Abstract
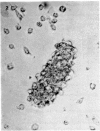
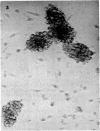
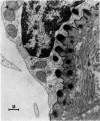
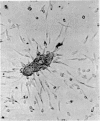
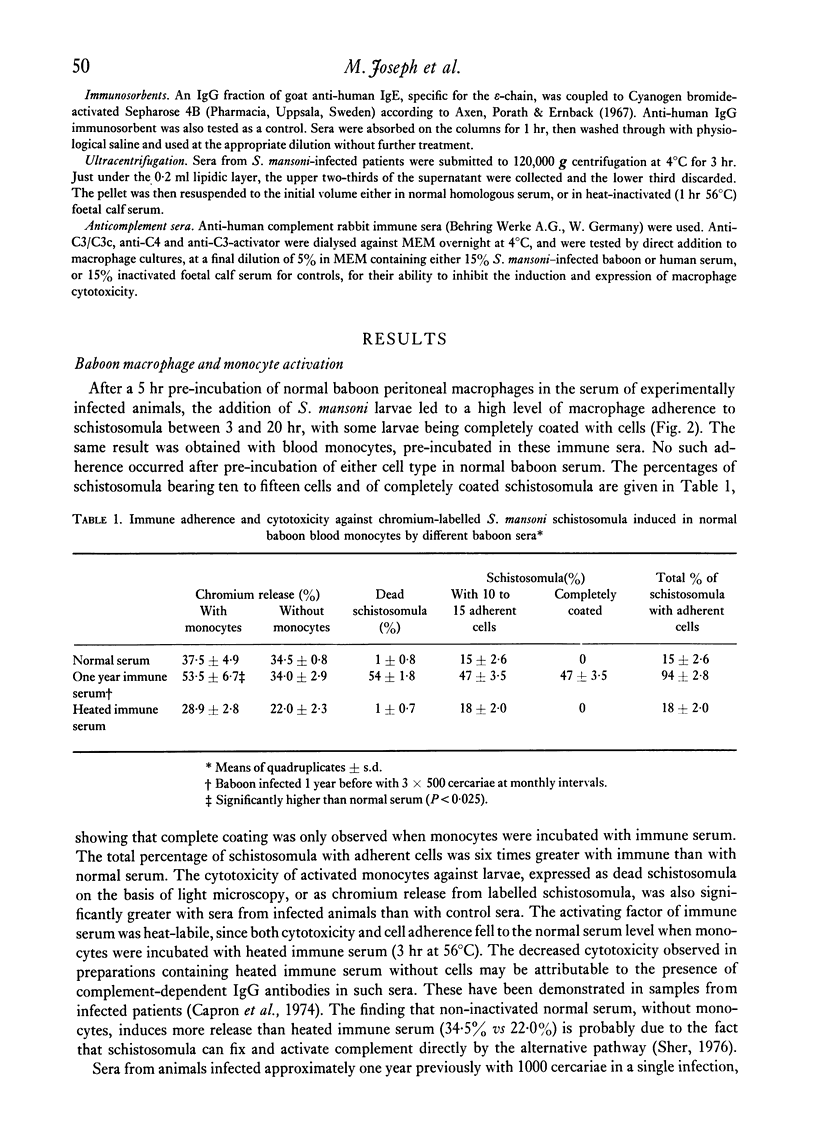
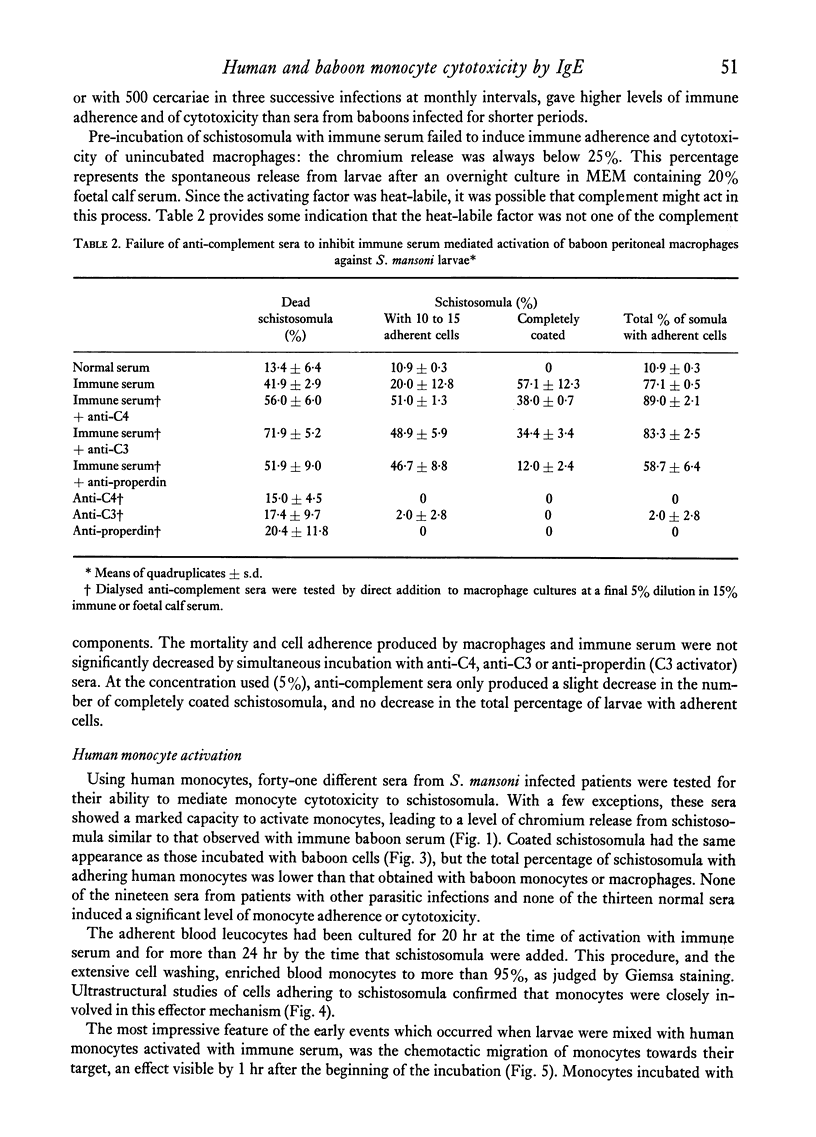
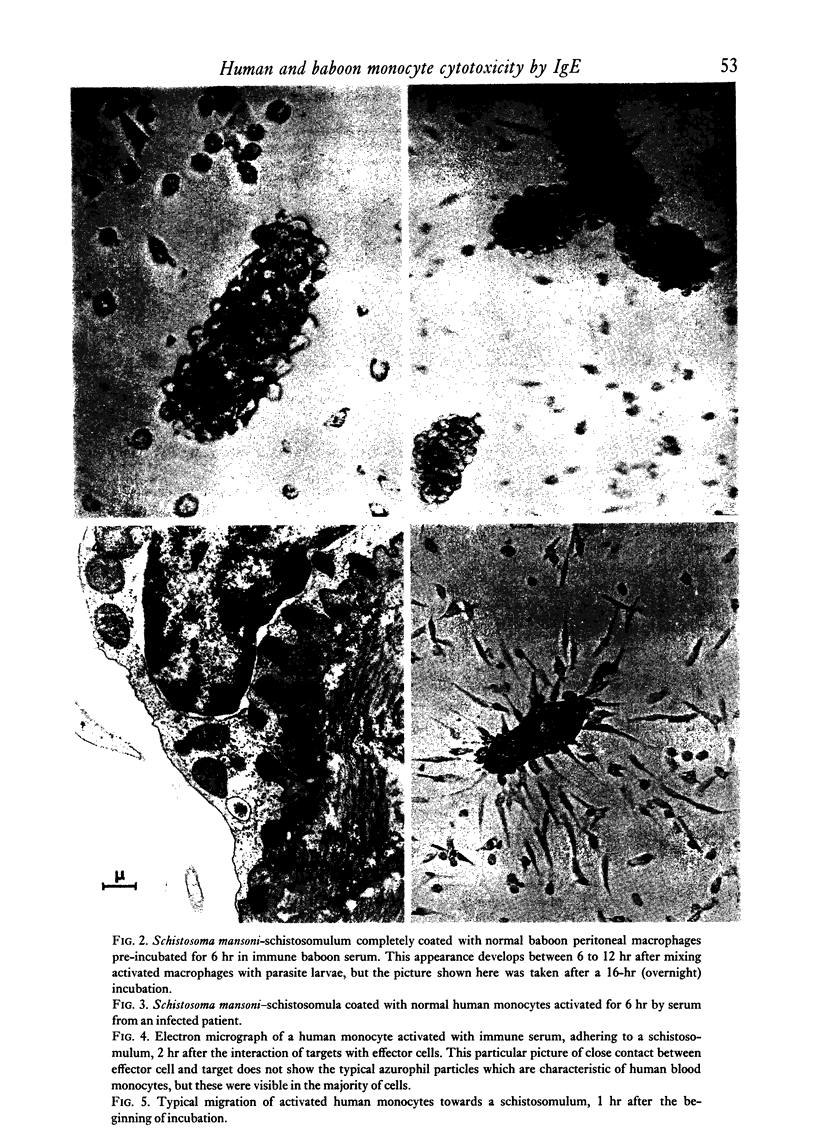
Normal human blood monocytes, pre-incubated at 37 degrees C with sera from patients infected with Schistosoma mansoni, strongly adhered to S. mansoni schistosomula in vitro, whereas no significant adherence was induced by sera from uninfected individuals. Comparable adherence occurred with normal baboon blood monocytes or peritoneal macrophages when these cells were incubated with sera from S. mansoni-infected baboons. Adherence of macrophages to schistosomula was associated with damage to the larvae, as estimated by a 51Cr release technique. Neither adherence nor cytotoxicity was induced by pre-incubation of the schistosomula, instead of the monocytes, with immune serum. The relevant factor in immune serum was heat-labile, but was not a complement component. Absorption and ultracentrifugation experiments showed that immune complexes, containing S. mansoni-specific IgE antibody and soluble parasite antigens, produced monocyte or macrophage adherence and cytotoxicity. Similar observations have been reported previously in the rat model. Since the production of large amounts of IgE is a predominant feature of schistosome infections in man and experimental animals, it is possible that this new mode of mononuclear phagocyte activation could act as an immune effector mechanism against S. mansoni.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V., Mahmoud A. A., Sher A., Rees P. H. Eosinophils as mediators of antibody-dependent damage to schistosomula. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):727–729. doi: 10.1038/256727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V., Taylor R. Schistosoma mansoni in baboons. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated damage to 51Cr-labelled schistosomula. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):95–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Dessaint J. P., Capron M., Bazin H. Specific IgE antibodies in immune adherence of normal macrophages to Schistosoma mansoni schistosomules. Nature. 1975 Feb 6;253(5491):474–475. doi: 10.1038/253474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Dessaint J. P., Joseph M., Rousseaux R., Capron M., Bazin H. Interaction between IgE complexes and macrophages in the rat: a new mechanism of macrophage activation. Eur J Immunol. 1977 May;7(5):315–322. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Capron A., Torpier G., Bazin H., Bout D., Joseph M. Eosinophil-dependent cytotoxicity in rat schistosomiasis. Involvement of IgG2a antibody and role of mast cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. A., Smithers S. R. The effects of immune rhesus monkey serum on schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni during cultivation in vitro. Int J Parasitol. 1972 Mar;2(1):79–98. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(72)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. A., Wistar R., Murrell K. D. Combined in vitro effects of rat antibody and neutrophilic leukocytes on schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 May;23(3):420–428. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER G. W., 3rd, CRANDALL R. B., ZICKAFOOSE D. E., PURVIS Q. B. Studies on schistosomiasis. 18. Some factors affecting resistance to Schistosoma mansoni infections in albino mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1962 Jan;11:17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph M., Dessaint J. P., Capron A. Characteristics of macrophage cytotoxicity induced by IgE immune complexes. Cell Immunol. 