Abstract
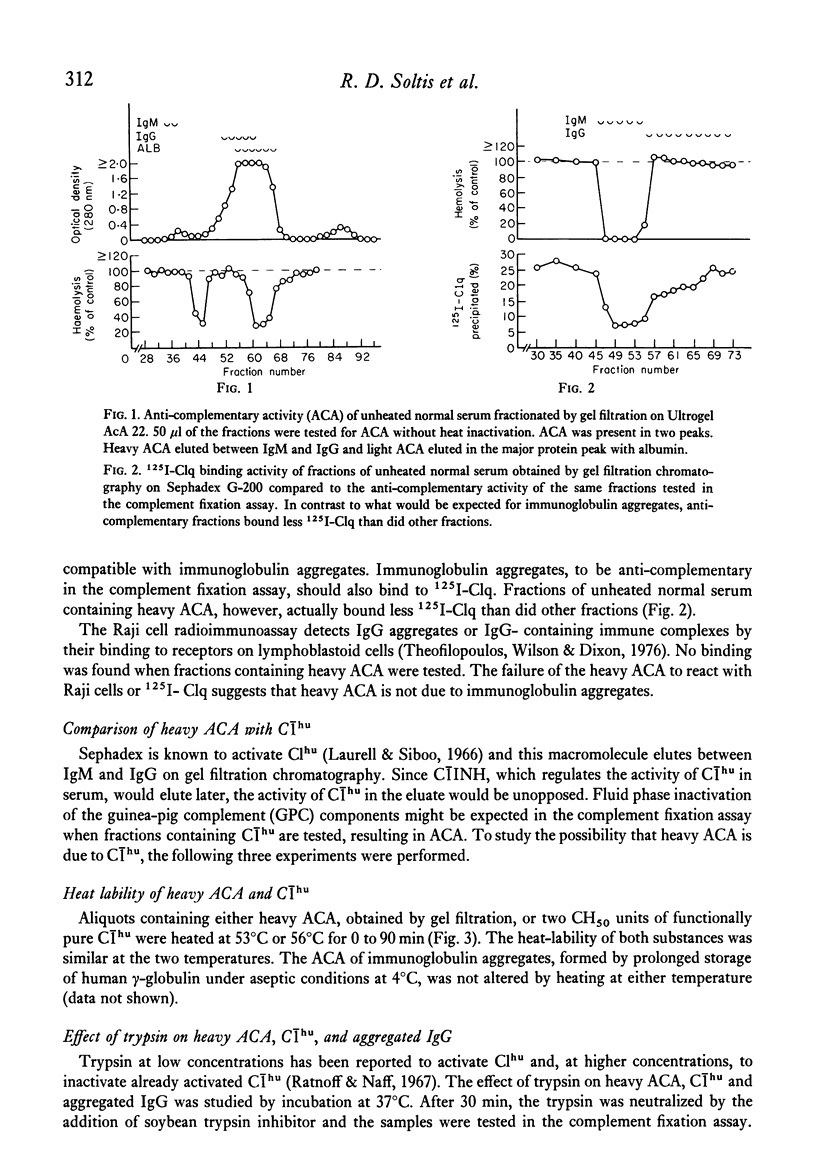
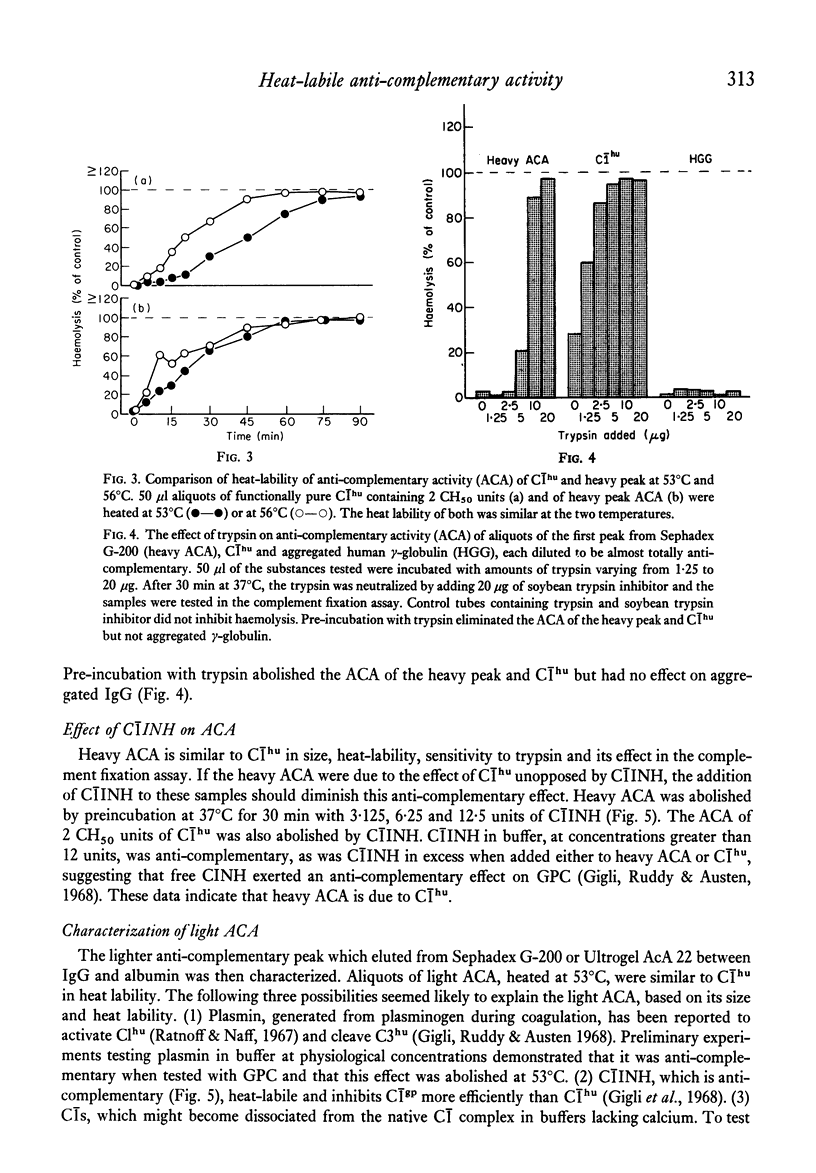
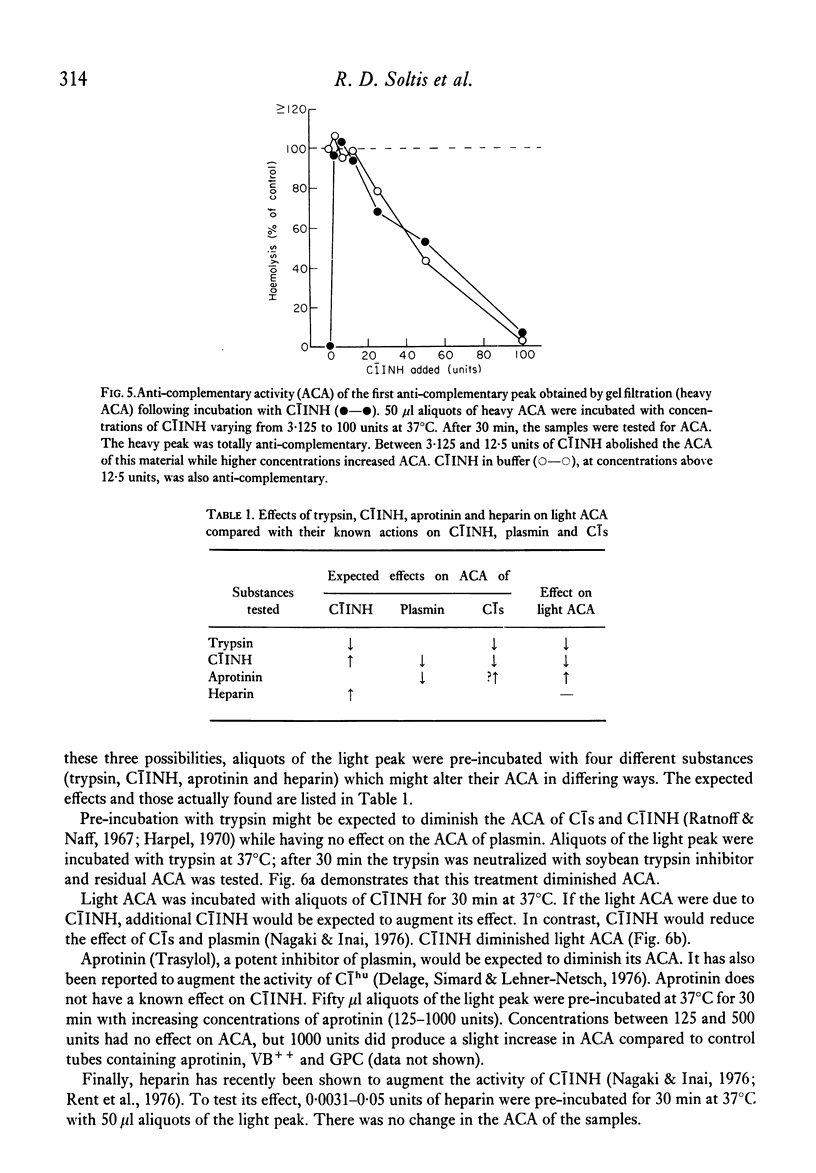
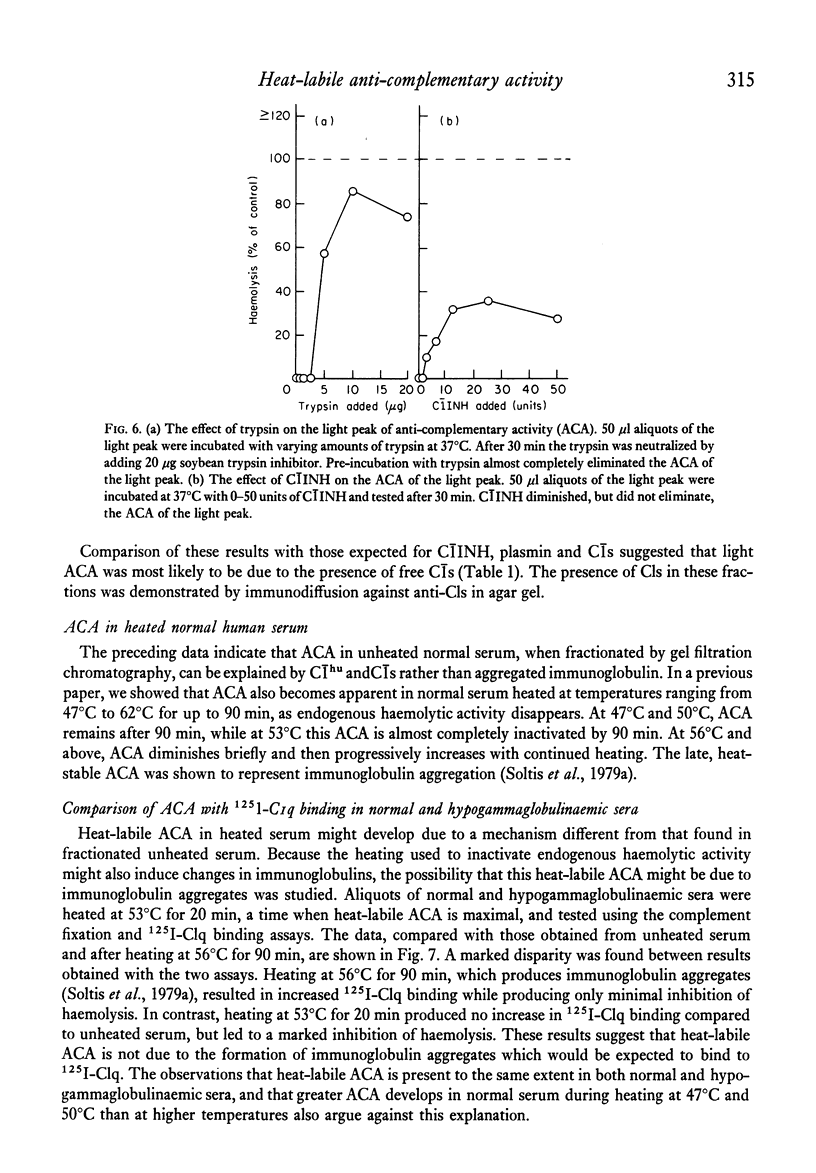
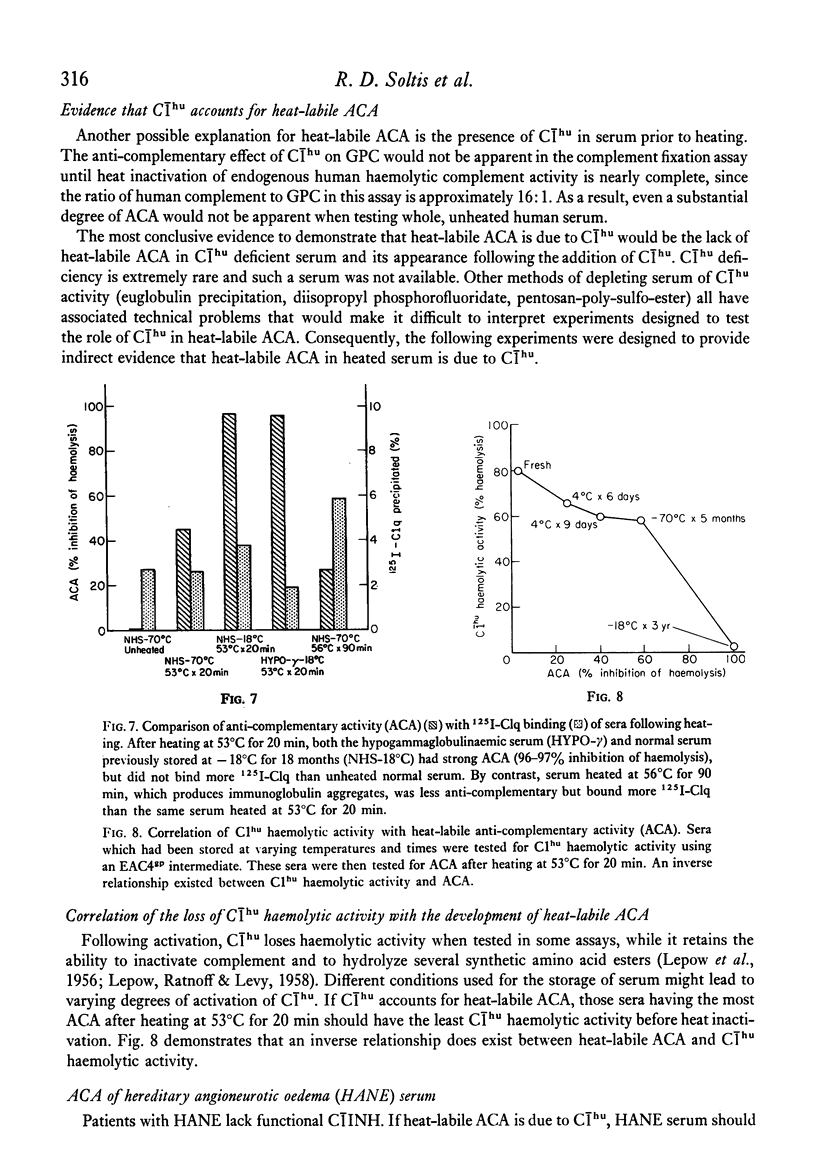
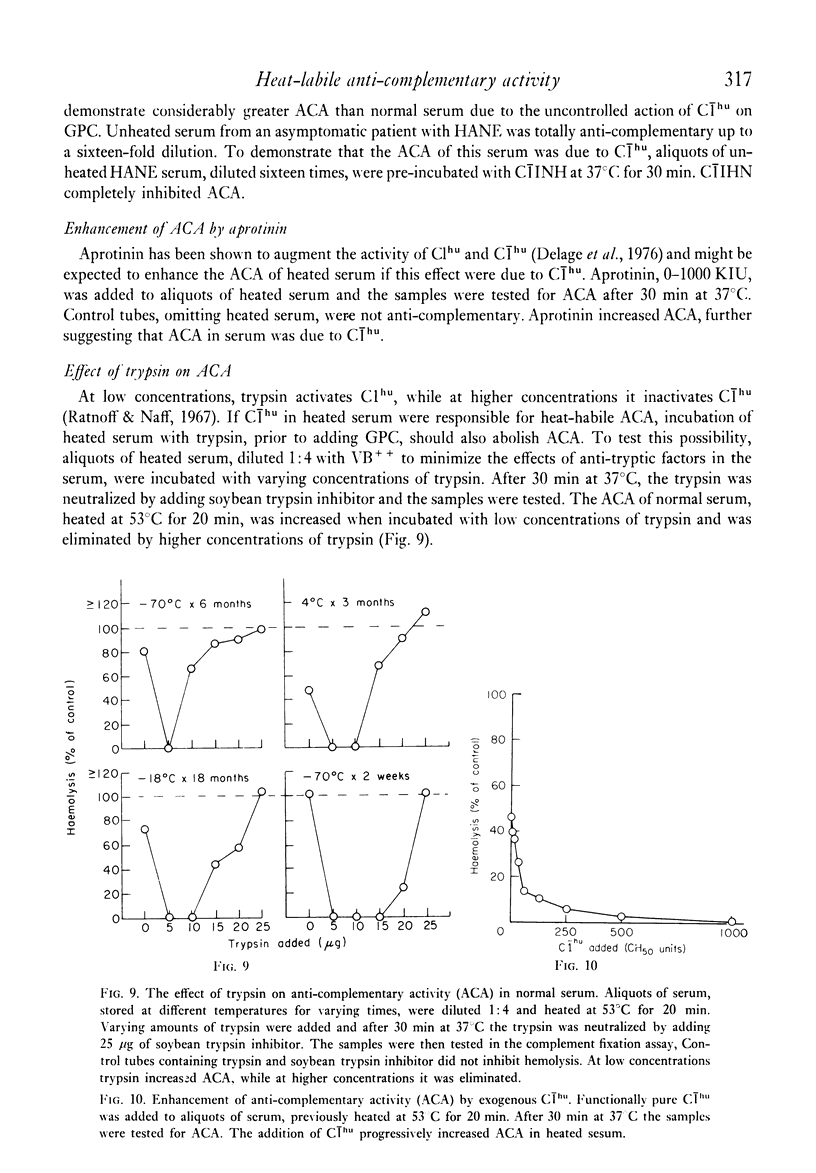
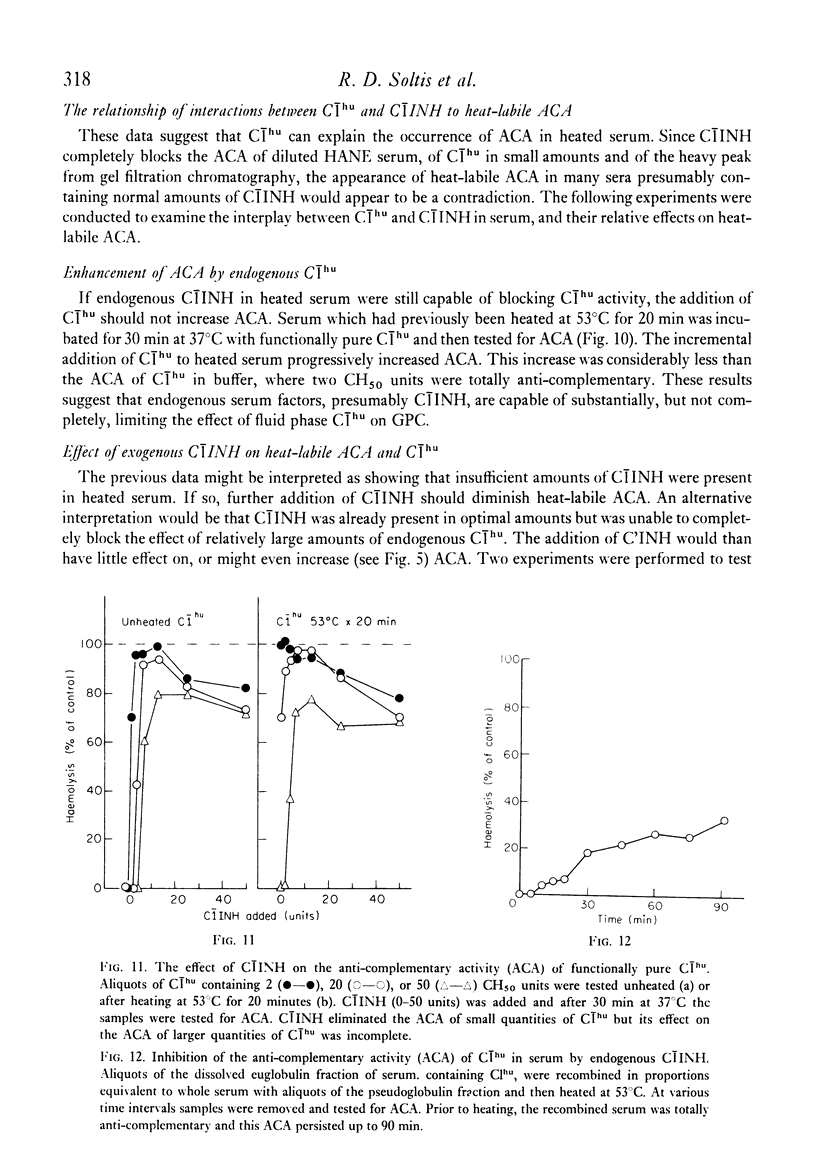
Heat-labile anti-complementary activity (ACA) appears in normal human serum during storage or heating as endogenous haemolytic activity disappears. Following gel filtration of unheated serum, two peaks of heat-labile ACA are present. The ACA of both whole and fractionated serum has previously been attributed to the presence of heat-labile immunoglobulin aggregates or immune complexes. Our data demonstrate that the heavy peak of ACA obtained by gel filtration does not bind to 125I-C1q or to Raji cells, and that its effect is abolished to C1INH, suggesting that it represents C1 rather than immunoglobulin aggregates or immune complexes. The lighter peak of ACA in fractionated