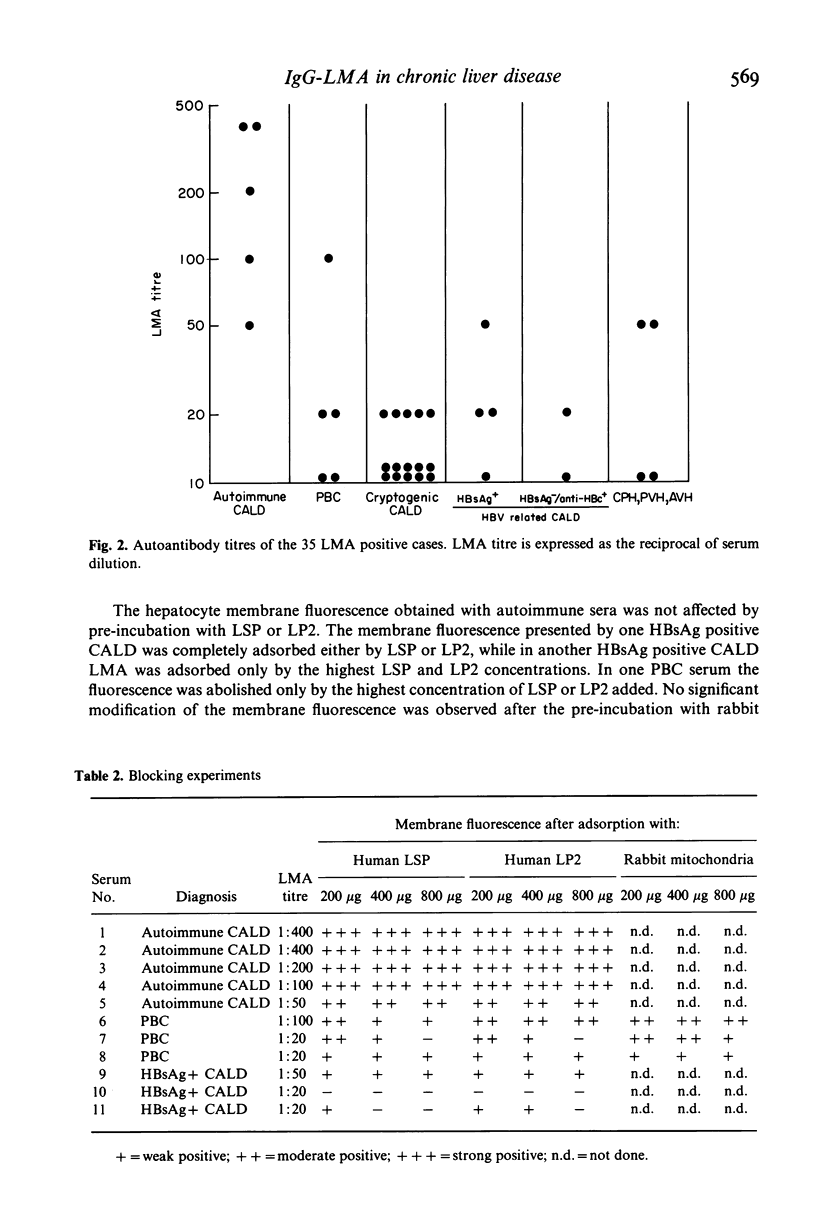
The prevalence of liver cell membrane antibodies (LMA) was evaluated in the sera of 124 untreated patients with various chronic liver diseases, in 17 acute hepatitis patients and in 40 normal controls by indirect immunofluorescence on rabbit hepatocytes, isolated by non-enzymatic method. The presence of LMA was compared with the presence of HBs Ag, anti-HBc and non-organ specific autoantibodies (anti-nuclear antibody, ANA; smooth muscle antibody, SMA; anti-mitochondrial antibody, AMA; liver-kidney microsomal antibody, LKM). LMA was found in 83% of autoimmune chronic active liver disease (CALD), in 47% of cryptogenic CALD and in 42% of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). LMA prevalence both in HBsAg positive and HBsAg negative/anti-HBc positive CALD was 11%, significantly lower than in the other three groups. In the cryptogenic group the prevalence of non-organ specific autoantibodies was significantly lower than LMA prevalence. The 35 LMA positive sera were titred to end point dilution. Autoimmune cases presented titres higher than those of all the other groups. Adsorption experiments showed that in autoimmune cases LMA fluorescence is not blocked by pre-incubation with liver antigens LSP and LP2, while a mild blocking effect was observed in some HBsAg positive cases or PBC sera. No cross-reaction with mitochondrial antigens was observed in PBC sera. LMA can still be considered a marker of autoimmune CALD only when present at high titre and without cross-reactivity with other liver antigens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behrens U. J., Paronetto F. Studies on "liver-specific" antigens. I. Evaluation of the liver specificity of "LSP" and "LP-2". Gastroenterology. 1979 Nov;77(5):1045–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büschenfelde K. H., Kössling F. K., Miescher P. A. Experimental chronic active hepatitis in rabbits following immunization with human liver proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):99–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facchini A., Stefanini G. F., Bernardi M., Miglio F., Gasbarrini G., Labö G. Lymphocytotoxicity test against rabbit hepatocytes in chronic liver diseases. Gut. 1978 Mar;19(3):189–193. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.3.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geubel A. P., Keller R. H., Summerskill W. H., Dickson E. R., Tomasi T. B., Shorter R. G. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity and inhibition studied with autologous liver cells: observations in chronic active liver disease and the primary biliary cirrhosis syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1976 Sep;71(3):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen D. M., McFarlane I. G., Portmann B. S., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Detection of antibodies directed against a liver-specific membrane lipoprotein in patients with acute and chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jul 6;299(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197807062990101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manns M., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Hütteroth T. H., Hess G. Detection and characterization of liver membrane autoantibodies in chronic active hepatitis by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):263–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane I. G., Wojcicka B. M., Zucker G. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Purification and characterization of human liver-specific membrane lipoprotein (LSP). Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):381–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meliconi R., Baraldini M., Stefanini G. F., Facchini A., Miglio F., Bortolotti F., Alberti A., Realdi G., Amoroso P. Antibodies against human liver-specific protein (LSP) in acute and chronic viral hepatitis types A, B and non-A, non-B. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Nov;46(2):382–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meliconi R., Perperas A., Jensen D., Alberti A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Anti-LSP antibodies in acute liver disease. Gut. 1982 Jul;23(7):603–607. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.7.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Manns M., Hütteroth T. H., Hopf U., Arnold W. LM-Ag and LSP--two different target antigens involved in the immunopathogenesis of chronic active hepatitis? Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Aug;37(2):205–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tage-Jensen U., Arnold W., Dietrichson O., Hardt F., Hopf U., Meyer Zum Büschenfelde K. H., Nielsen J. O. Liver-cell-membrane autoantibody specific for inflammatory liver diseases. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 22;1(6055):206–208. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6055.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tage-Jensen U., Permin H., Hardt F., Juhl E., Mathiesen L. R., Nielsen J. O., Ranek L. Circulating autoantibodies in patients with acute viral hepatitis. Relation to etiology and clinical course. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(2):229–235. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]