Abstract
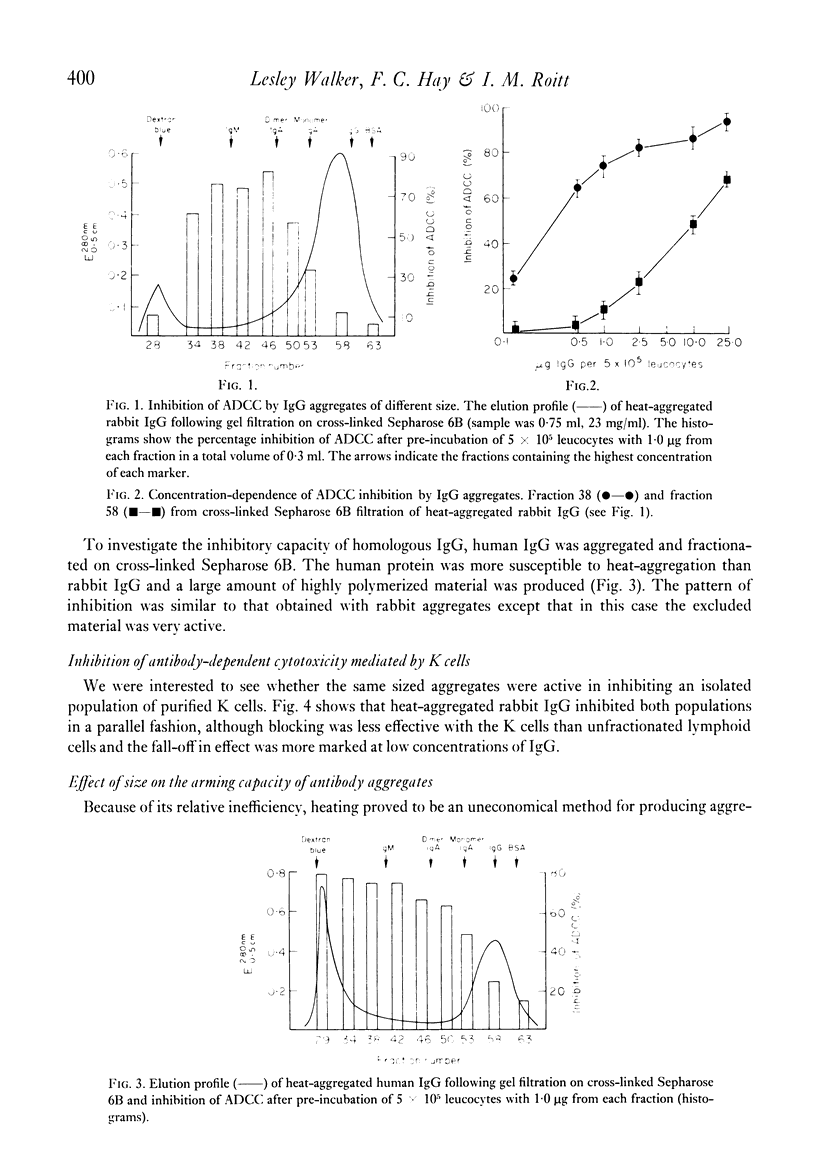
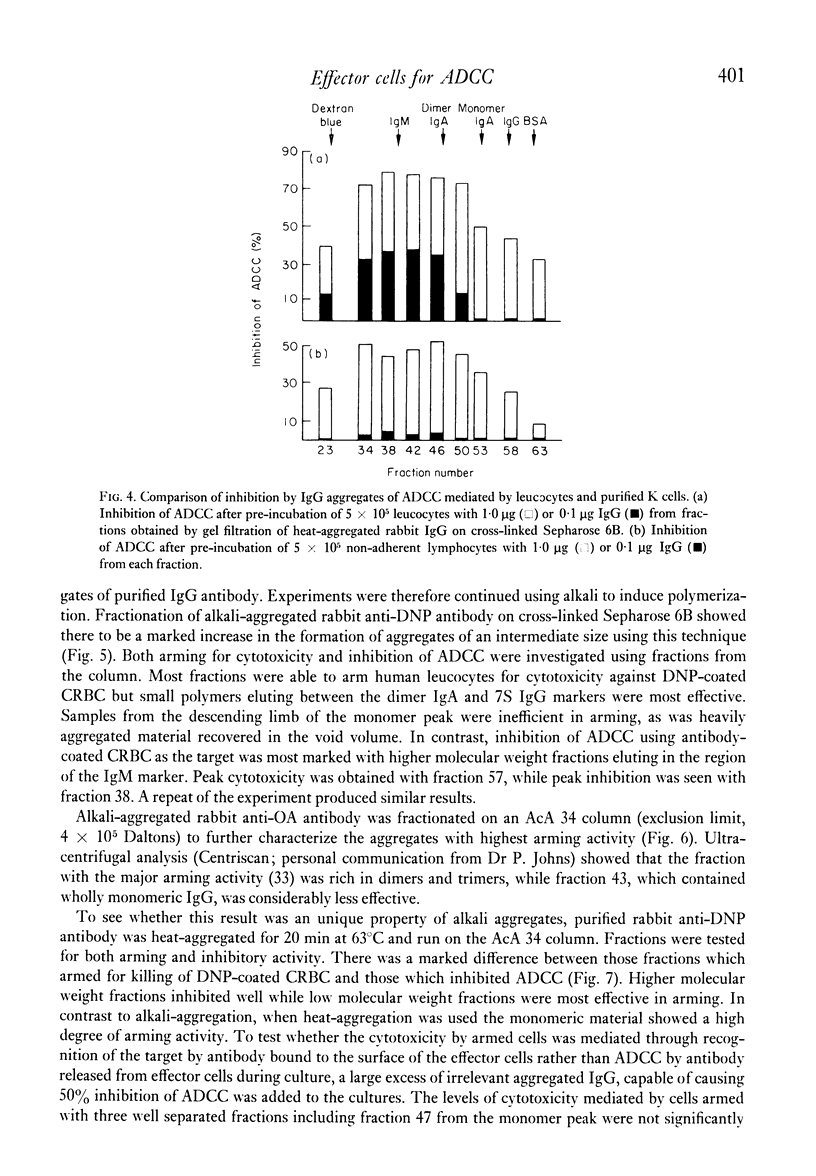
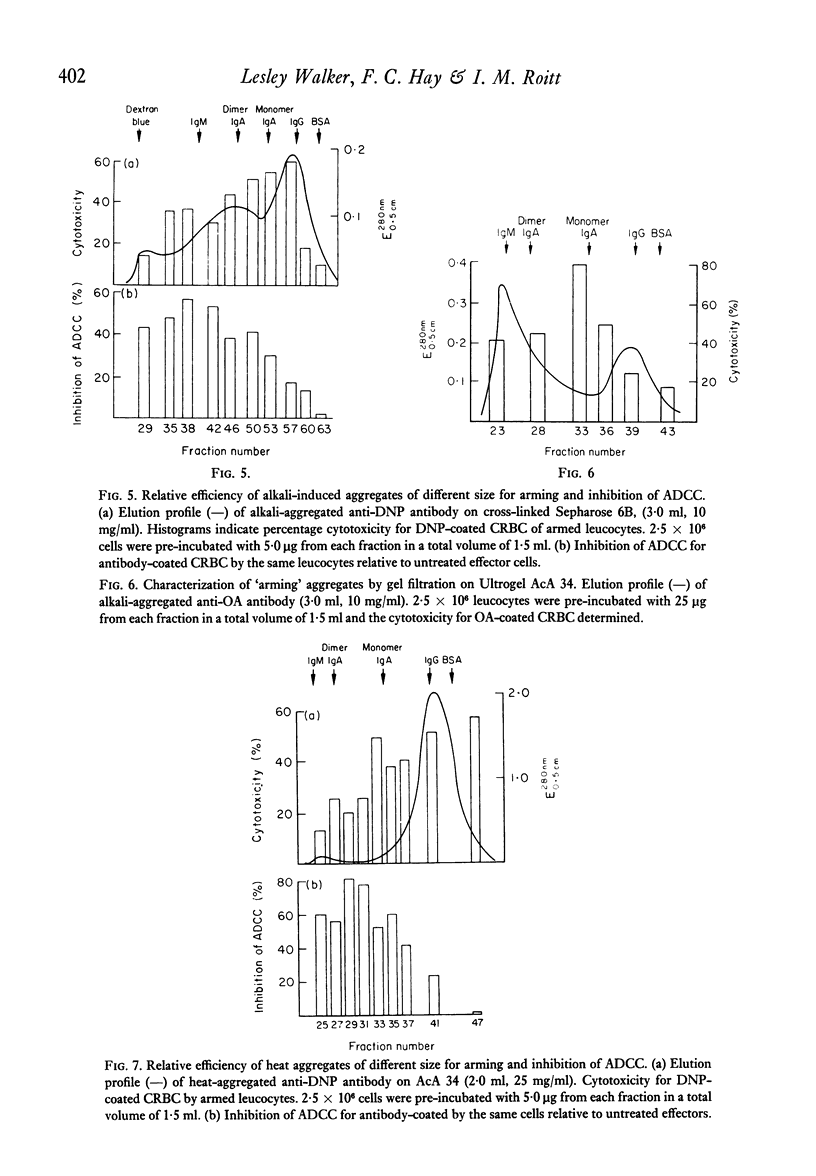
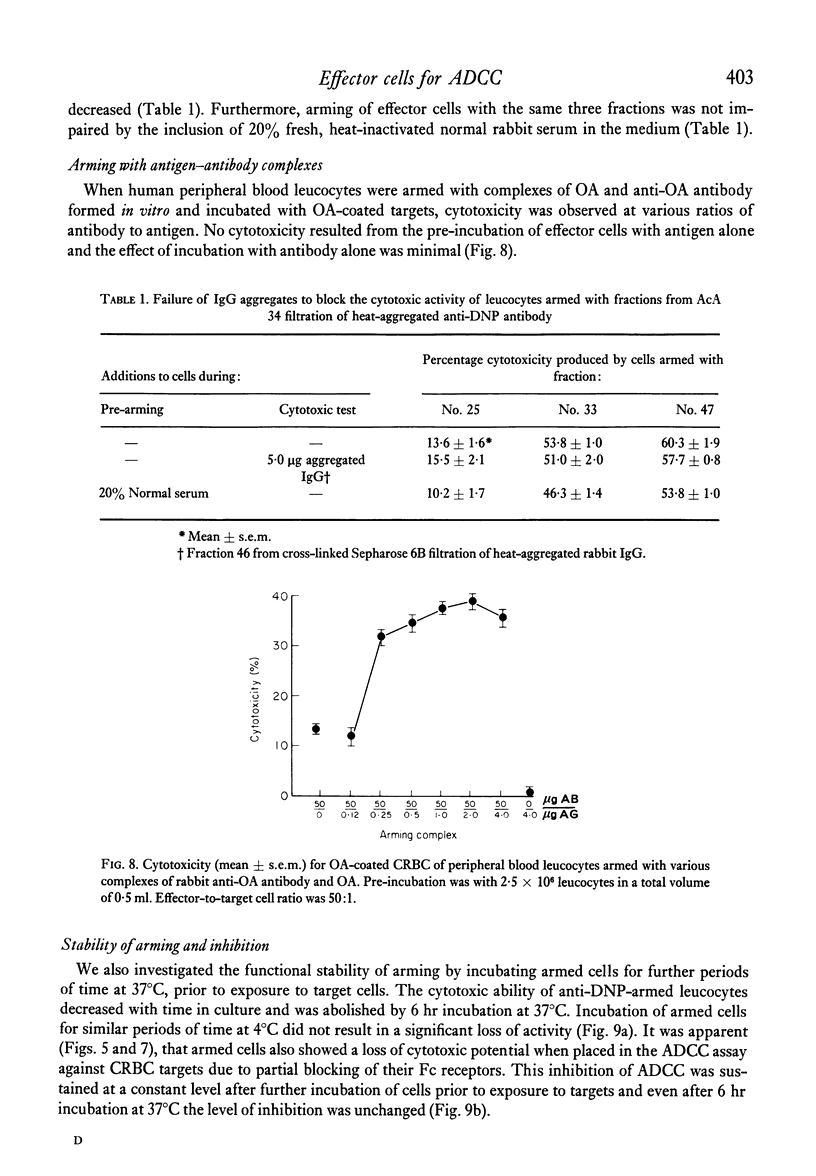
The size of IgG aggregate effective in the inhibition or arming of human effector cells for antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) was investigated using heat- and alkalipolymerized rabbit IgG or purified antibody fractionated by gel filtration. In contrast to the inhibition of ADCC against chicken erythrocytes, which was marked when effector cell were pre-incubated with high molecular weight aggregates (19S or greater), small polymers were most effective in arming for cytotoxicity against antigen-coated chicken red cells. Our data also demonstrate that while the cytotoxic potential of armed cells is short-lived and rapidly lost during culture at 37 degrees C but not 4 degrees C, the reduced capacity of these cells to kill antibody-coated targets is not altered by similar incubation at 37 degrees C. The differences in the size of aggregate active in arming and inhibition, and the stability of the two phenomena are compatible with the hypothesis that large aggregates may cause more cross-linking and redistribution of effector cell Fc receptors than small polymers of IgG.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. In vitro adherence of soluble immune complexes to macrophages. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):514–531. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augener W., Grey H. M. Studies on the mechanism of heat aggregation of human gamma-G. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):1024–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin R. W., Embleton M. J., Robins R. A. Cellular and humoral immunity to rat hepatoma-specific antigens correlated with tumour status. Int J Cancer. 1973 Jan 15;11(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin R. W., Embleton M. J., Robins R. A. Humoral factors influencing cell-mediated immune responses to tumour-associated antigens. Proc R Soc Med. 1973 May;66(5):466–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity, allograft rejection, and tumor immunity. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:67–132. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D. Antibody-dependent killing of Cryptococcus neopormans by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nature. 1974 Jan 18;247(5437):148–150. doi: 10.1038/247148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Jouanen E., Bankhurst A. D., Williams R. C., Jr Antibody-mediated lymphocytotoxicity in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Mar-Apr;19(2):133–141. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B. Studies of the human lymphocyte receptor for heat-aggregated or antigen-complexed immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):508–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Shen L. A class of specific cytotoxic cells demonstrated in vitro by arming with antigen-antibody complexes. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 31;245(148):282–285. doi: 10.1038/newbio245282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Shen L., Roitt I. M. Characterization of the antibody-dependent cytotoxic cell. A non-phagocytic monocyte? Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Oct;15(2):251–259. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Shen L., Walker L., Arnaiz-Villena A., Roitt I. M. Characteristics of the effector cells mediating cytotoxicity against antibody-coated target cells. II. The mouse nonadherent K cell. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;5(7):474–480. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg T. Inhibition of cytotoxicity of nonimmune human lymphocytes for sensitized chicken erythrocytes by aggregated human IgG. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):117–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson U. B. Ultracentrifugal studies of the aggregation of human immunoglobulin G by freezing and by heating. Acta Chem Scand. 1968;22(3):953–960. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.22-0953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasek M., Skamene E., Karakoz I., Chutná J., Nouza K., Bubeník J., Sovová V., Nemec M., Jonák J. Studies on the mechanism of rejection of tolerated skin homografts and abrogation of immunological tolerance by hyperimmune serum. Folia Biol (Praha) 1968;14(6):411–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M. The binding of human IgG subclasses to human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Jun;2(3):257–261. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imir T., Saksela E., Mäkelä O. Two types of antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, arming and sensitization. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1938–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne D. W., Simmons R. L. Passive serologic transfer of allograft immunity in immunologically suppressed mice. II. Effect of graft exposure to immune serum in primary hosts. J Immunol. 1971 Mar;106(3):629–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamon E. W., Wigzel H., Klein E., Andersson B., Skurzak H. M. The lymphocyte response to primary Moloney sarcoma virus tumors in BALB-c mice. Definition of the active subpopulations at different times after infection. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1472–1493. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Perlmann P., Natvig J. B. Cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes induced by rabbit antibodies to chicken erythrocytes. Inhibition by normal IgG and by human myeloma proteins of different IgG subclasses. Immunology. 1973 Oct;25(4):675–686. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig H. J., Bianco C. Antibody-mediated cell cytotoxicity in a defined system: regulation by antigen, antibody, and complement. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):253–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C. Competition for receptors for immunoglobulin on cytotoxic lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):275–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C., Howard A., Gotch F. M., Quie P. G. Effector activating determinants on IgG. I. The distribution and factors influencing the display of complement, neutrophil and cytotoxic B-cell determinants on human IgG sub-classes. Immunology. 