serum has the functional characteristics of C1s and free C1s is demonstrable in fractions containing this activity. The ACA of whole serum likewise has functional characteristics of C1. The anti-complementary effect of C1 on guinea-pig complement would not be evident in the complement fixation assay until most endogenous haemolytic activity in human serum has been inactivated, either by heat or by storage. C1INH only partially inhibits this ACA in serum or in solutions containing isolated C1 in high concentrations. These observations indicate that heat-labile ACA in whole or fractionated sera is due to the presence of C1 and C1s and that this activity cannot be taken as evidence for the presence of immune complexes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew R. M., Esser A. F. The first complement component: evidence for an equilibrium between C1s free in serum and C1s bound in the C1 complex. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):1916–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castanedo J. P., Williams R. C., Jr Anticomplementary activity of sera from patients with connective tissue disease and normal subjects. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Feb;69(2):217–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delage J. M., Simard J., Lehner-netsch G. The enhancement of the haemolytic activity of the first component of complement by trasylol. Immunology. 1976 Oct;31(4):601–606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Austen K. F. Fluid phase destruction of C2hu by C1hu. II. Unmasking by C4ihu of C1hu specificity for C2hu. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):833–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The stoichiometric measurement of the serum inhibition of the first component of complement by the inhibition of immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1154–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. C1 