Abstract
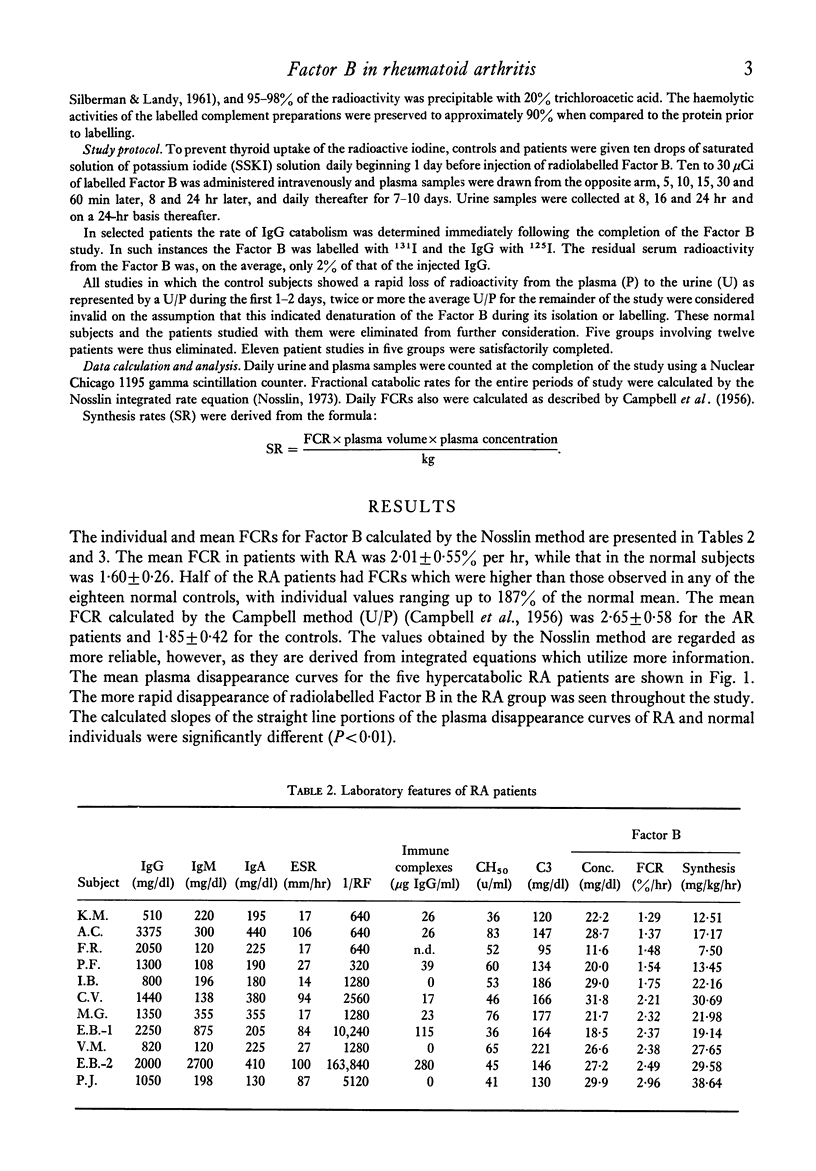
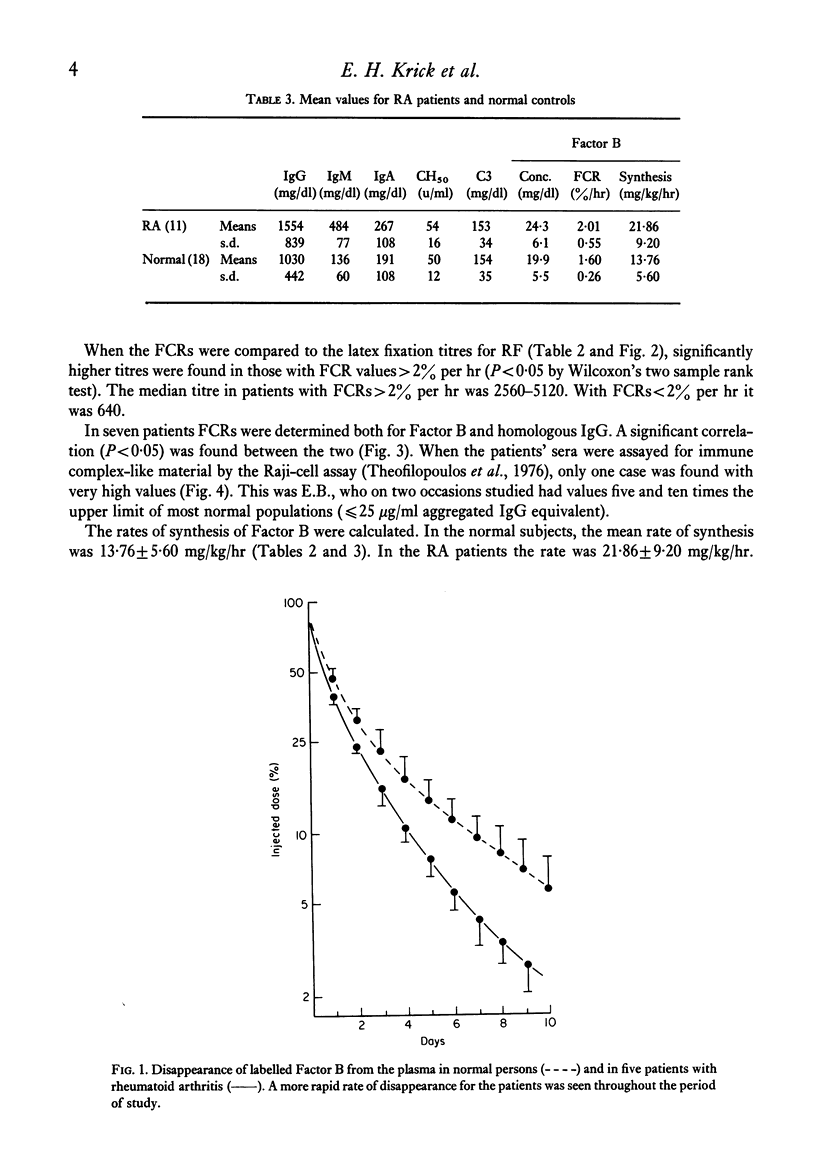
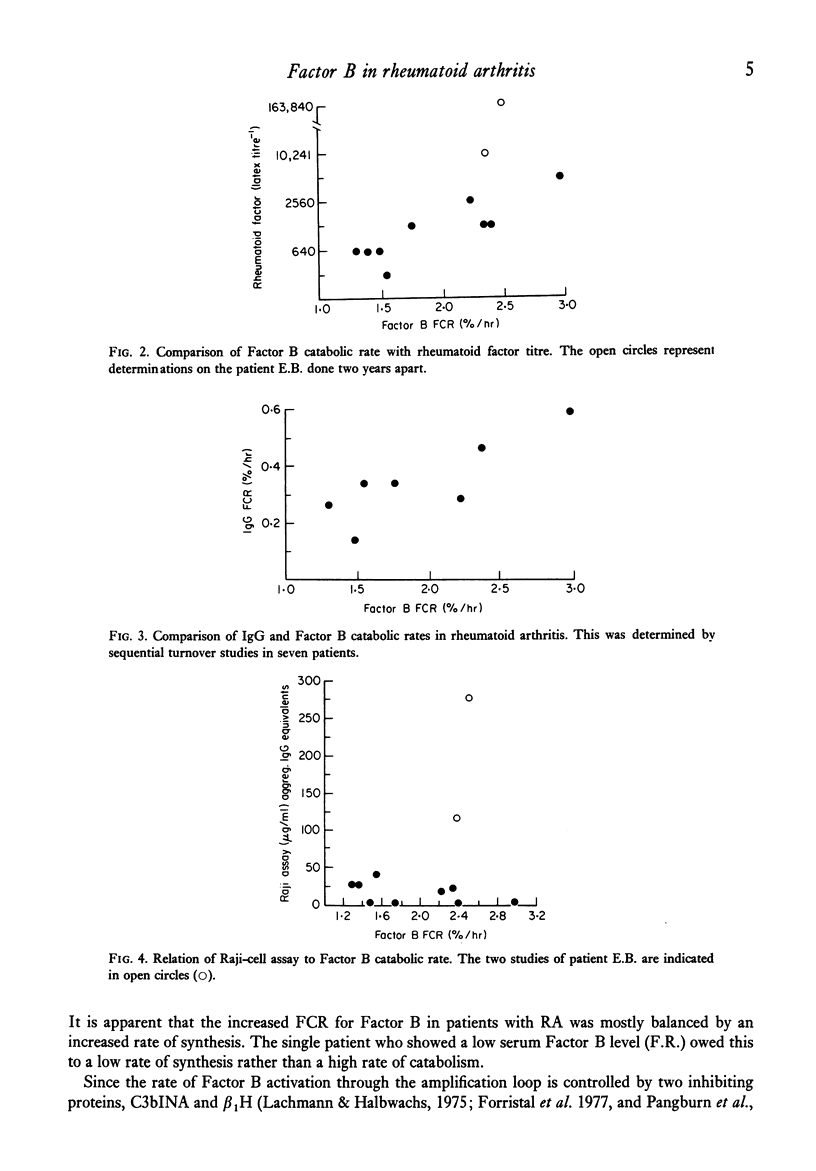
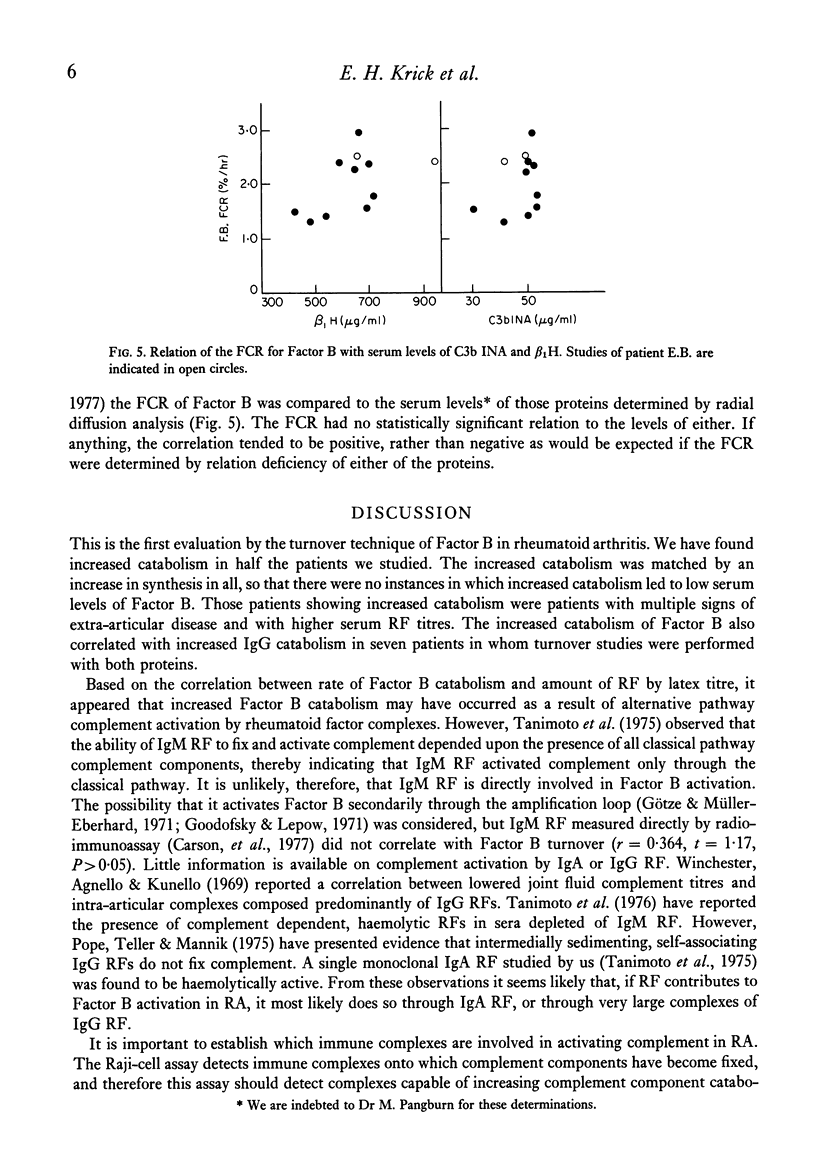
An increased rate of catabolism of radio-iodinated Factor B has been shown in five out of ten patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Serum levels of Factor B were normal, the increased catabolism being matched by increased synthesis. The patients showing high catabolic rates had more manifestations of extra articular disease than did those with normal catabolic rates and they had higher rheumatoid factor titres. In seven patients, the catabolic rate for Factor B correlated significantly with the rate of IgG catabolism. In this series, the Raji-cell assay for immune complex-like material was in the normal or near normal range in all but one patient.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Alper CA, Rosen FS: Studies of the in vivo behavior of human C'3 in normal subjects and patients. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):2021–2034. doi: 10.1172/JCI105691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyave C. M., Bhat K. N., Crown R. Activation of the alternative pathway of the complement system by radiographic contrast media. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1866–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Cathcart E. S., Cohen A. S. Studies of immune deposits in synovial membranes and corresponding synovial fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Oct;72(4):631–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton M. C., Schur P. H. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. II. Intracytoplasmic inclusions of immunoglobulins and complement. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Jan-Feb;14(1):87–95. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL R. M., CUTHBERTSON D. P., MATTHEWS C. M., MCFARLANE A. S. Behaviour of 14C- and 131I-labelled plasma proteins in the rat. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1956 Jul;1(1-2):66–84. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(56)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Lawrance S., Catalano M. A., Vaughan J. H., Abraham G. Radioimmunoassay of IgG and IgM rheumatoid factors reacting with human IgG. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):295–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. A., Krick E. H., De Heer D. H., Nakamura R. M., Theofilopoulos A. N., Vaughan J. H. Metabolism of autologous and homologous IgG in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):313–322. doi: 10.1172/JCI108779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn D. L., McDuffie F. C., Dyck P. J. Immunopathologic study of sural nerves in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):135–143. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forristal J., Iitaka K., Vallota E. H., West C. D. Correlations between serum factor B and C3b inactivator levels in normal subjects and in patients with infections, nephrosis and hypocomplementaemic glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Apr;28(1):61–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay R., Micheli A., Fallet G. H. Behaviour of synovial complement C3 and C4 components in inflammatory and degenerative joint diseases, before and after synoviorthesis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Apr;34(2):166–170. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroud J. P., Willoughby D. A. The interrelations of complement and a prostaglandin-like substance in acute inflammation. J Pathol. 1970 Jul;101(3):241–249. doi: 10.1002/path.1711010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodkofsky I., Lepow I. H. Functional relationship of factor B in the properdin system to C3 proactivator of human serum. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1200–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEDBERG H. STUDIES ON THE DEPRESSED HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT ACTIVITY OF SYNOVIAL FLUID IN ADULT RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1963;9:165–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLANDER J. L., MCCARTY D. J., Jr, ASTORGA G., CASTRO-MURILLO E. STUDIES ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID JOINT INFLAMMATION. I. THE "R.A. CELL" AND A WORKING HYPOTHESIS. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Feb;62:271–280. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannestad K. Rheumatoid factors reacting with autologous native gamma-G-globulin and joint fluid gamma-G aggregates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Sep;3(7):671–690. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEENE W. R., SILBERMAN H. R., LANDY M. Observations on the pyrogenic response and its application to the bioassay of endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:295–301. doi: 10.1172/JCI104256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Halbwachs L. The influence of C3b inactivator (KAF) concentration on the ability of serum to support complement activation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jul;21(1):109–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongan E. S., Cass R. M., Jacox R. F., Vaughen J. H. A study of the relation of seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis to each other and to necrotizing vasculitis. Am J Med. 1969 Jul;47(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osler A. G., Sandberg A. L. Alternate complement pathways. Prog Allergy. 1973;17(0):51–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEKIN T. J., Jr, ZVAIFLER N. J. HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT IN SYNOVIAL FLUID. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1372–1382. doi: 10.1172/JCI105013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERNIS B., BALLABIO C. B., CHIAPPINO G. PRESENZA DEL FATTORE REUMATOIDE NELLE LESIONI VASCOLARI IN CASI DI ARTRITE REUMATOIDE AGGRAVATA (MALIGNA). STUDIO CON ANTICORPI FLUORESCENTI. Reumatismo. 1963 May-Jun;15:187–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Human complement C3b inactivator: isolation, characterization, and demonstration of an absolute requirement for the serum protein beta1H for cleavage of C3b and C4b in solution. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltier A. P., de Sèze S. Pathogénie de la baisse du complément dans le liquide synovial au cours de la polyarthrite rhumatoïde et du lupus érythémateux disséminé. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1971 Jan;38(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., Teller D. C., Mannik M. Intermediate complexes formed by self-association of IgG-rheumatoid factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:82–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman W. S., Williams R. C., Jr, Bilka P. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Immunofluorescent localization of the third and the fourth component of complement in synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):141–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Depressed synovial fluid levels of properdin and properdin factor B in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jul-Aug;18(4):289–295. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubart A. F., Ewald R. W., Schroeder W. C., Rothschild H. J., Bhatavadekar D. N., Pullen P. K. Serum complement levels in rheumatoid arthritis. A longitudinal study of 43 cases with correlation of clinical and serological data including rheumatoid factor and thermolabile inhibitor of the F-II L.P. test. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Sep;24(5):439–450. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.5.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Cooper N. R., Johnson J. S., Vaughan J. H. Complement fixation by rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):437–445. doi: 10.1172/JCI107949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Moritoh T., Azuma T., Horiuchi Y. Detection of IgG rheumatoid factor by concanavalin A treatment and complement fixation with IgG rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Jun;35(3):240–245. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.3.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN J. H., BAYLES T. B., FAVOUR C. B. Serum complement in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med Sci. 1951 Aug;222(2):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallota E. H., Götze O., Spiegelberg H. L., Forristal J., West C. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A serum factor in chronic hypocomplementemic hephritis distinct from immunoglobulins and activating the alternate pathway of complement. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1249–1261. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Jacox R. J., Noell P. Relation of intracytoplasmic inclusions in joint fluid leukocytes to anti-gamma-G globulins. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Apr;11(2):135–144. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versey J. M., Hobbs J. R., Holt P. J. Complement metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. I. Longitudinal studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Nov;32(6):557–564. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.6.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., Jr, LAW D. H., 4th Serum complement in connective tissue disorders. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Aug;52(2):273–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein A., Peters K., Brown D., Bluestone R. Metabolism of the third component of complement (C3) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jan-Feb;15(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. R., Arroyave C. M., Nakamura R. M., Vaughan J. H., Tan E. M. Activation of the alternative complement pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):11–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. The joint-fluid gammaG-globulin complexes and their relationship to intraarticular complement dimunition. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Dec 10;168(1):195–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb43108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Rheumatoid synovitis. An extravascular immune complex disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 May-Jun;17(3):297–305. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


