Abstract
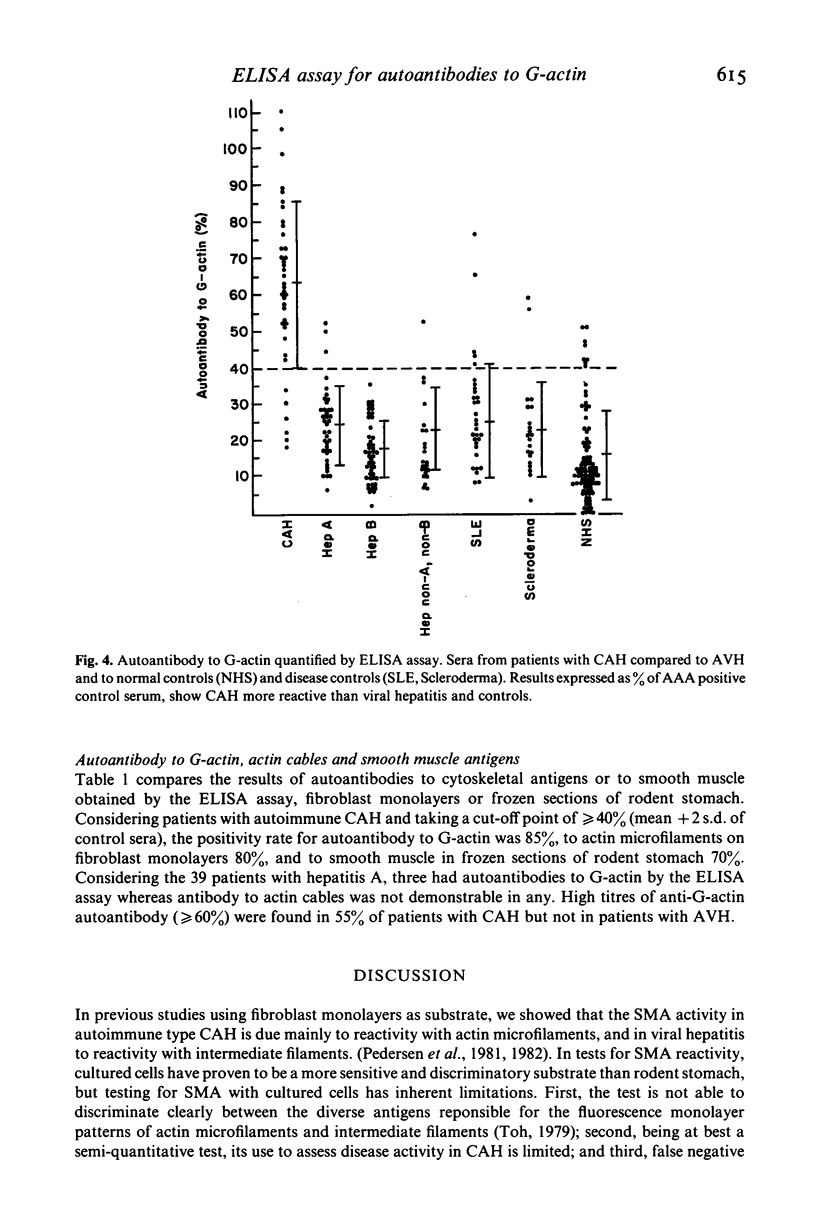
An ELISA was developed to test for IgG autoantibody to rabbit skeletal muscle G-actin in liver disease. To express results of the ELISA, we used a single reference serum with known high anti-actin activity, and assessed binding of test sera as a percentage of that displayed by the reference antiserum. Antibody to G-actin was measured in 40 sera from patients with chronic active hepatitis (CAH), 39 from acute viral hepatitis A (Hep A), 46 from acute viral hepatitis B (Hep B), 23 from non-A, non-B hepatitis (Hep non-A, non-B), 31 from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), 21 from scleroderma and 93 from normal persons. The results were compared with those obtained using indirect immunofluorescence tests with frozen sections of rodent stomach or fibroblast monolayers as substrates. Anti-G-actin activity of serum was significantly higher (P less than 0.001) in CAH (mean 63% +/- 23, range 18-110) than in controls (mean 15% +/- 12, range 0-51), systemic lupus erythematosus (mean 25% +/- 16, range 8-76), scleroderma (mean 23% +/- 13, range 3-59), Hep A (mean 24% +/- 11, range 6-25), Hep B (17% +/- 8, range 2-36), or Hep non-A, non-B (mean 23% +/- 11, range 7-53). There was no significant difference (P greater than 0.05) in the occurrence of anti-G-actin activity of serum in Hep A, Hep B or non-A, non-B compared with controls. At an ELISA reading of greater than or equal to 40% (mean + 2 s.d. of controls) the assay detected autoantibodies to G-actin in 85% of CAH, compared to 80% on fibroblast monolayers and 70% on rodent stomach. The ELISA described in the present study is a simple, sensitive and quantitative assay for autoantibody to G-actin. It should prove useful in assessing subspecificities of actin antibodies in liver diseases, and in differential diagnosis, particularly CAH from acute viral hepatitis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaponnier C., Borgia R., Rungger-Brändle E., Weil R., Gabbiani G. An actin-destabilizing factor is present in human plasma. Experientia. 1979 Aug 15;35(8):1039–1041. doi: 10.1007/BF01949928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke F. M., Lovell S. J., Masters C. J., Winzor D. J. Beef muscle troponin: evidence for multiple forms of troponin-T. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 14;427(2):617–626. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow L. J., Holborow E. J., Johnson G. D., Lamb S. G., Stewart J. S., Taylor P. E., Zuckerman A. J. Autoantibodies and the hepatitis-associated antigen in acute infective hepatitis. Br Med J. 1970 Jun 20;2(5711):693–695. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5711.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J., Glynn L. E. Antibody to smooth muscle in patients with liver disease. Lancet. 1965 Oct 30;2(7418):878–879. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. S., Toh B. H., Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D., Shyamala G. N. Autoantibody to intermediate filaments in viral hepatitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Nov;21(2):154–161. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. S., Toh B. H., Mackay I. R., Tait B. D., Gust I. D., Kastelan A., Hadzic N. Segregation of autoantibody to cytoskeletal filaments, actin and intermediate filaments with two types of chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):527–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce A. J., Mendoza N., Boreisha I., Gaizutis M. A., Pollak V. E. Use of enzyme-linked antibodies to measure serum anti-DNA antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Chem. 1974 Mar;20(3):353–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Gallichio H. A., Jeffrey P. L., Livett B. G., Muller H. K., Cauchi M. N., Clarke F. M. Anti-actin stains synapses. Nature. 1976 Dec 16;264(5587):648–650. doi: 10.1038/264648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H. Smooth muscle autoantibodies and autoantigens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):621–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bartlett A., Bidwell D. E. Enzyme immunoassays with special reference to ELISA techniques. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):507–520. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Mackay I. R., Irwin J. Autoimmune hepatitis. Immunofluorescence reactions with cytoplasm of smooth muscle and renal glomerular cells. Lancet. 1966 Jun 18;1(7451):1333–1335. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