inactivator inhibition by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):568–575. doi: 10.1172/JCI106267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton A. M., Moore M., Howat J. M. Detection of circulating anticomplementary factors in chronic lung diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Feb;31(2):237–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Potter B. J., Jewell D. P. Immune complexes in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Aug;29(2):187–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. H., Mowbray J. F., Porter K. A. Detection of circulating immune complexes in pathological human sera. Lancet. 1975 Apr 5;1(7910):762–765. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Gigli I., Austen K. F. Fluid phase destruction of C2 hu by C1 hu. 3. Changes in activity for synthetic substrates upon cell binding, heat inactivation and interaction with C1INH. Immunology. 1972 Mar;22(3):305–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., RATNOFF O. D., LEVY L. R. Studies on the activation of a proesterase associated with partially purified first component of human complement. J Exp Med. 1958 Mar 1;107(3):451–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., RATNOFF O. D., ROSEN F. S., PILLEMER L. Observations on a pro-esterase associated with partially purified first component of human complement (C'1). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 May;92(1):32–37. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Siboo R. Activation of C'1 to C'1 esterase on gel filtration on Sephadex G-200. Studies on normal human serum, euglobulin and hereditary angioneurotic edema serum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;68(2):230–242. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.68.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Activation of the first component of complement evidence for an internal activation step. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):683–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaki K., Inai S. Inactivator of the first component of human complement (C1INA). Enhancement of C1INA activity against C1s by acidic mucopolysaccharides. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;50(2):172–180. doi: 10.1159/000231494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Naff G. B. The conversion of C'IS to C'1 esterase by plasmin and trypsin. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):337–358. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemasu K., Stroud R. M. Clq: rapid purification method for preparation of monospecific antisera and for biochemical studies. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. Demonstration and quantitation of activation of the first component of complement in human serum. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):385–395. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


