Abstract
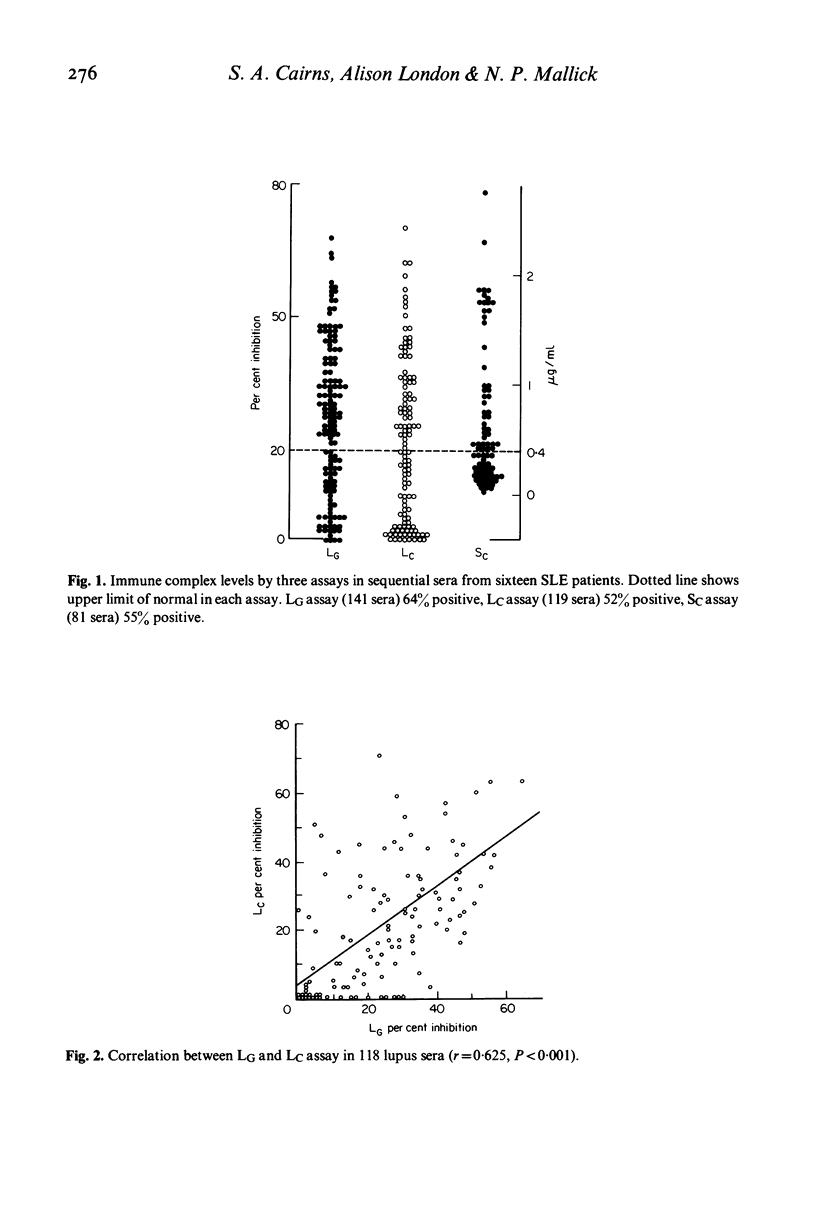
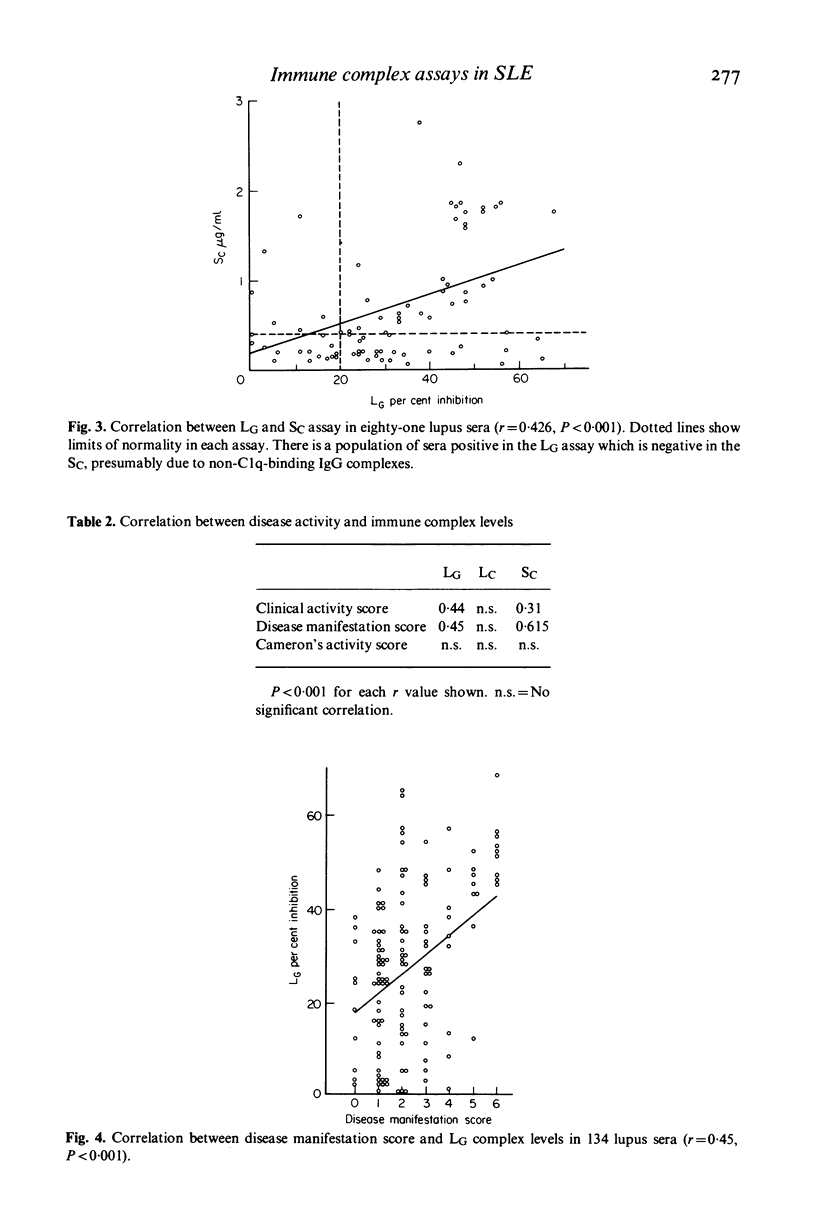
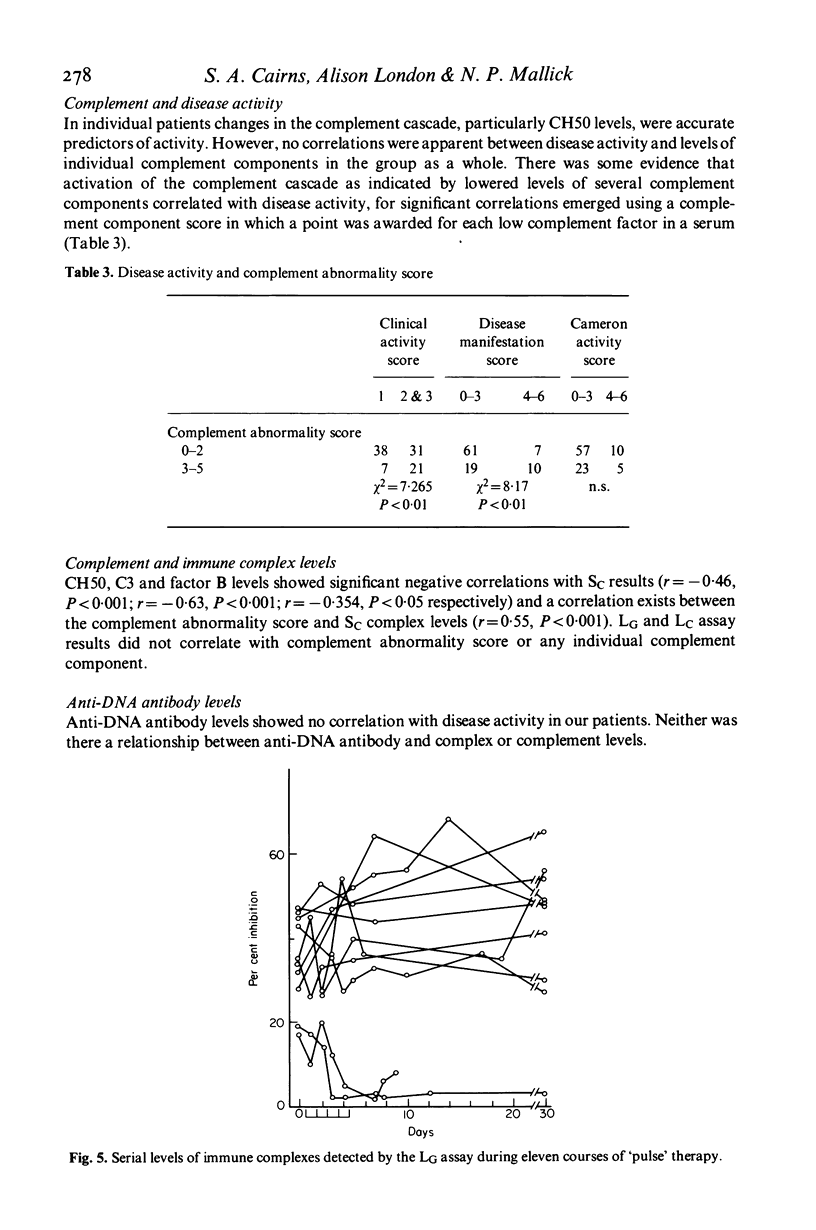
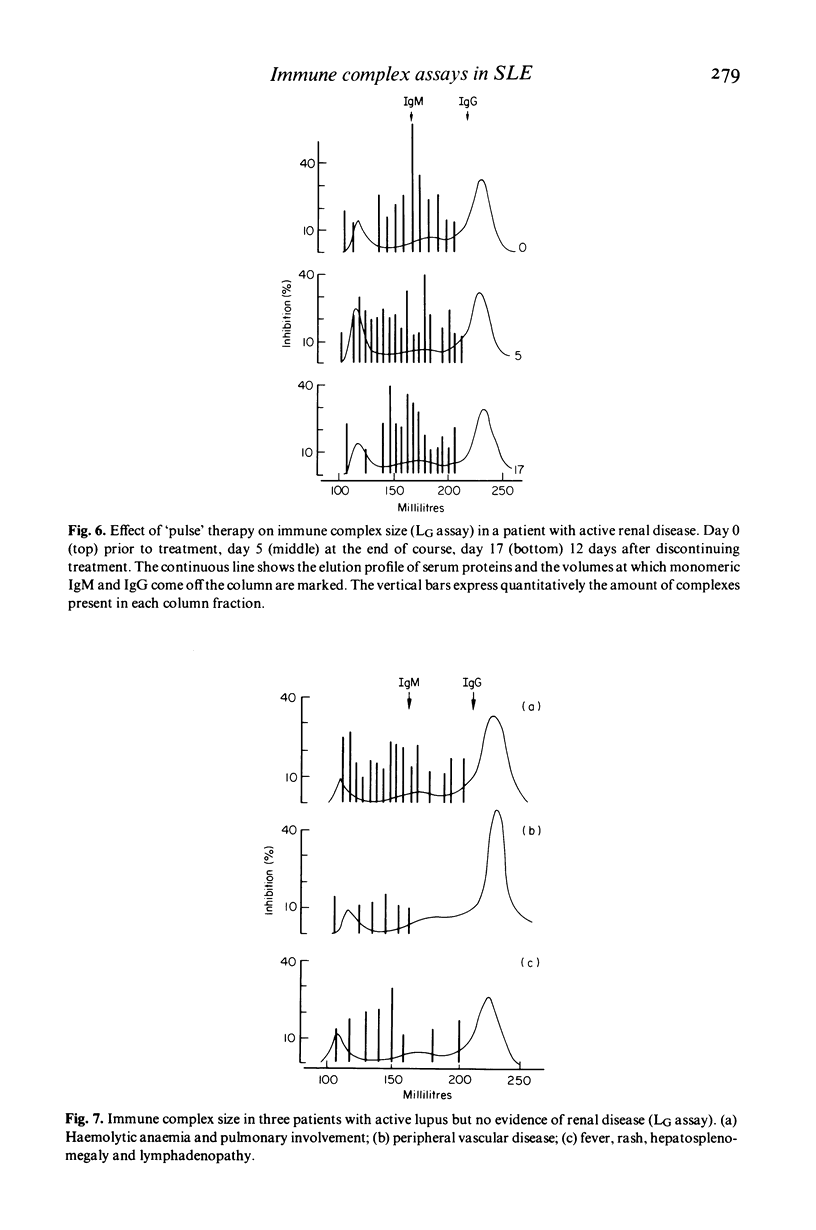
Sixteen patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, fourteen with renal involvement have been studied over a 30-month period. Circulating immune complex levels have been assayed by three techniques. The results of tests on 141 sequential sera suggest that the three assays detected overlapping populations of the range of complexes present. Immune complex levels are shown to be good markers of disease activity and certain immunochemical properties of the complexes emerged as better markers than others. Immune complex size is a more important determinant of disease manifestation than are overall immune complex levels. High doses of intravenous methyl prednisolone, which did not reduce overall complex levels, reduced levels of those complexes (molecular weight 600,000-900,000 Daltons) associated with renal involvement.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cameron J. S., Lessof M. H., Ogg C. S., Williams B. D., Williams D. G. Disease activity in the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus in relation to serum complement