Abstract
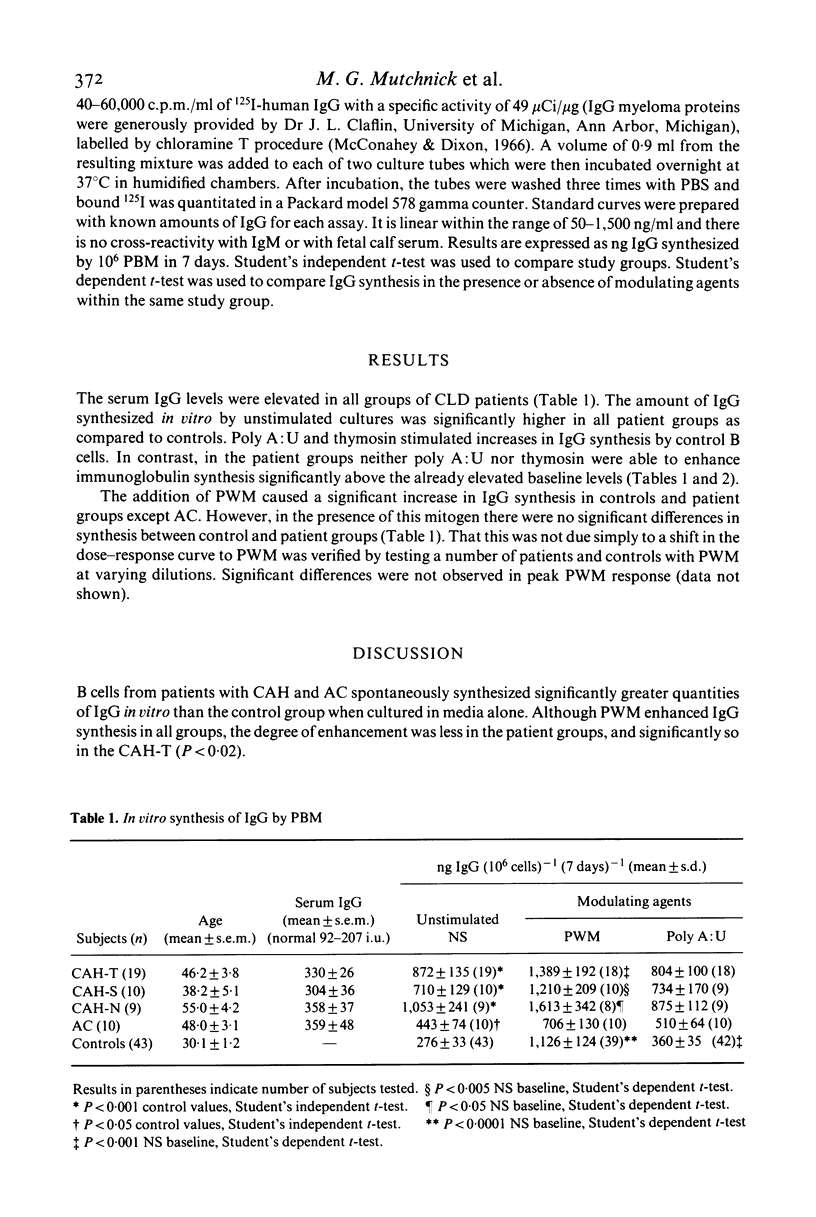
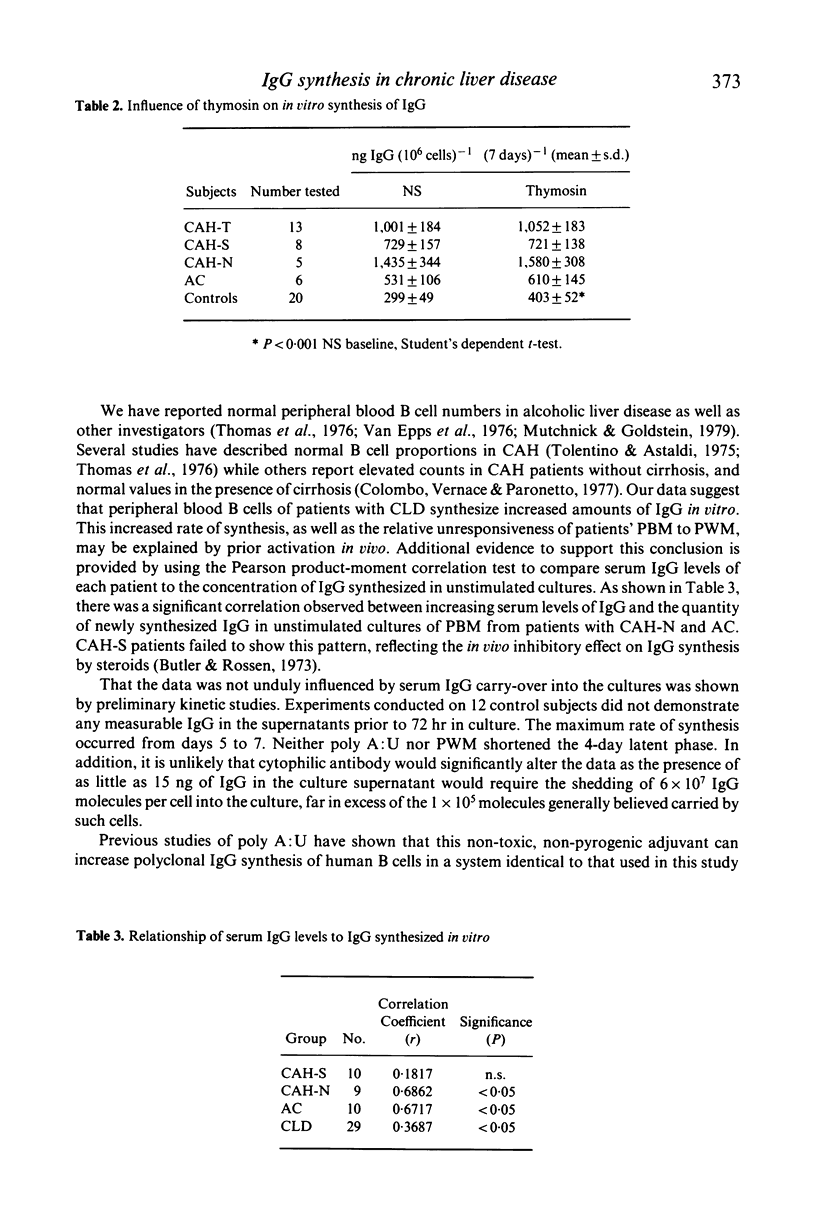
In vitro IgG synthesis by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBM) from patients with chronic liver disease (CLD) was studied. In addition, the effect of pokeweed mitogen (PWM), polyadenylic-polyuridylic acid complexes (poly A:U) and thymosin fraction 5 on IgG synthesis was determined. Unstimulated cultures of PBM from patients with chronic active hepatitis (CAH) and alcoholic cirrhosis (AC) synthesized significantly higher quantities of IgG than the controls. Moreover, there was a direct correlation between serum IgG concentrations and the quantity of newly synthesized IgG in these unstimulated cultures. PWM, poly A:U and thymosin each stimulated increased IgG synthesis in the controls. While neither poly A:U nor thymosin enhanced IgG synthesis in patients with CLD, PWM increased IgG synthesis in CAH but not AC. These results indicate that spontaneous in vitro B cell synthesis of IgG is enhanced in CLD and may reflect antigenic stimulation in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askenase P. W., Leonard E. J. Solid phase radioimmunoassay of human beta 1C globulin. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jan;7(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M., Vernace S. J., Paronetto F. T and B lymphocytes in patients with chronic active hepatitis (CAH). Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):4–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfraissy J. F., Galanaud P., Dormont J., Wallon C. Primary in vitro antibody response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes: role of phagocytic mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1283–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosch H-M, Gelfand E. W. Generation of human plaque-forming cells in culture: tissue distribution, antigenic and cellular requirements. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feizi T. Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease. Gut. 1968 Apr;9(2):193–198. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.2.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAGOV S., KENT G., POPPER H. Relation of splenic and lymph node changes to hypergammaglobulinemia in cirrhosis. AMA Arch Pathol. 1959 Jan;67(1):9–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVENS W. P., Jr, DICKENSHEETS J., BIERLY J. N., EBERHARD T. P. The half-life of I131 labeled normal human gamma globulin in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Immunol. 1954 Oct;73(4):256–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han I. H., Johnson A. G. The mitogenic activity of polyadenylic-polyuridyclic acid complexes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:370–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Wands J. R., Isselbacher K. J. Alteration in suppressor cell activity in chronic active hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1549–1553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. D., Goldstein A. L. The in vitro induction of differentiation of putative human stem cells by thymosin and agents that affect cyclic AMP. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Apr;9(4):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka M., Braun W., Matsumoto T. Cyclic AMP and immune responses. I. Influence of poly A:U and cAMP on antibody formation in vitro. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1027–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrold T., Vilter R. W. HEMATOLOGIC OBSERVATIONS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEPATIC INSUFFICIENCY: STERNAL BONE MARROW MORPHOLOGY AND BONE MARROW PLASMACYTOSIS. J Clin Invest. 1949 Mar;28(2):286–292. doi: 10.1172/JCI102070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. B., Jarnum S., Ranek L., Westergaard H. IgM turnover in chronic liver disease. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(2):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER L. L., BALE W. F. Synthesis of all plasma protein fractions except gamma globulins by the liver; the use of zone electrophoresis and lysine-epsilon-C14 to define the plasma proteins synthesized by the isolated perfused liver. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):125–132. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutchnick M. G., Goldstein A. L. In vitro thymosin effect on T lymphocytes in alcoholic liver disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Mar;12(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortmans H., Wildhirt E., Welcke U. Die diagnostische Bedeutung der Immunglobulinbestimmung bei chronischen Lebererkrankungen. III. Verlaufsbeobachtungen. MMW Munch Med Wochenschr. 1976 Jan 23;118(4):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prytz H., Bjorneboe M., Christoffersen P., Poulsen H., Orskov F. Correlation between hepatic morphology and immunoglobulins and antibodies to Escherichia coli in cirrhosis. Gut. 1977 Jan;18(1):28–32. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J. R., Johnson A. G. Regulation of the immune system by synthetic polynucleotides. I. Characteristics of adjuvant action on antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1191–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulof R. S., Goldstein A. L. Thymosin and the endocrine thymus. Adv Intern Med. 1977;22:121–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., Freni M., Sanchez-Tapias J., de Villiers D., Jain S., Sherlock S. Peripheral blood lymphocyte populations in chronic liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):222–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., McSween R. N., White R. G. Role of the liver in controlling the immunogenicity of commensal bacteria in the gut. Lancet. 1973 Jun 9;1(7815):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolentino P., Astaldi A. Letter: T cells, B cells, and HL-A8 in chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1975 Mar 22;1(7908):690–690. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91797-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps E., Husby G., Williams R. C., Jr, Strickland R. G. Liver disease--a prominent cause of serum IgE elevation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Mar;23(3):444–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. D., Onstad G., Williams R. C., Jr Serum immunoglobulin concentrations in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jul;57(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZLOTNICK A., KARSHAI A. The bone marrow of patients with hypergammaglobulinemia of different etiologies. Isr Med J. 1961 Jan-Feb;20:1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