1977 Dec;34(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Geiger S. J., Botero B., Kagan I. G. Schistosoma mansoni infection in the rat. II. Effects of immunosuppression and serum and cell transfer on innate and acquired immunity. J Parasitol. 1970 Dec;56(6):1066–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud A. A., Warren K. S., Peters P. A. A role for the eosinophil in acquired resistance to Schistosoma mansoni infection as determined by antieosinophil serum. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):805–813. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. A., Smithers S. R. Schistosoma mansoni in the rat: the adherence of macrophages to schistosomula in vitro after sensitization with immune serum. Int J Parasitol. 1977 Aug;7(4):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(77)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A. Complement-dependent adherence of mast cells to schistosomula. Nature. 1976 Sep 23;263(5575):334–336. doi: 10.1038/263334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithers S. R., Terry R. J. Naturally acquired resistance to experimental infections of Schistosoma mansoni in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Parasitology. 1965 Nov;55(4):701–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithers S. R., Terry R. J. The immunology of schistosomiasis. Adv Parasitol. 1969;7:41–93. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. F., Butterworth A. E., Houba V. Schistosoma mansoni in the baboon (Papio anubis): parasitological responses of Kenyan baboons to different exposures of a local parasite strain. Parasitology. 1976 Dec;73(3):239–252. doi: 10.1017/s003118200004693x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]