Abstract
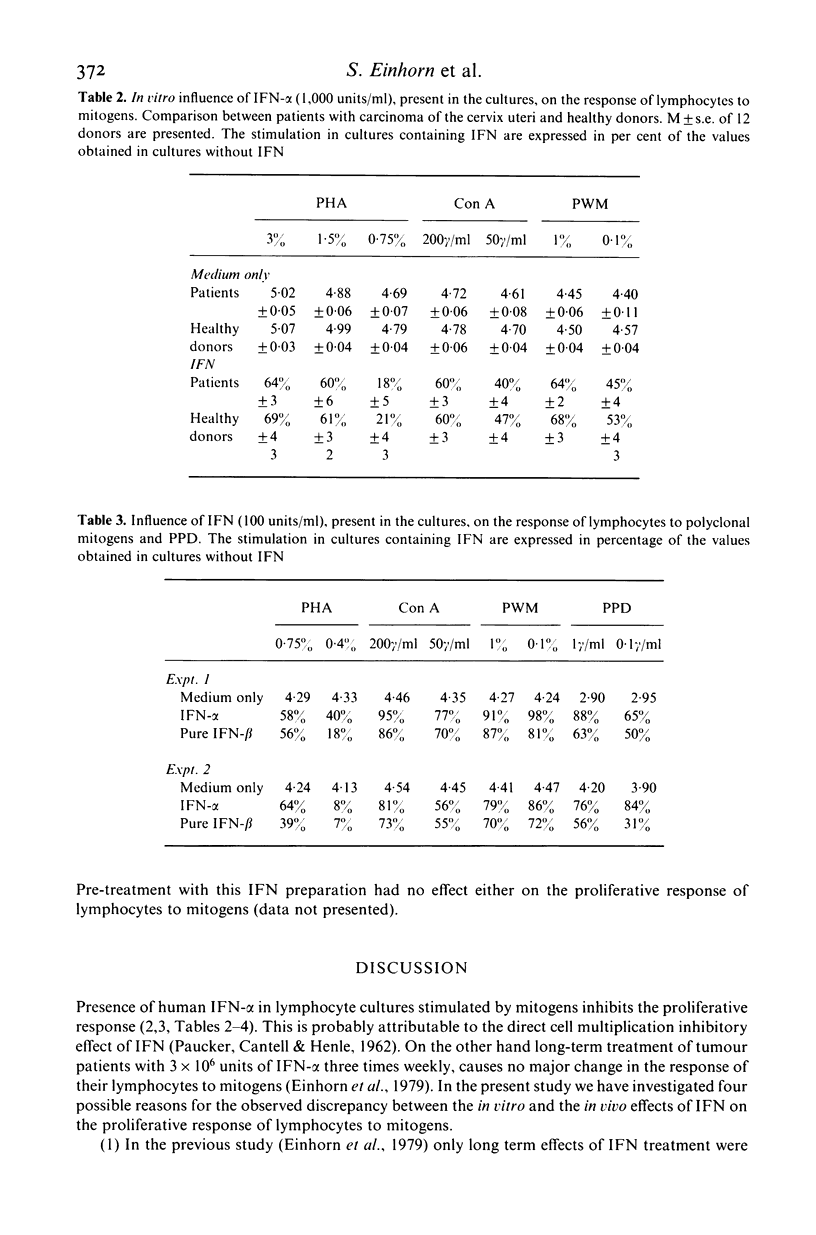
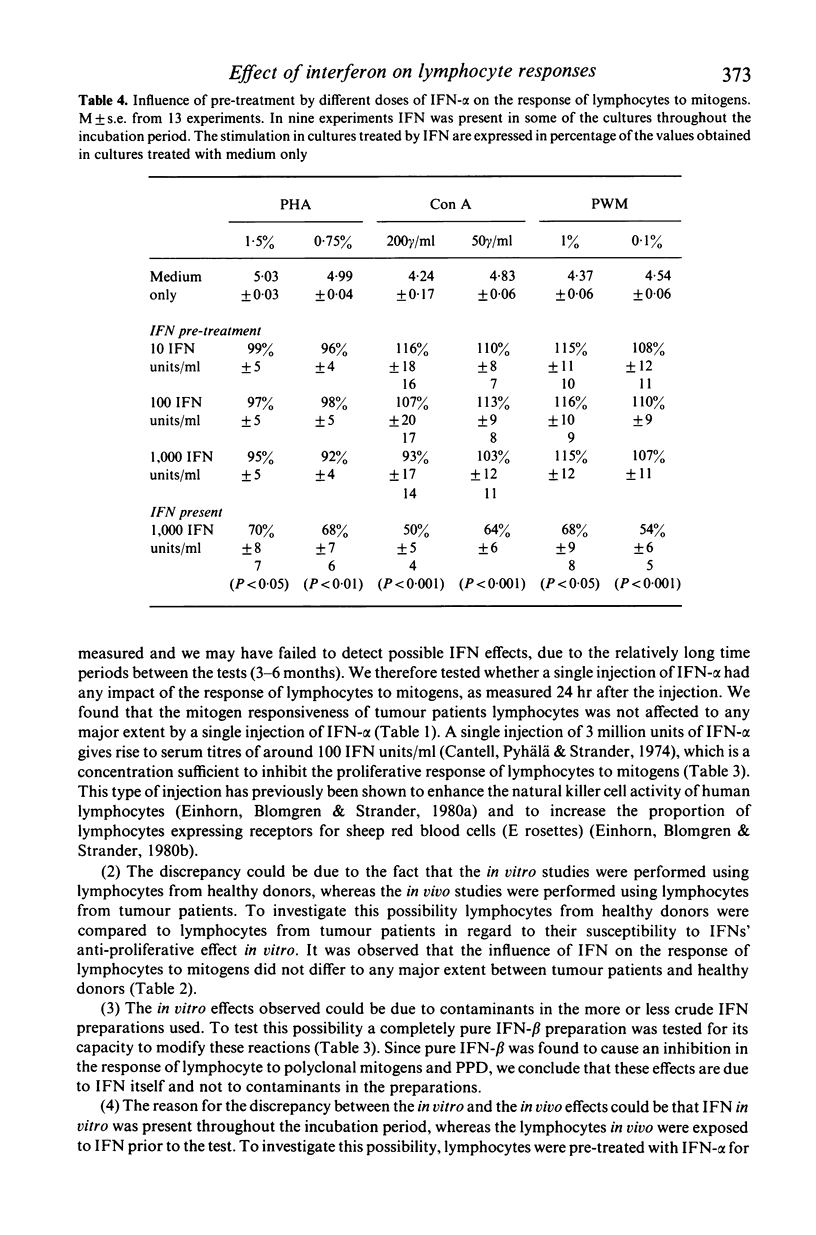
Previous studies have shown that addition of IFN to the assay in vitro inhibits the proliferative response of lymphocytes to mitogens, whereas long term treatment by IFN in vivo has no major effect on the mitogen responsiveness of tumour patient's lymphocytes. Possible reasons for the discrepancy between the results obtained following treatment by IFN in vitro and in vivo were investigated. It was observed that the proliferative response of tumour patients lymphocytes to various mitogens was not affected to any major extent 24 hr after a single injection of 3 million units of interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha). Lymphocytes from tumour patients and healthy donors were found not to differ in their susceptibility to IFNs' anti-proliferative effect in vitro. Pure IFN-beta, present in the assay throughout the incubation period, inhibited the response of lymphocytes to polyclonal mitogens and PPD showing IFN and not contaminants in the preparations to be responsible for this effect. Although the presence of IFN in the assay throughout the incubation period inhibited the proliferative response of lymphocytes, pre-treatment of these cells with IFN-alpha in vitro was found to have no major effect on their response to mitogens. We conclude that the lack of effect on the proliferative response of lymphocytes following treatment by IFN in vivo, is probably due to the fact that the lymphocytes were only treated with IFN prior to the assay.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomgren H., Strander H., Cantell K. Effect of human leukocyte interferon on the response of lymphocytes to mitogenic stimuli in vitro. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):697–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantell K., Pyhälä L., Strander H. Circulating human interferon after intramuscular injection into animals and man. