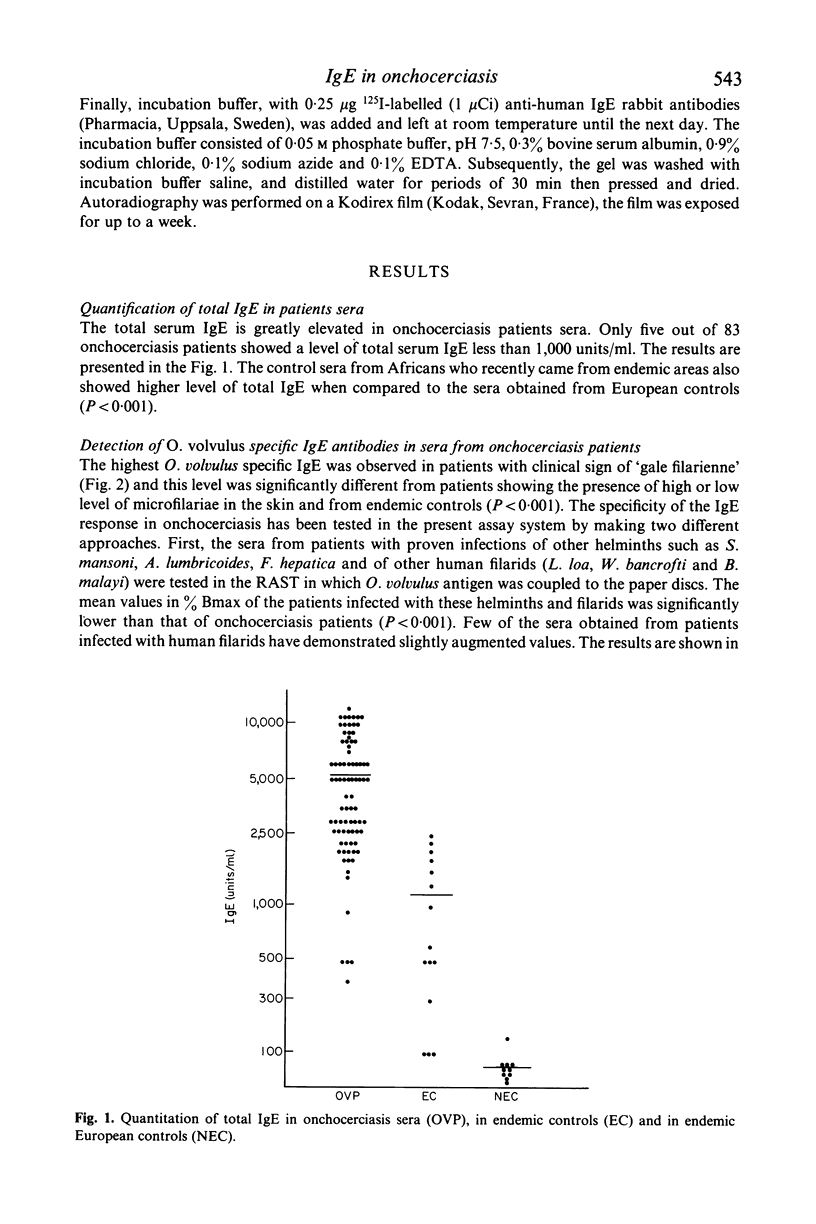
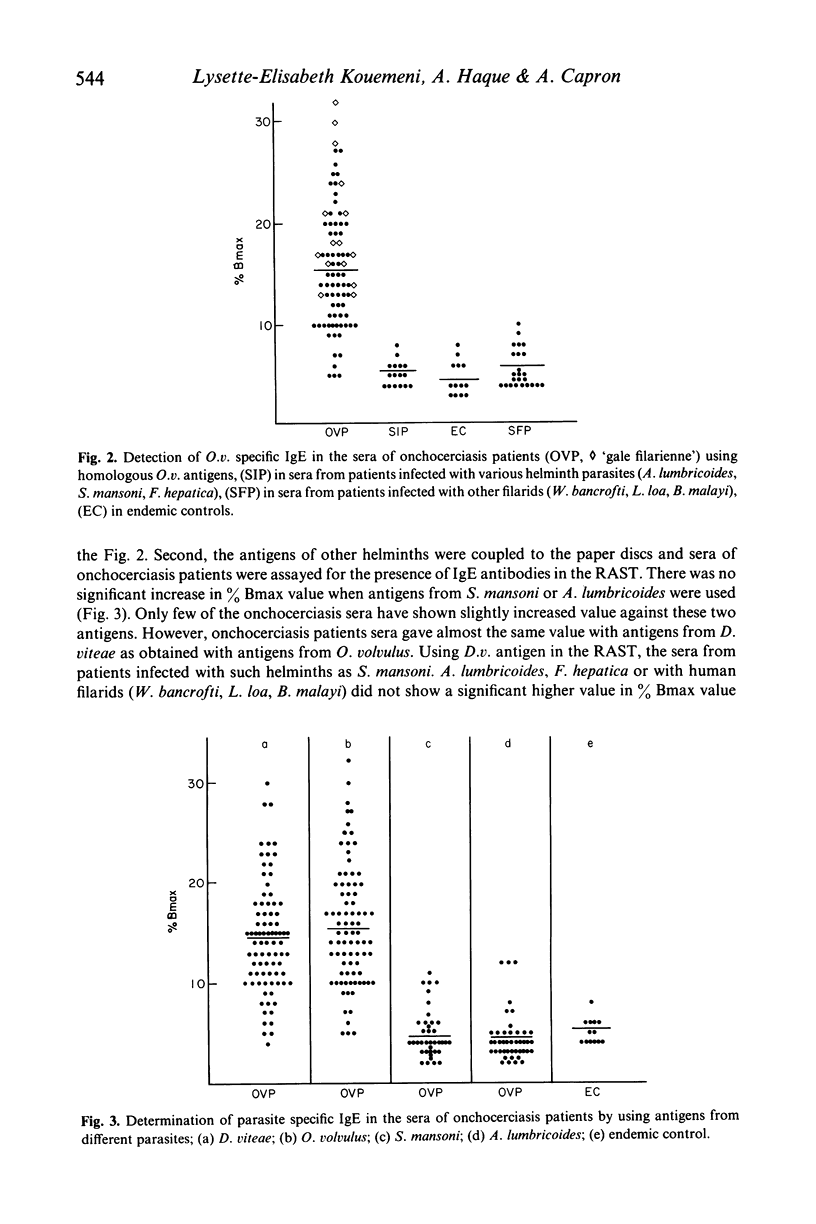
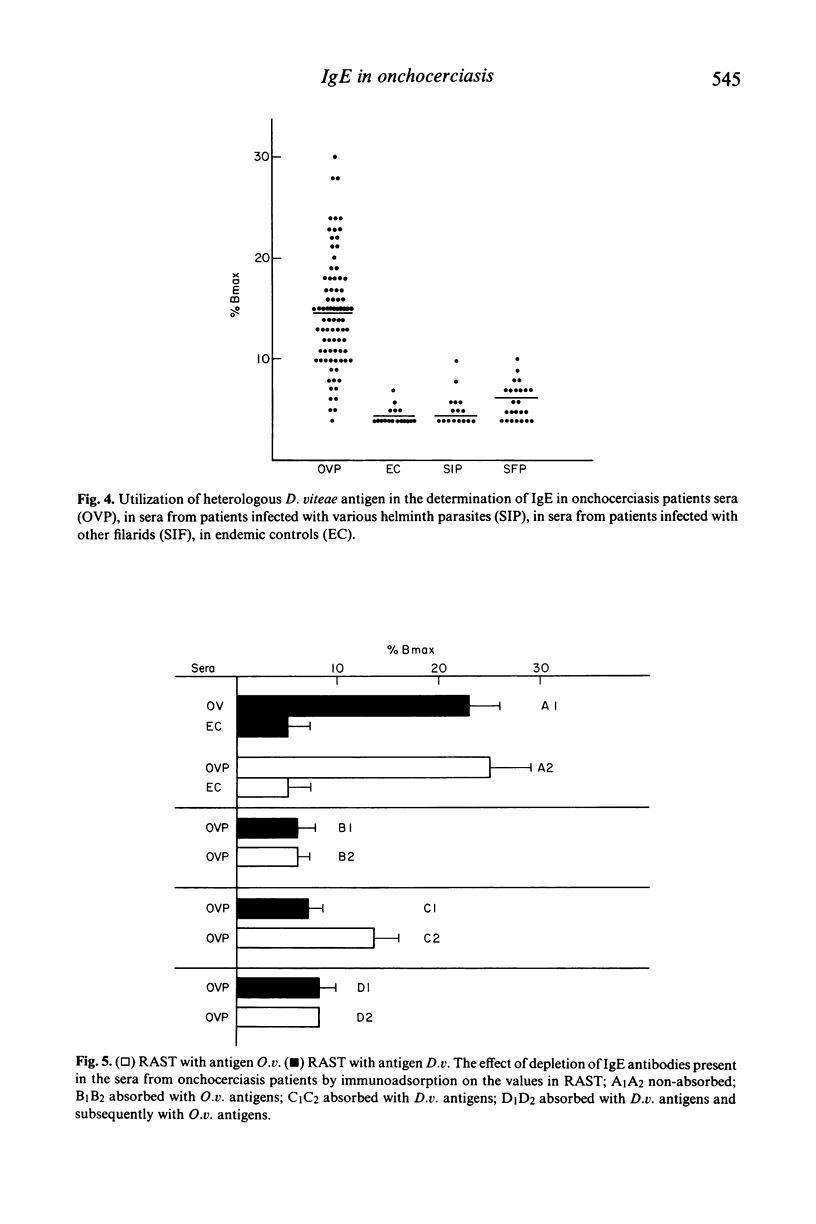
Abstract
The present study reports the presence of Onchocerca volvulus specific IgE in the sera obtained from onchocerciasis patients. About 70% of onchocerciasis patients showed a raised level of O. volvulus specific IgE compared to patients infected either with other human filarids (Loa loa, Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi) or with other helminths (Schistosoma mansoni, Ascaris lumbricoides, Fasciola hepatica). The O. volvulus specific IgE level was significantly higher in patients exhibiting 'gale filarienne' than in microfilaremic patients or in endemic controls. The total IgE level was significantly raised in the serum samples of all groups of subjects from endemic areas compared to European controls. There was no significant increase in the level of IgE in the onchocerciasis sera when O. volvulus antigen was replaced by the antigens from various helminths in the present assay system (radioallergosorbent test). However, there was a clear evidence of the presence of cross-reacting allergens in the crude extracts from adults of O. volvulus and Dipetalonema viteae (a rodent filarial parasite) because there was a significant reduction in IgE level in onchocerciasis sera following absorption with either O. volvulus or D. viteae sorbents. Moreover, the IgE antibodies in onchocerciasis patients sera recognized the allergens which were present in the somatic extracts of O. volvulus and D. viteae as revealed by radiolabelled anti-IgE.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Structure and function of human immunoglobulin E. