Abstract
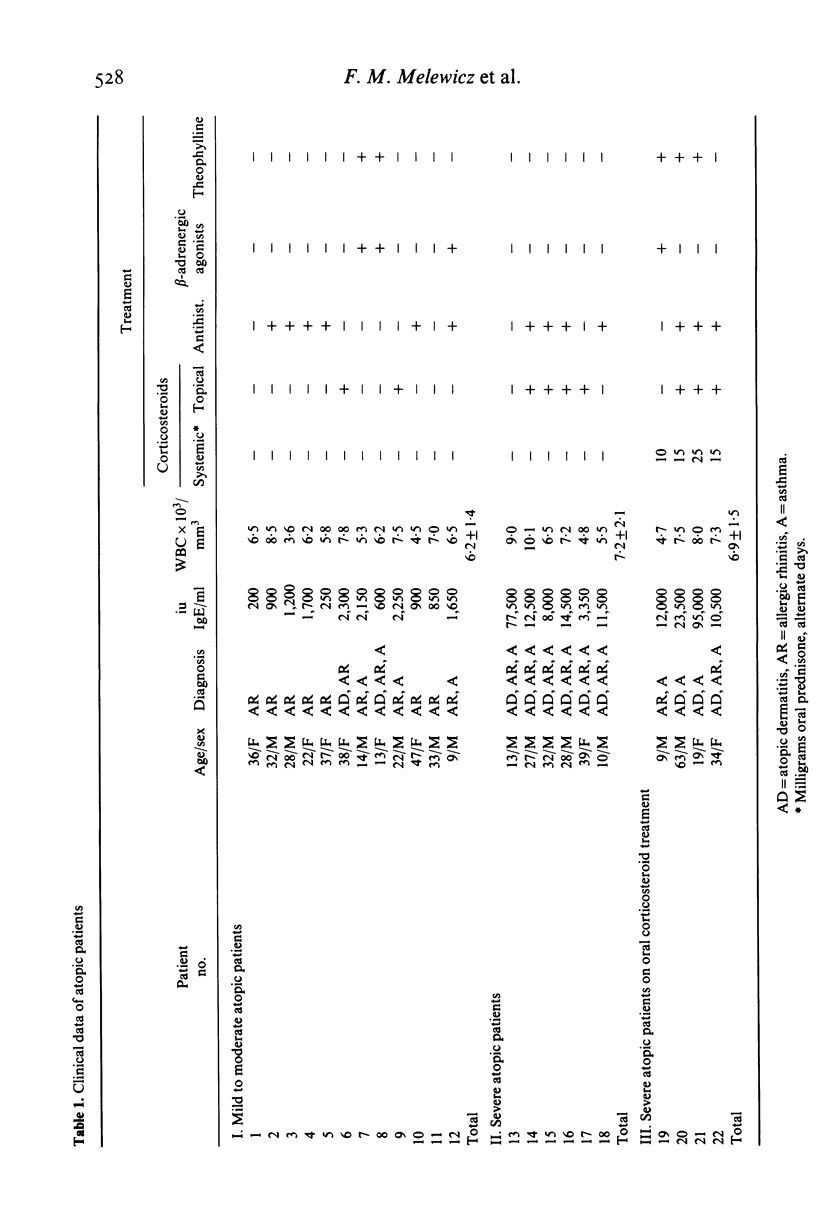
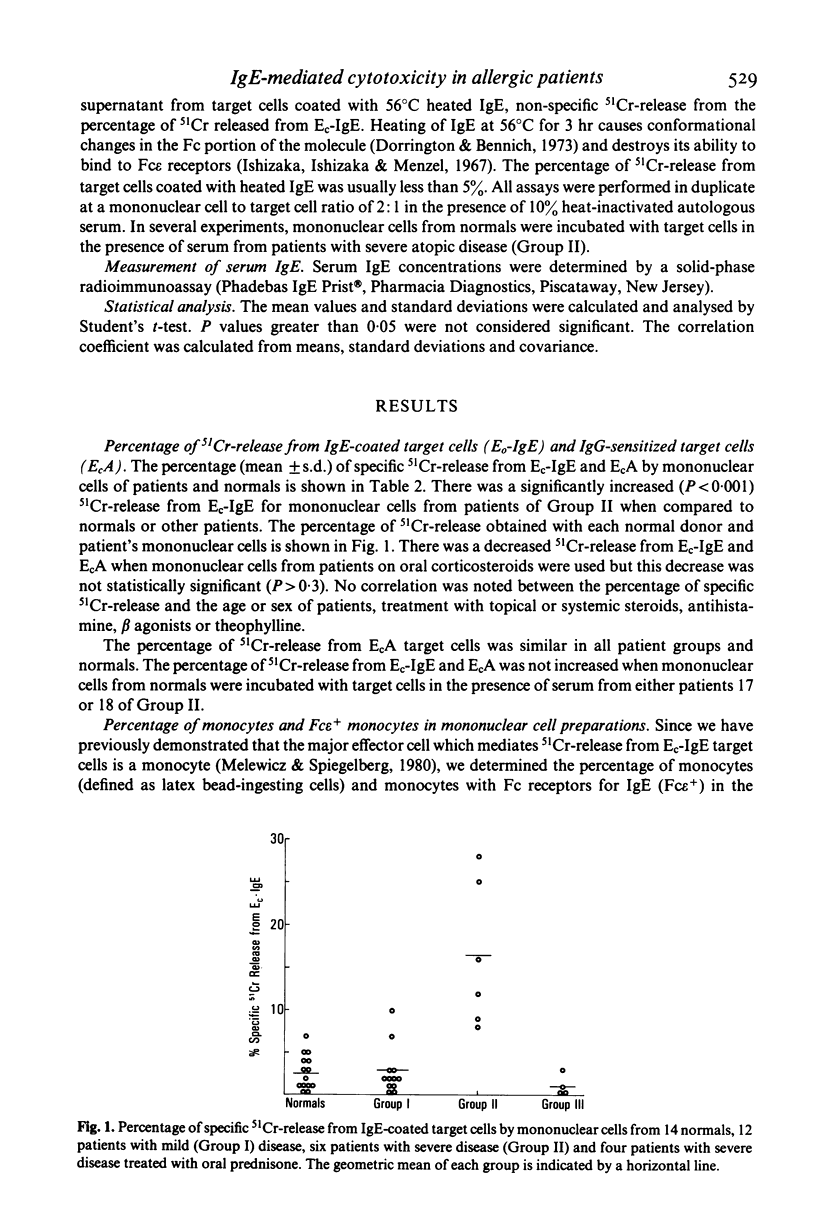
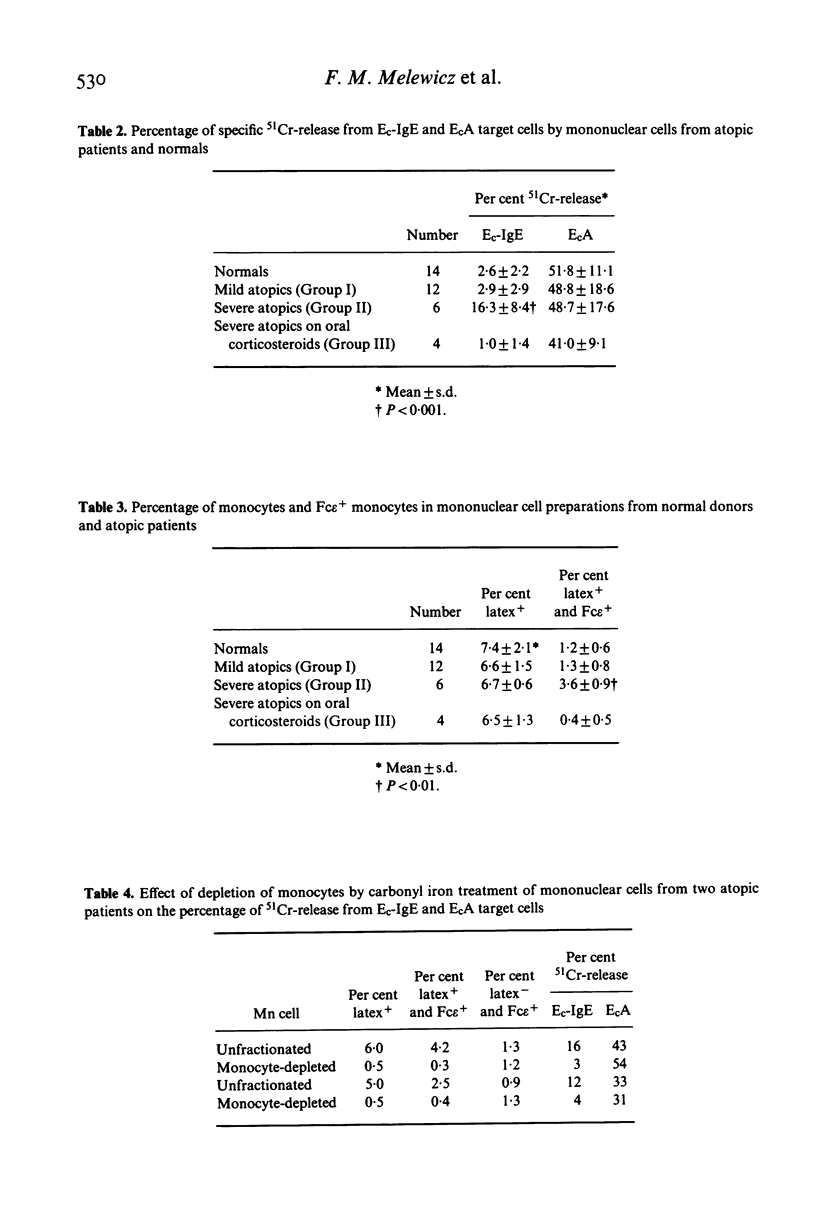
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 14 healthy donors and 22 allergic patients were incubated with 51Cr-labelled chicken erythrocytes coated with an IgE myeloma protein or rabbit IgG antibodies. Mononuclear cells from patients with severe atopic disorders released a significantly greater percentage of 51Cr (P less than 0.001) from IgE-coated target cells than mononuclear cells from healthy controls, patients with mild atopic disease, or patients with severe atopic disease taking oral prednisone. Specific 51Cr-release from IgE-coated target cells was directly correlated to the percentage of monocytes (latex-ingesting cells) with Fc receptors for IgE (r = 0.87, P less than 0.01) as detected by a rosette assay employing ox erythrocytes coated with IgE. Mononuclear cells from patients and normals released similar amounts of 51Cr from IgG-sensitized target cells. Depletion of monocytes from mononuclear cell preparations from two severe atopic patients decreased 51Cr-release from IgE-coated target cells to levels seen in healthy donors or patients with mild allergic disease. These results demonstrate that mononuclear cells from severely allergic patients have a significantly increased cytotoxicity toward IgE-coated targets coated target cells and that this cytotoxicity correlates highly with the percentage of monocytes with Fc receptors for IgE in these mononuclear preparations.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brostoff J., Johns P., Stanworth D. R. Complexed IgE in atopy. Lancet. 1977 Oct 8;2(8041):741–742. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøyum A. Isolation of lymphocytes, granulocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessaint J. P., Capron A., Joseph M., Bazin H. Cytophilic binding of IgE to the macrophage. II. Immunologic release of lysosomal enzyme from macrophages by IgE and anti-IgE in the rat: a new mechanism of macrophage activation. Cell Immunol. 1979 Aug;46(1):24–34. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessaint J. P., Waksman B. H., Metzger H., Capron A. Cytophilic binding of IgE to the macrophage. III. Involvement of cyclic GMP and calcium in macrophage activation by dimeric or aggregated rat myeloma IgE. Cell Immunol. 1980 May;51(2):280–292. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Bennich H. Thermally induced structural changes in immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8378–8384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Molina A., Spiegelberg H. L. A subpopulation of normal human peripheral B lymphcytes that bind IgE. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):616–624. doi: 10.1172/JCI108679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K. Human reaginic antibodies. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:187–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Menzel A. E. Physicochemical properties of reaginic antibody. VI. Effect of heat on gamma-E-, gamma-G- and gamma-A-antibodies in the sera of ragweed sensitive patients. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):610–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph M., Tonnel A. B., Capron A., Voisin C. Enzyme release and superoxide anion production by human alveolar macrophages stimulated with immunoglobulin E. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 May;40(2):416–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. S., Stobo J. D., Goldyne M. E. In vitro synthesis of prostaglandins and related lipids by populations of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Prostaglandins. 1980 Jul;20(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragballe K. Antibody-dependent monocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in severe atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 1979 Feb;34(1):35–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1979.tb01998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malveaux F. J., Conroy M. C., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Lichtenstein L. M. IgE receptors on human basophils. Relationship to serum IgE concentration. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):176–181. doi: 10.1172/JCI109103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melewicz F. M., Spiegelberg H. L. Fc receptors for IgE on a subpopulation of human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1026–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Cohn Z. A., Blackburn P., Manning J. M. Mouse peritoneal macrophages release leukotriene C in response to a phagocytic stimulus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4928–4932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Levy P. C., LoBuglio A. F. Human monocyte antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to tumor cells. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1172–1180. doi: 10.1172/JCI109236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Melewicz F. M. Fc receptors specific for IgE on subpopulations of human lymphocytes and monocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):424–433. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., O'Connor R. D., Simon R. A., Mathison D. A. Lymphocytes with immunoglobulin E Fc receptors in patients with atopic disorders. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):714–720. doi: 10.1172/JCI109514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