concentrations. DNA-binding capacity and precipitating anti-DNA antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Sep;25(3):418–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart E. S., Idelson B. A., Scheinberg M. A., Couser W. G. Beneficial effects of methylprednisolone "pulse" therapy in diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. Lancet. 1976 Jan 24;1(7952):163–166. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Koffler D. Immune complex disease in experimental animals and man. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):185–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruchaud A., Chenais F., Fournié G. J., Humair L., Lambert P. H., Mulli J. C., Chatelanat F. Immune complex deposits in systemic lupus erythematosus kidney without histological or functional alterations. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun 12;5(3):297–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P., Percy J. S., Russell A. S. Correlation between levels of DNA antibodies and clinical disease activity in SLE. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Apr;36(2):157–159. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosa S., Cairns S. A., Lawler W., Mallick N. P., Slotki I. N. The treatment of lupus nephritis by methyl prednisolone pulse therapy. Postgrad Med J. 1978 Sep;54(635):628–632. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.54.635.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for the detection of immune complexes of known immunoglobulin class using solid phase C1q. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):396–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holborow E. J. The serology of connective tissue disorders. Br J Hosp Med. 1978 Mar;19(3):250, 252, 257-8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Fournié G. J., Türler H., Miescher P. A. Features of systemic lupus erythematosus in mice injected with bacterial lipopolysaccharides: identificantion of circulating DNA and renal localization of DNA-anti-DNA complexes. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1115–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinsky R. J., Cameron J. S., Soothill J. F. Serum immune complexes and disease activity in lupus nephritis. Lancet. 1977 Mar 12;1(8011):564–567. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91998-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinsky R. J., Soothill J. F. A test for antigen--antibody complexes in human sera using IgM of rabbit antisera to human immunoglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Sep;29(3):428–435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood C. M., Worlledge S., Nicholas A., Cotton C., Peters D. K. Reversal of impaired splenic function in patients with nephritis or vasculitis (or both) by plasma exchange. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 8;300(10):524–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903083001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Schur P. H., Rose J. A., Decker J. L., Talal N. Measurement of serum DNA-binding activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 25;281(13):701–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909252811304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pussell B. A., Lockwood C. M., Scott D. M., Pinching A. J., Peters D. K. Value of immune-complex assays in diagnosis and management. Lancet. 1978 Aug 12;2(8085):359–364. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92954-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemasu K., Stroud R. M. Clq: rapid purification method for preparation of monospecific antisera and for biochemical studies. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