1973 Sep;25(3):459–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole C., Perlmann P., Wigzell H., Unsgaard B., Zetterlund C. G. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity in bladder cancer. No requirement for thymus-derived effector cells? Lancet. 1973 May 19;1(7812):1085–1088. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90396-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMANN P., BROBERGER O. In vitro studies of ulcerative colitis. II. Cytotoxic action of white blood cells from patients on human fetal colon cells. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:717–733. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penfold P. L., Greenberg A. H., Roitt I. M. Characteristics of the effector cells mediating cytotoxicity against antibody-coated target cells. III. Ultrastructural studies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jan;23(1):91–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penfold P. L., Walker L. C., Roitt I. M. Complex arming in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity: ultrastructural studies of the interaction between human effector cells armed with aggregated anti-DNP antibody and DNP-coated erythrocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Feb;31(2):197–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Biberfeld P. Specifically cytotoxic lymphocytes produced by preincubation with antibody-complexed target cells. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):558–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H. Contactual lysis of antibody-coated chicken erythrocytes by purified lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):300–315. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Induction and inhibition by humoral antibody and nature of effector cells. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:91–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S. Specific "arming" of normal lymph-node cells by sera from tumor-bearing mice. Int J Cancer. 1973 Jan 15;11(1):138–142. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Bloom B. R. Immunological destruction of herpes simplex virus I infected cells. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):542–543. doi: 10.1038/251542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Clark I. A., Taylor G. A. Different effector cell types in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):376–377. doi: 10.1038/253376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Binding of affinity cross-linked oligomers of IgG to cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1338–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren H. O., Hellström I., Bansal S. C., Hellström K. E. Suggestive evidence that the "blocking antibodies" of tumor-bearing individuals may be antigen--antibody complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1372–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. H. Immunoglobulins and lymphokines as mediators of inflammatory cell mobilization and target cell killing. Cell Immunol. 1976 Dec;27(2):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisloff F., Michaelsen T. E., Froland S. S. Inhibition of antibody-dependent human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity by immunoglobulin classes, IgG subclasses, and IgG fragments. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(1):29–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeijlemaker W. P., Roos M. T., Schellekens P. T., Eijsvoogel V. P. Antibody-dependent human lymphocytotoxicity: a micro assay system. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Aug;5(8):579–584. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler H. K., Henney C. S. Antibody-dependent cytolytically active human leukocytes: an analysis of inactivation following in vitro interaction with antibody-coated target cells. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1500–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler H. K., Henney C. S. Studies on the cytotoxic activity of human lymphocytes. II. Interactions between IgG and Fc receptors leading to inhibition of K cell function. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1010–1017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


