Abstract
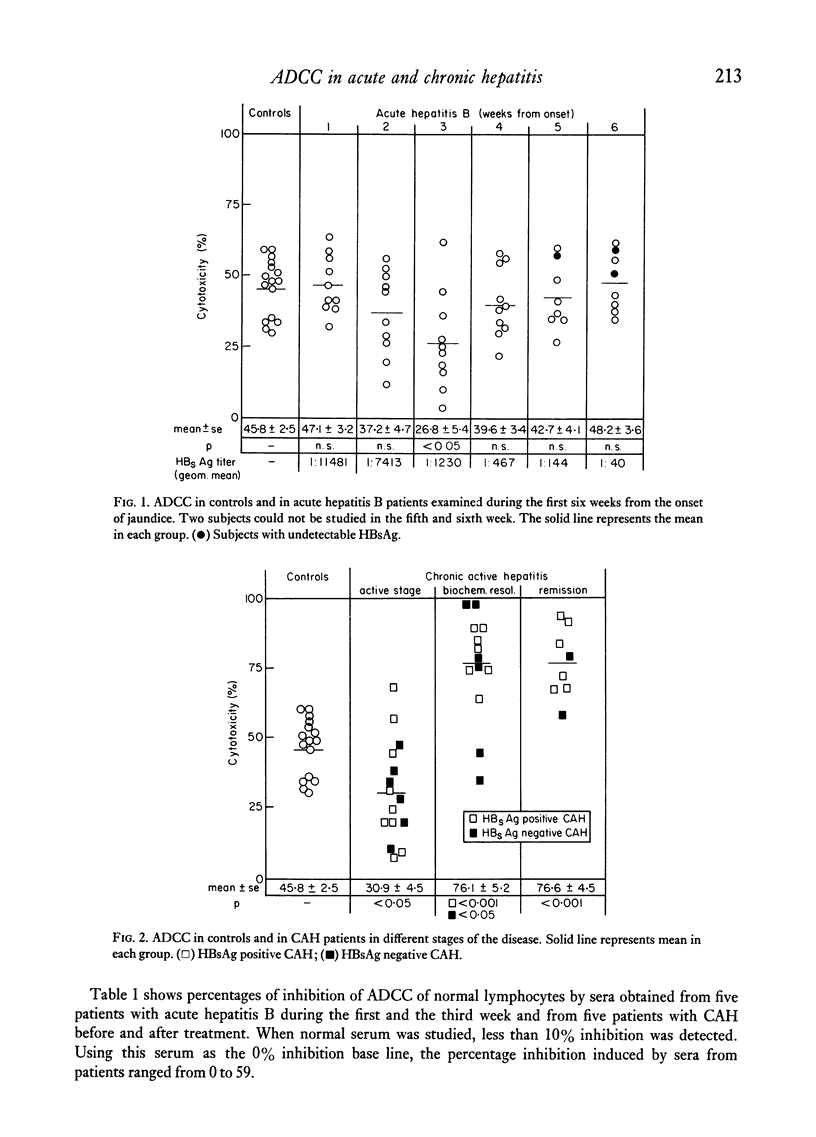
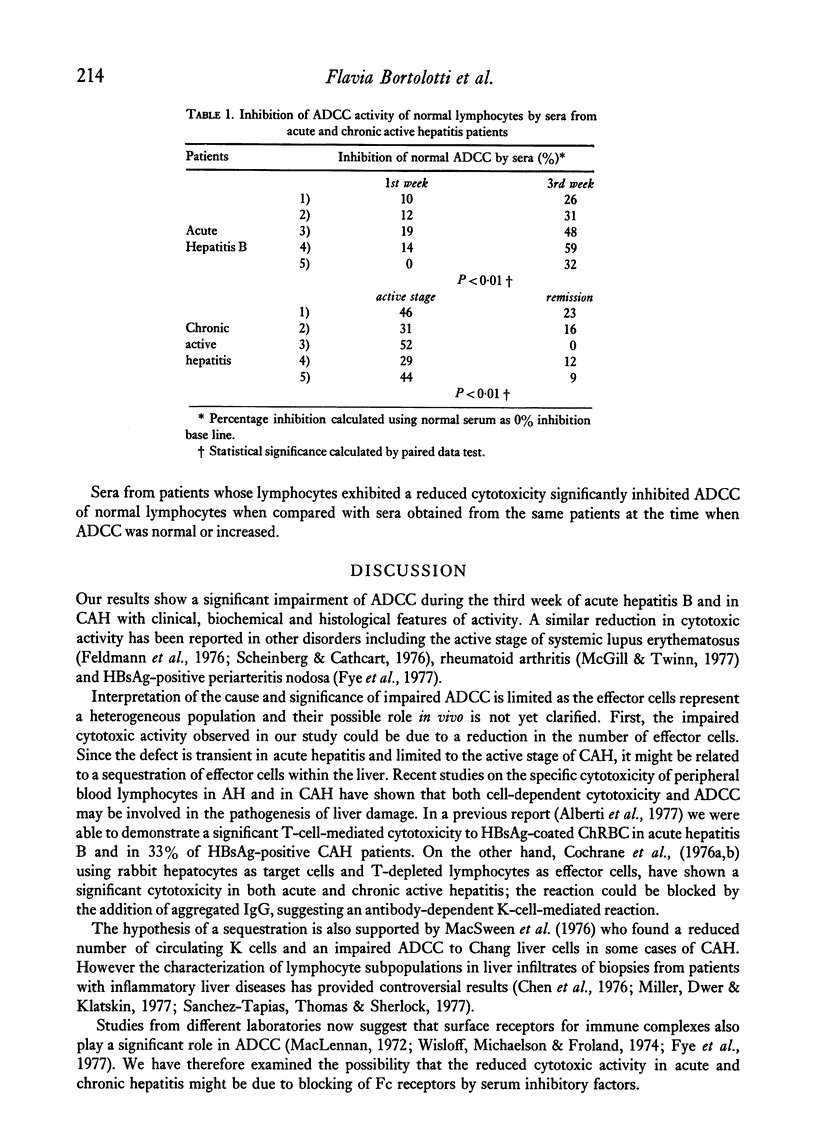
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of peripheral blood lymphocytes against chicken red blood cells (ChRBC) in the presence of specific antiserum has been studied in normal subjects and in patients with acute hepatitis B and with chronic active hepatitis (CAH). ADCC was significantly reduced in patients with acute hepatitis B studied three weeks after the onset of jaundice and in patients with CAH showing clinical, biochemical and histological features of activity. On the other hand, lymphocytes from patients with CAH in histological remission or in clinical and biochemical resolution, showed a significantly increased cytotoxicity. The effect of serum factors on ADCC of normal lymphocytes was investigated using serial serum samples from five patients with acute hepatitis B and five with CAH. Our data suggest that serum factors may be responsible for the impairment of ADCC in our patients, although other mechanisms may also be implied. Sera obtained at the time when ADCC of patients' lymphocytes was reduced, significantly inhibited ADCC of normal lymphocytes when compared with sera obtained at the time when ADCC of patients' lymphocytes was normal or increased. In all cases with CAH, the disappearance or reduction of inhibiting activity correlated with histological remission. In patients with CAH the study of serum factors inhibiting ADCC of normal lymphocytes may be a useful parameter in assessing disease activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti A., Realdi G., Bortolotti F., Rigoli A. M. T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity to HBsAg-coated target cells in hepatitis b virus infection. Gut. 1977 Dec;18(12):1004–1009. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.12.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Madalinski K., Krawczynski K., Skwarska H., Nowoslawski A. Australia antigen immune complexes in patients with different forms of hepatitis. J Infect Dis. 1971 Mar;123(3):251–256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.3.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Irvine W. J., Davidson N. M., Wu F. T, B and K cells in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Smith A., Thomson A. D., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Autoimmune reaction to a liver specific membrane antigen during acute viral hepatitis. Gut. 1976 Sep;17(9):714–718. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.9.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Thomsom A. D., Eddleston A. L., Wiiliams R. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated (K cell) cytotoxicity against isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):441–444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groote J., Desmet V. J., Gedigk P., Korb G., Popper H., Poulsen H., Scheuer P. J., Schmid M., Thaler H., Uehlinger E. A classification of chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1968 Sep 14;2(7568):626–628. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90710-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann J. L., Becker M. J., Moutsopoulos H., Fye K., Blackman M., Epstein W. V., Talal N. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in selected autoimmune diseases. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):173–179. doi: 10.1172/JCI108447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fye K. H., Becker M. J., Theofilopoulos A. N., Moutsopoulos H., Feldman J. L., Talal N. Immune complexes in hepatitis B antigen-associated periarteritis nodosa. Detection by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and the Raji cell assay. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):783–791. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90884-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffar A., Calder E. A., Irvine W. J. K cell cytotoxicity against antibody-coated chicken erythrocytes in tumor-bearing mice: its development with progressively growing tumor and the effect of immunization against the tumor. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):315–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Shen L., Roitt I. M. Characterization of the antibody-dependent cytotoxic cell. A non-phagocytic monocyte? Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Oct;15(2):251–259. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C. Competition for receptors for immunoglobulin on cytotoxic lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):275–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill P. E., Twinn I. Antibody-mediated cytotoxicity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Jun;36(3):268–270. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.3.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. J., Dwyer J. M., Klatskin G. Identification of lymphocytes in percutaneous liver biopsy cores. Different T:B cell ratio in HB sAg-positive and -negative hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jun;72(6):1199–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G. Induction of DNA synthesis in normal human lymphocyte cultures by antigen-antibody complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jan;4(1):65–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Tapias J., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. Lymphocyte populations in liver biopsy specimens from patients with chronic liver disease. Gut. 1977 Jun;18(6):472–475. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.6.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg M. A., Cathcart E. S. Antibody-dependent direct cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes. I. Studies on peripheral blood lymphocytes and sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):317–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway R. D., Summerskill W. H., Baggenstoss A. H., Geall M. G., Gitnićk G. L., Elveback I. R., Schoenfield L. J. Clinical, biochemical, and histological remission of severe chronic active liver disease: a controlled study of treatments and early prognosis. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):820–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisloff F., Michaelsen T. E., Froland S. S. Inhibition of antibody-dependent human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity by immunoglobulin classes, IgG subclasses, and IgG fragments. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):29–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