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):453–455. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Cantell K., Strander H. Effect of prolonged in vivo administration of leukocyte interferon on the mitogen responsiveness of human lymphocytes. Acta Med Scand. 1979;206(5):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb13525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Strander H. Effect of an intramuscular injection of human leukocyte interferon on blood leukocyte counts and proportions of lymphocytes forming E, EA and EAC rosettes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;63(2):139–144. doi: 10.1159/000232619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Strander H. Interferon and spontaneous cytotoxicity in man. V. Enhancement of spontaneous cytotoxicity in patients receiving human leukocyte interferon. Int J Cancer. 1980 Oct 15;26(4):419–428. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Hunkapiller M. W., Korant B. D., Hardy R. W., Hood L. E. Human fibroblast interferon: amino acid analysis and amino terminal amino acid sequence. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):525–526. doi: 10.1126/science.7352259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr Interferon: purification and initial characterization from human diploid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):520–523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilliehök B., Blomgren H. Strong stimulation of CBA lymphocytes in the mixed lymphocyte interaction with cells from the H-2-indentical strain C3H. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(5):627–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUCKER K., CANTELL K., HENLE W. Quantitative studies on viral interference in suspended L cells. III. Effect of interfering viruses and interferon on the growth rate of cells. Virology. 1962 Jun;17:324–334. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


