Abstract
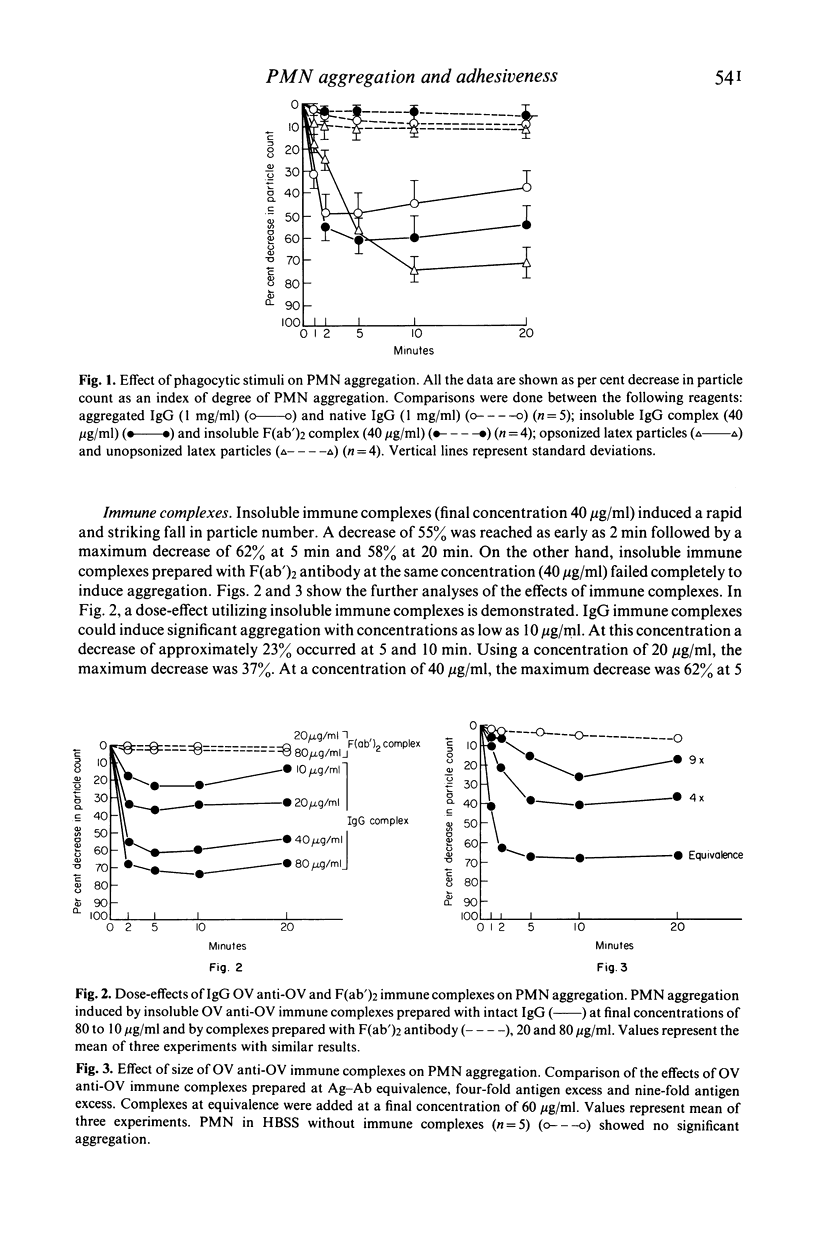
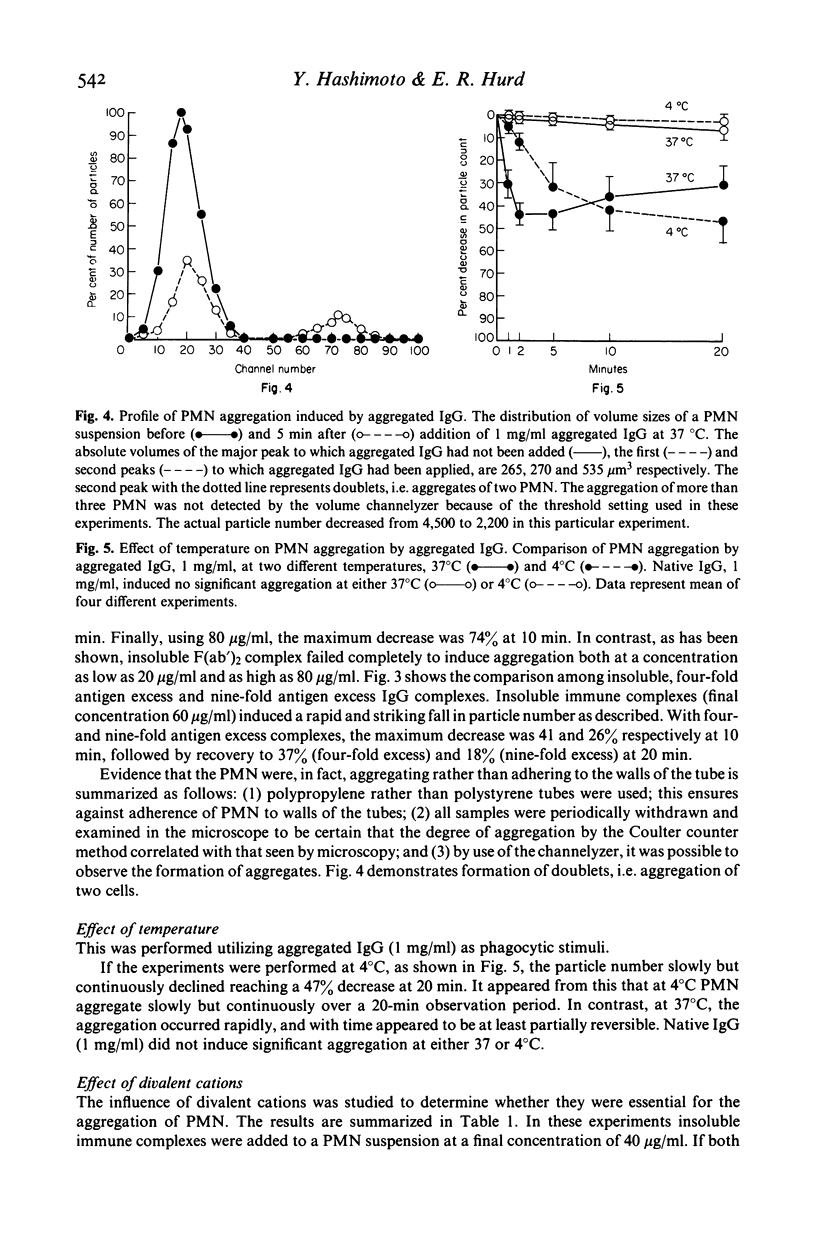
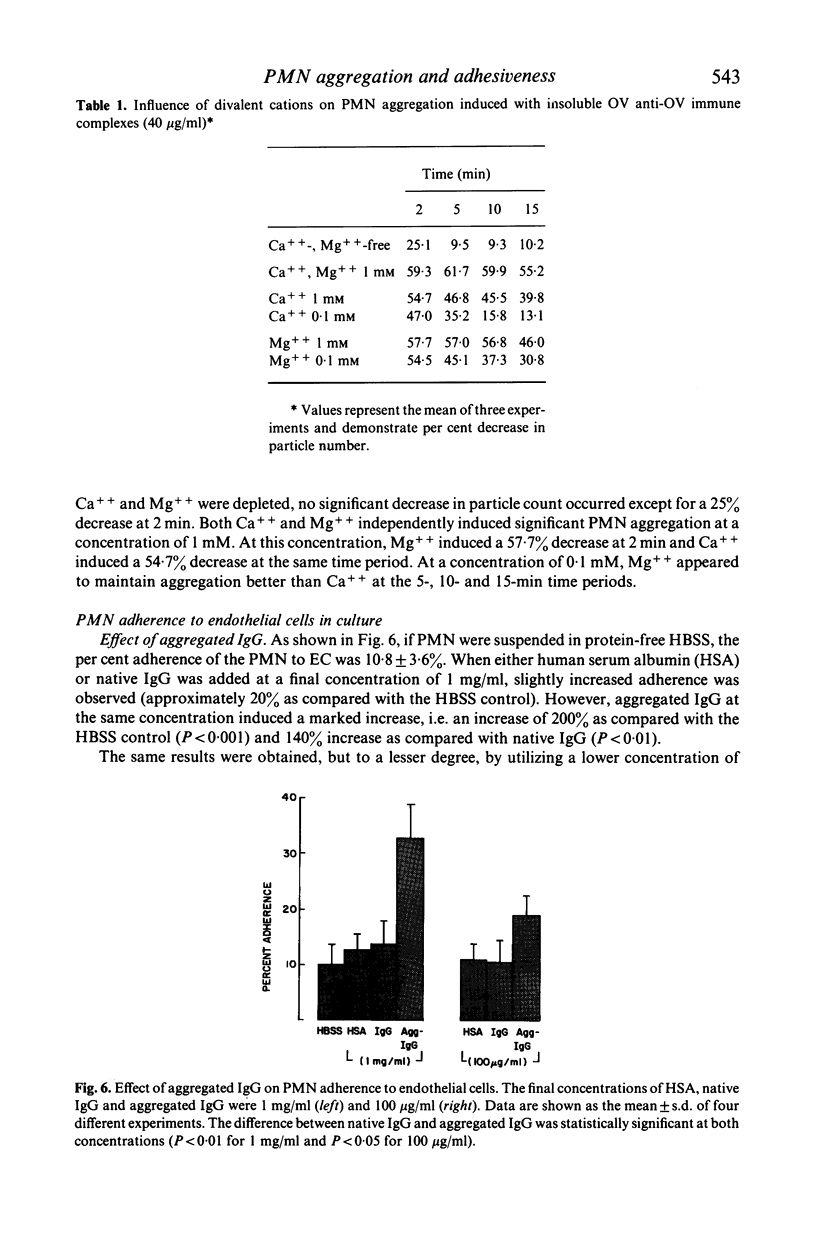
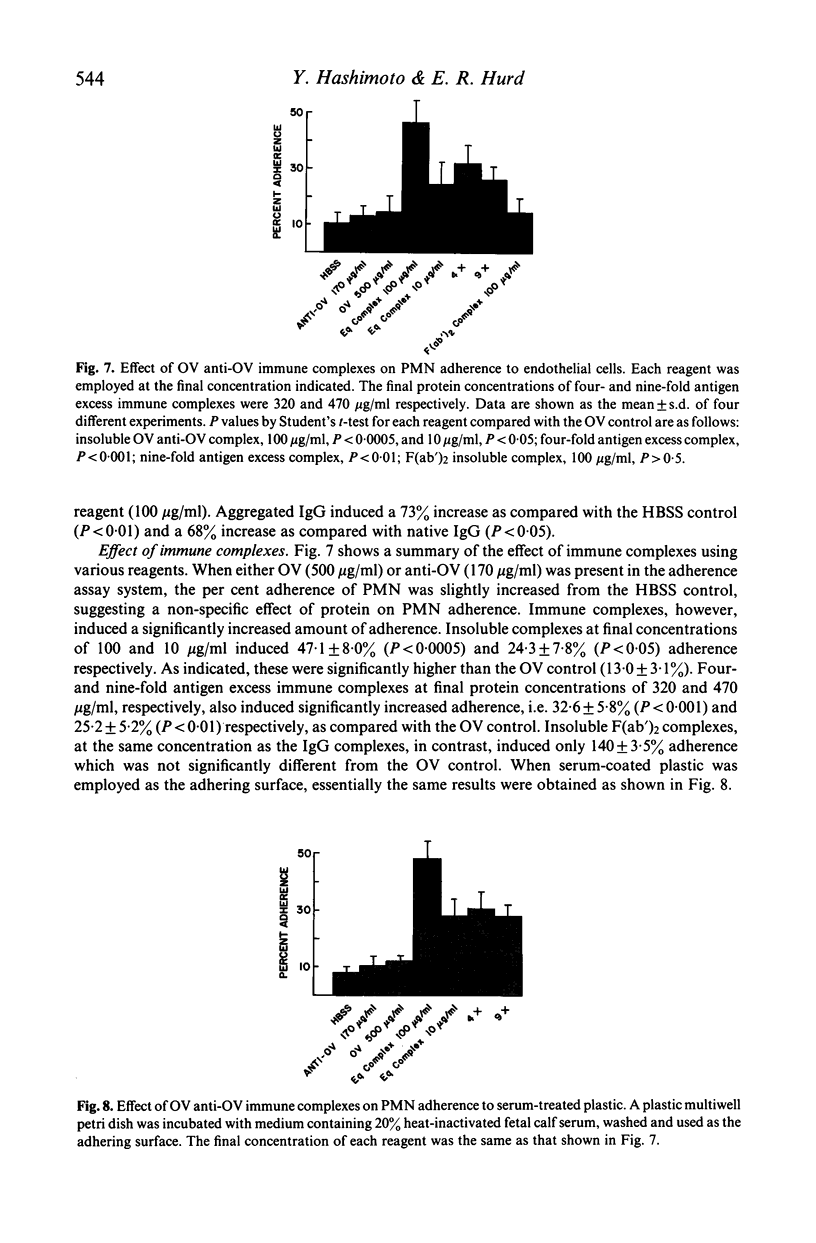
Several types of IgG-dependent phagocytic stimuli independent of complement were investigated for their property to induce human polymorphonuclear neutrophil leucocyte (PMN) aggregation and adherence to human endothelial cells (EC) in culture. A Coulter counter method was employed for the detection of cell aggregation. Aggregated IgG, ovalbumin-anti-ovalbumin (OV anti-OV) immune complexes (both insoluble and soluble) and opsonized latex particles induced a significant degree of PMN aggregation which was detectable as early as 2 min after exposure of PMN to these stimuli. This aggregation was dependent on divalent cations (Ca++, Mg++). The same phagocytic stimuli furthermore significantly increased adherence of PMN to cultured human EC and serum-coated plastic. Controls consisting of native IgG, and OV anti-OV complexes prepared from Fab')2 antibody failed to induce either aggregation or increased adherence of PMN. These data suggest that exposure of PMN to IgG-dependent phagocytic stimuli induces increased adhesiveness of PMN and that interaction between the Fc-receptor of PMN and the Fc-portion of phagocytic stimuli is essential for this effect.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreis M., Hurd E. R., Lospalluto J., Ziff M. Comparison of the presence of immune complexes in Felty's syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Apr;21(3):310–315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswanikumar S., Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. Role of a peptidase in phagocyte chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2439–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L. Some interrelations of neutrophil chemotaxis, lysosomal enzyme secretion, and phagocytosis as revealed by synthetic peptides. Am J Pathol. 