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Biguet J., Vernes A., Afchain D. Structure antigénique des helminthes. Aspects immunologiques des relations hote-parasite. Pathol Biol. 1968 Feb;16(3):121–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Dessaint J. P. IgE and cells in protective immunity. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1977 May;25(5):287–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., WILLIAMS C. A. Méthode permettant l'étude conjuguée des proprietés électrophorétiques et immunochimiques d'un mélange de protéines; application au sérum sanguin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jan;10(1):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Averbeck A. K., Swedlund H. A. Measurement of IgE in normal and allergic serum by radioimmunoassay. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Apr;77(4):690–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. G., Hussain R., Ottesen E. A., Adkinson N. F., Jr The quantitation of parasite-specific human IgG and IgE in sera: evaluation of solid-phase RIA and ELISA methodology. J Immunol Methods. 1981;44(1):101–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Sawada T., Sato S. Increased serum IgE level in individuals infected with Schistosoma japonicum, Wuchereria bancrofti or hook worm, and the changes by treatment in schistosomiasis. Jpn J Exp Med. 1972 Apr;42(2):115–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E., Haig D. M. Time course studies on rat IgE production in N. Brasiliensis infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):346–351. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima S., Ovary Z. Effect of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection on anti-hapten IgE antibody response in the mouse. II. Mechanism of potentiation of the IgE antibody response to a heterologous hapten-carrier conjugate. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jun;17(2):383–391. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima S., Yokogawa M., Tada T. Raised levels of serum IgE in human helminthiases. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1972 Nov;21(6):913–918. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1972.21.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neva F. A., Kaplan A. P., Pacheco G., Gray L., Danaraj T. J. Tropical eosinophilia. A human model of parasitic immunopathology, with observations on serum IgE levels before and after treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Jun;55(6):422–429. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottesen E. A., Neva F. A., Paranjape R. S., Tripathy S. P., Thiruvengadam K. V., Beaven M. A. Specific allergic sensitsation to filarial antigens in tropical eosinophilia syndrome. Lancet. 1979 Jun 2;1(8127):1158–1161. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91842-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S. Radioactive single radial diffusion: a method for increasing the sensitivity of immunochemical quantification of proteins in agar gel. Bull World Health Organ. 1969 Apr;40(4):613–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss N., Speiser F., Hussain R. IgE antibodies in human onchocerciasis. Application of a newly developed radioallergosorbent test (RAST). Acta Trop. 1981 Sep;38(3):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wide L., Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Diagnosis of allergy by an in-vitro test for allergen antibodies. Lancet. 1967 Nov 25;2(7526):1105–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90615-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]