Abstract
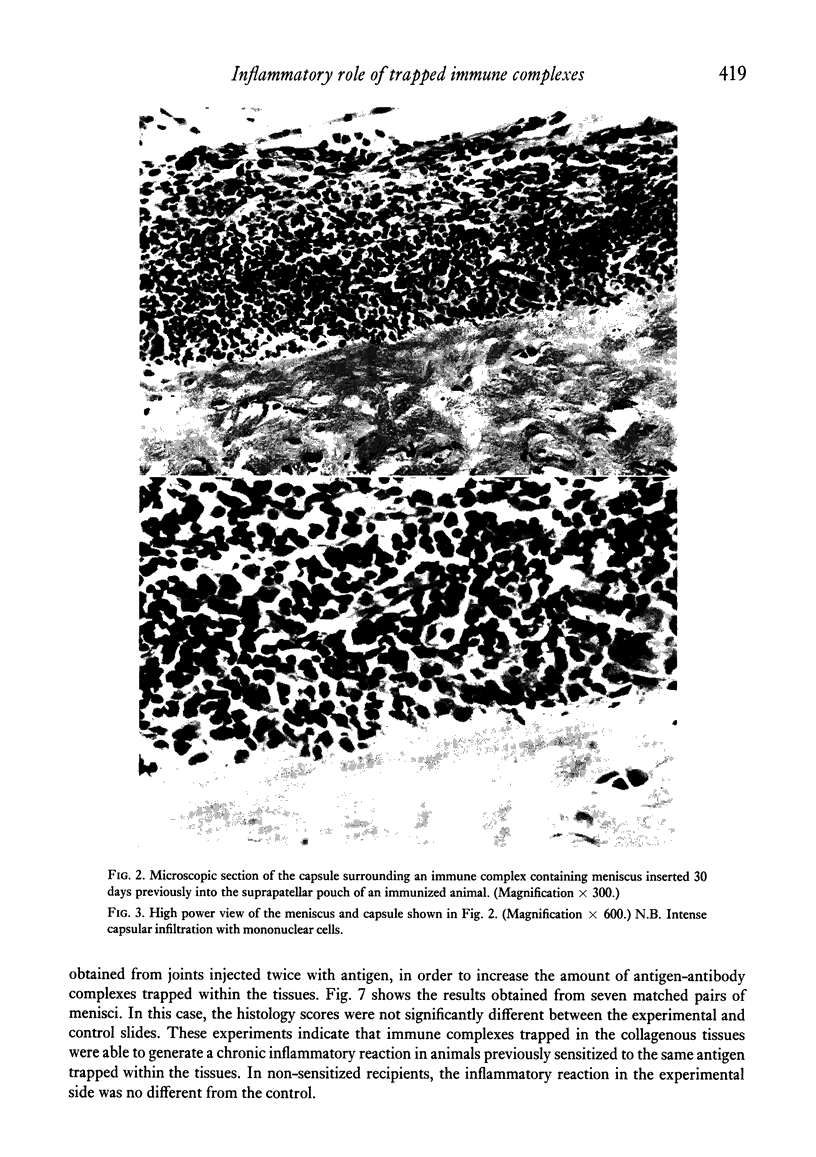
The inflammatory role of immune complexes trapped in joint collagenous tissues has been investigated. Joint collagenous tissues obtained from rabbits with antigen-induced arthritis generated mediators of acute inflammation when incubated with fresh normal rabbit serum as a source of complement. The role of trapped immune complexes in chronic inflammation was also studied by the surgical insertion of menisci, obtained from arthritic and control joints, into the suprapatellar pouches of previously immunized or naive recipient animals. It was shown that when immune complex containing menisci were inserted into immune rabbits, a chronic inflammatory capsule developed around the donor tissue, reminiscent of the inflammatory pannus seen in rheumatoid cartilage. Normal menisci and immune complex containing menisci inserted in naive animals developed capsules rich in fibroplasts and collagen fibres. Since we have previously shown the presence of immune complexes in the great majority of joint collagenous tissues obtained from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, our results suggest that these complexes may play a role in the formation of pannus, which constitutes a major mechanism responsible for cartilage destruction.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark R. A., Frank M. M., Kimball H. R. Generation of chemotactic factors in guinea pig serum via activation of the classical and alternate complement pathways. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Apr;1(3):414–426. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consden R., Doble A., Glynn L. E., Nind A. P. Production of a chronic arthritis with ovalbumin. Its retention in the rabbit knee joint. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 May;30(3):307–315. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Hurd E. R., Jasin H. E., Bienenstock J., Ziff M. Identification of immunoglobulins and complement in rheumatoid articular collagenous tissues. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):541–551. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Hurd E. R., Ziff M., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. II. Preferential localization of antigen-antibody complexes to collagenous tissues. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. I. The role of antigen on the local immune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):327–337. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elling P., Graudal H., Faber V. Granulocyte-specific antinuclear factors in serum and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 May;27(3):225–233. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elves M. W. A study of the transplantation antigens on chondrocytes from articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974 Feb;56(1):178–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A., Glynn L. E. Persistence of antigen in nonarthritic joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Oct;34(5):431–437. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn L. E. Aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis with regard to its chronicity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Sep;28(5 Suppl):3–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn L. E. The chronicity of inflammation and its significance in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Mar;27(2):105–121. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Smiley J. D., Ziff M. Electron microscopic demonstration of immunoglobulin deposition in rheumatoid cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):563–576. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E. Mechanism of trapping of immune complexes in joint collagenous tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Dec;22(3):473–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane A. S. IN VIVO BEHAVIOR OF I-FIBRINOGEN. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42(3):346–361. doi: 10.1172/JCI104721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menard H. A., Dion J. Experimental immune arthritis: host factors. J Rheumatol. 1975 Dec;2(4):373–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel J., Steffen C., Kolarz G., Eberal G., Frank O., Thumb N. Demonstration of antibodies to collagen and of collagen-anticollagen immune complexes in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluids. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Oct;35(5):446–450. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.5.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Zvaifler N. J. Complement-derived leukotactic factors in inflammatory synovial fluids of humans. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):606–616. doi: 10.1172/JCI106531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]