1976 Nov;85(2):385–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockenstedt L. K., Goetzl E. J. Constituents of human neutrophils that mediate enhanced adherence to surfaces: purification and identification as acidic proteins of the specific granules. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1372–1381. doi: 10.1172/JCI109801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr J., Dahinden C. Modulating influence of chemotactic factor-induced cell adhesiveness on granulocyte function. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):8–16. doi: 10.1172/JCI109466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr J., Jacob H. S. In vitro granulocyte adherence and in vivo margination: two associated complement-dependent functions. Studies based on the acute neutropenia of filtration leukophoresis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):641–652. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I. Degranulating stimuli decrease the neagative surface charge and increase the adhesiveness of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):298–306. doi: 10.1172/JCI109672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Rosenthal A. S. The regulatory role of divalent cations in human granulocyte chemotaxis. Evidence for an association between calcium exchanges and microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):594–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Wright D. G., Schiffmann E. Role of secretory events in modulating human neutrophil chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1364–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI109257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbeck R. J., Bardana E. J., Kohler P. F., Carr R. I. DNA:anti-DNA complexes: their detection in systemic lupus erythematosus sera. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):789–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI107242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Briggs R. T., Karnovsky M. J. The adhesive interaction between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd E. R., Andreis M., Ziff M. Phagocytosis of immune complexes by polymorphonuclear leucocytes in patients with Felty's syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jun;28(3):413–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd E. R., Jasin H. E., Gilliam J. N. Correlation of disease activity and Clq-binding immune complexes with the neutrophil inclusions which form in the presence of SLE sera. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 May;40(2):283–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackie J. M. The aggregation of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes: effects of antimitotic agents, cyclic nucleotides and methyl xanthines. J Cell Sci. 1974 Oct;16(1):167–180. doi: 10.1242/jcs.16.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackie J. M. The aggregation of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN's): effects of agents which affect the acute inflammatory response and correlation with secretory activity. Inflammation. 1977 Mar;2(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00920870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn W. S., Mukherjee C. Motility of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Roles of hydroxy fatty acids, other lipids, and cations. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jun;91(3):581–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Jelinek J. Receptors for human gamma G globulin on human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2165–2171. doi: 10.1172/JCI106435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Neutrophil aggregation and swelling induced by chemotactic agents. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):232–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scribner D. J., Fahrney D. Neutrophil receptors for IgG and complement: their roles in the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):892–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C., Patrick R. A., Hassett C. Motility and adhesiveness in human neutrophils. Effects of chemotactic factors. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):221–229. doi: 10.1172/JCI109293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. P., Lackie J. M., Wilkinson P. C. The effects of chemotactic factors on the adhesiveness of rabbit neutrophil granulocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Aug;122(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90571-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Brand A., Franklin E. C. Interaction of immunoglobulins with liposomes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):536–543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Korchak H. M., Perez H. D., Smolen J. E., Goldstein I. M., Hoffstein S. T. The secretory code of the neutrophil. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Dec;26(Suppl):687–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


