Abstract
Endogenous immune complexes present in sera from 10 different patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in an active phase were allowed to bind to Raji cells; the ability of intact complement to release the cell-bound complexes from receptors was then examined. Fresh normal human serum, or, alternatively, zymosan-pretreated serum, was added to the complex-bearing Raji cells. Immune complexes remaining bound to Raji cell receptors after increasing times at 37 degrees C were quantitated by addition of 125I-labelled antiglobulin, after removal of serum by washing. In all 10 cases, complement-dependent release was observed. In parallel control studies performed under identical conditions, immune complexes prepared in vitro from bovine serum albumin (BSA) and guinea-pig anti-BSA antibody were used in place of the endogenous SLE complexes. The experimental complexes were released by fresh serum, but not by zymosan-treated serum, but not by zymosan-treated serum, when studied using either 125I-labelled anti-guinea-pig Ig or 125I-labelled complexes alone. The results suggest that intact complement can alter the immune complexes present in SLE sera and influence their interaction with receptors on lymphoid cells. The results further raise the possibility that hypocomplementaemia secondarily due to consumption of complement by immune complexes may contribute to the persistence of the complexes.
Full text
PDF


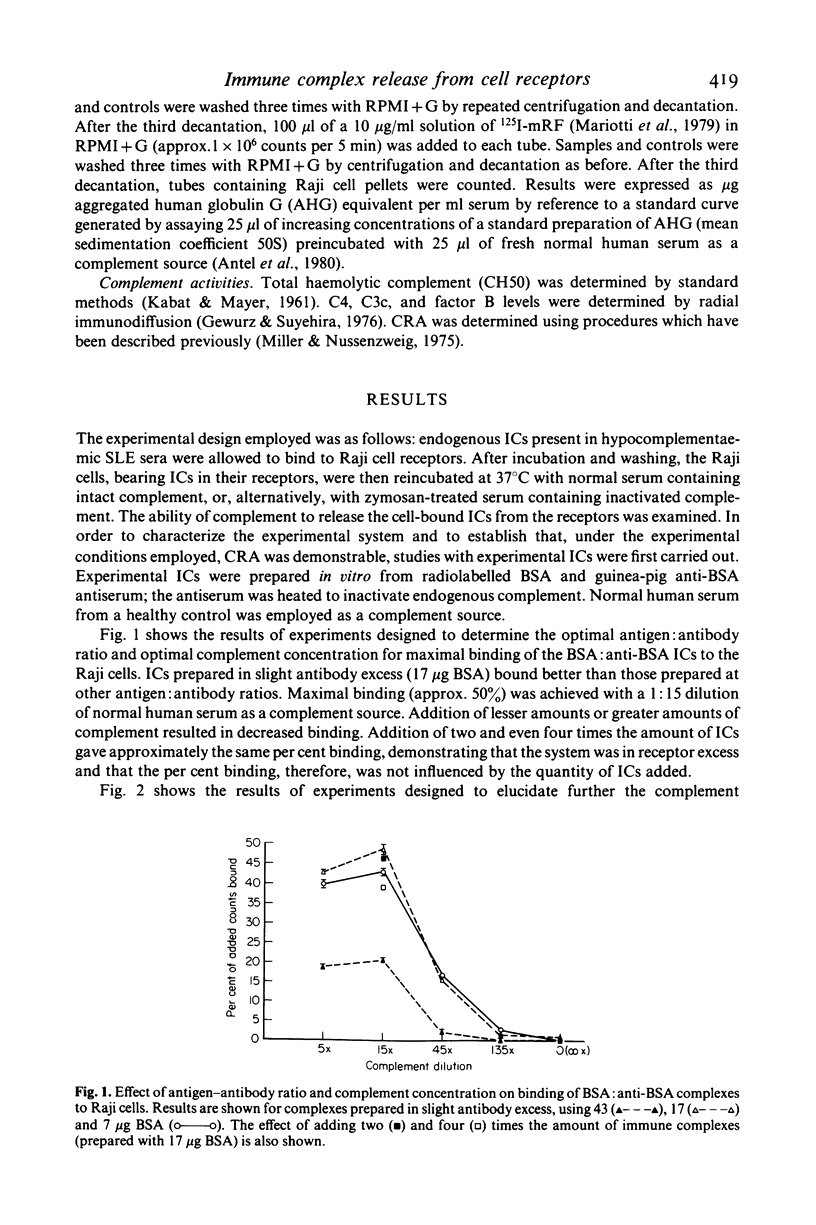
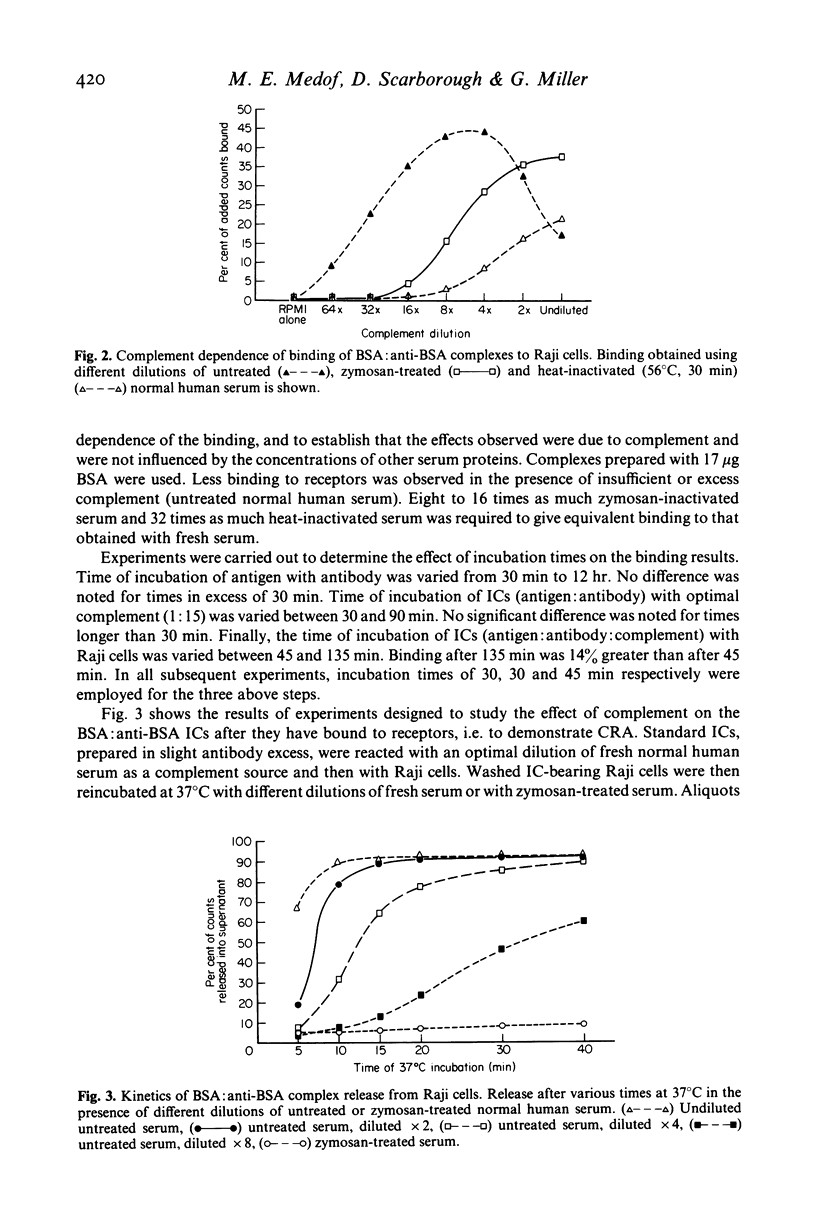
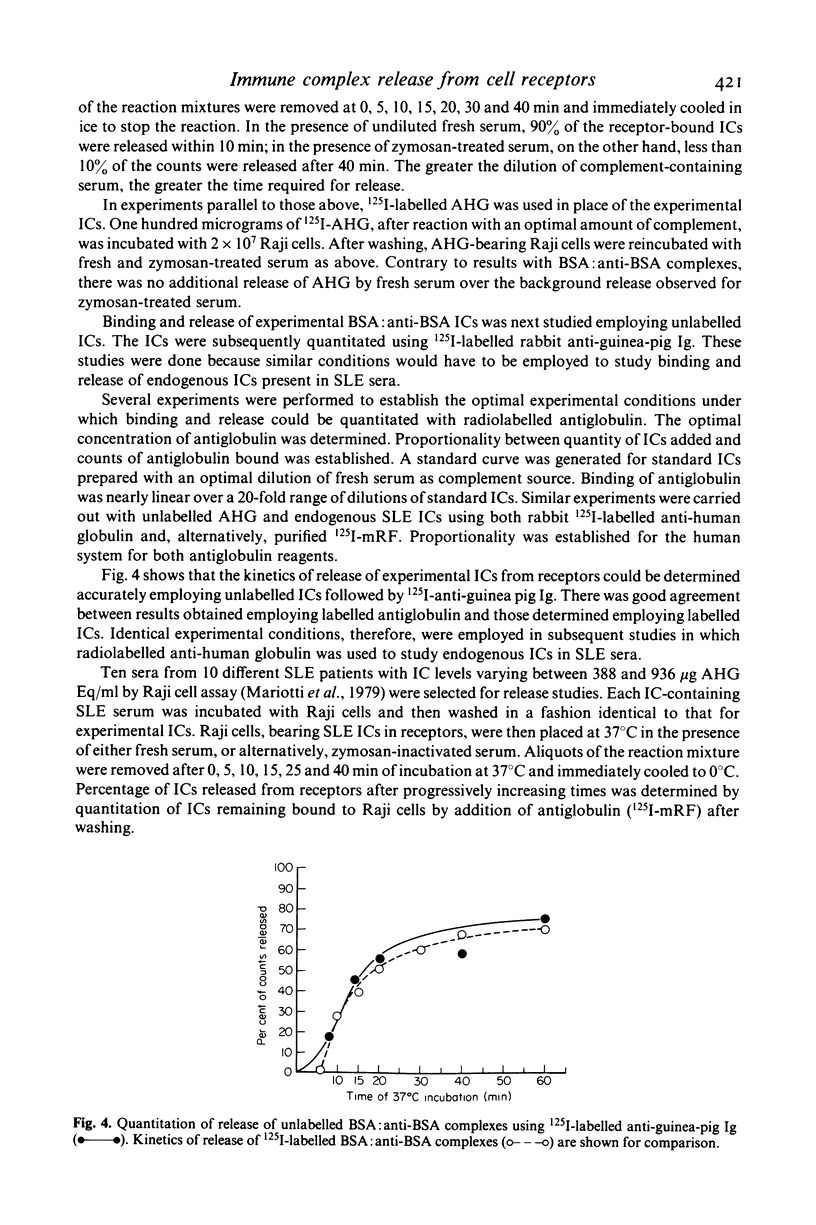
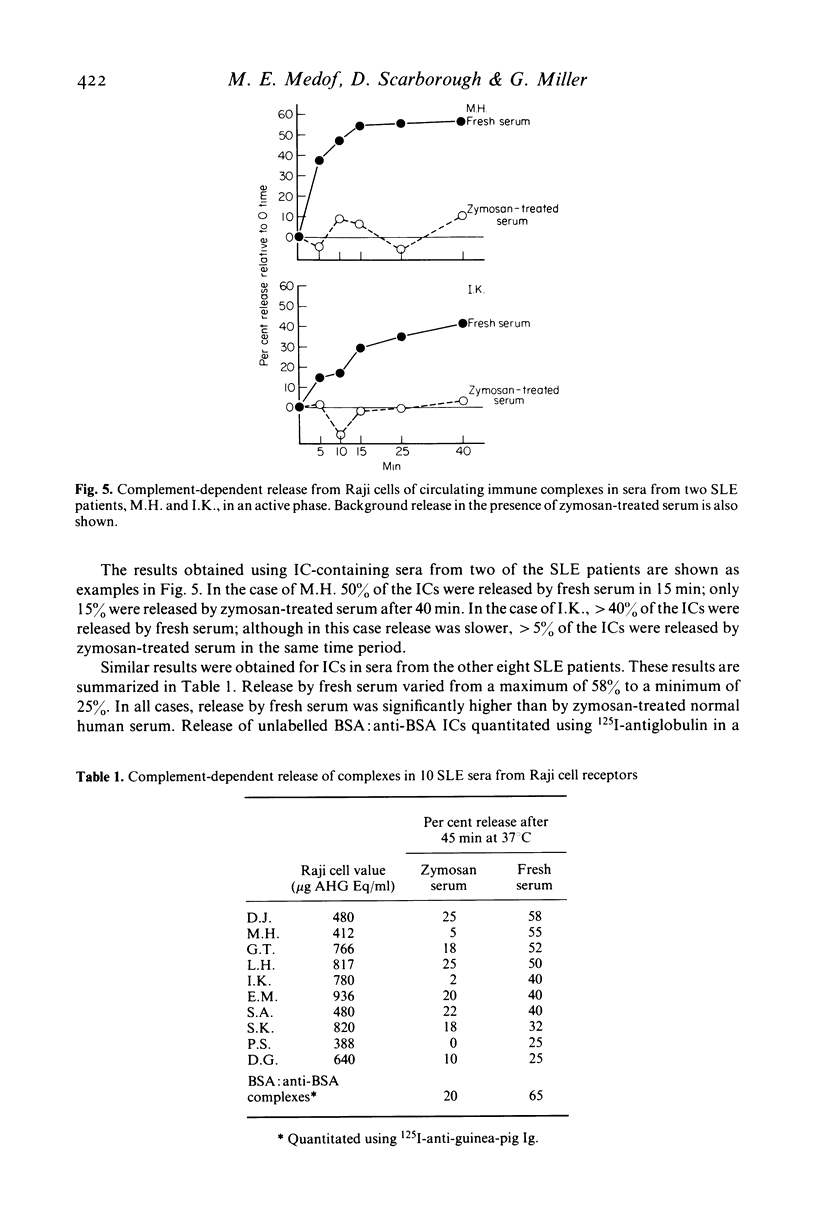



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Precipitin reactions of the C1q component of complement with aggregated gamma-globulin and immune complexes in gel diffusion. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):909–919. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden A., Bianco C., Nussenzweig Mechanism of binding of soluble immune complexes to lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jun;7(3):459–473. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J. D., Medof M. E., Bennett R. M., Sukhupunyaraksa S. Characterization of DNA used to assay sera for anti-DNA antibodies; determination of the specificities of anti-DNA antibodies in SLE and non-SLE rheumatic disease states. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):694–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariotti S., DeGroot L. J., Scarborough D., Medof M. E. Study of circulating immune complexes in thyroid diseases: comparison of Raji cell radioimmunoassay and specific thyroglobulin-antithyroglobulin radioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Nov;49(5):679–686. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-5-679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W. Complement-mediated dissociation of antibody from immobilized antigen. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):488–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Nussenzweig V. A new complement function: solubilization of antigen-antibody aggregates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):418–422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Nussenzweig V. Complement as a regulator of interactions between immune complexes and cell membranes. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):464–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Saluk P. H., Nussenzweig V. Complement-dependent release of immune complexes from the lymphocyte membrane. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):495–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nydegger U. E., Lambert P. H., Gerber H., Miescher P. A. Circulating immune complexes in the serum in systemic lupus erythematosus and in carriers of hepatitis B antigen. Quantitation by binding to radiolabeled C1q. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin M. L., Gelfand M. C., Nagle R. B., Carlo J. R., Green I., Frank M. M. Localization of receptors for activated complement on visceral epithelial cells of the human renal glomerulus. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):869–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Czop J., Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V. Mechanism of solubilization of immune aggregates by complement. Implications for immunopathology. Transplant Rev. 1976;32:121–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tack B. F., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement: assembly of a factor B-dependent C3-convertase on the immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):86–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tack B. F., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement: assembly of a factor B-dependent C3-convertase on the immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):86–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Brade V., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement. The role of the classical pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):349–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI109135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J., Bokisch V. A. Binding of soluble immune complexes to human lymphoblastoid cells. I. Characterization of receptors for IgG Fc and complement and description of the binding mechanism. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):877–894. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Bokisch V. A., Dixon F. J. Binding of soluble immune complexes to human lymphoblastoid cells. II. Use of Raji cells to detect circulating immune complexes in animal and human sera. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1230–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


