Abstract
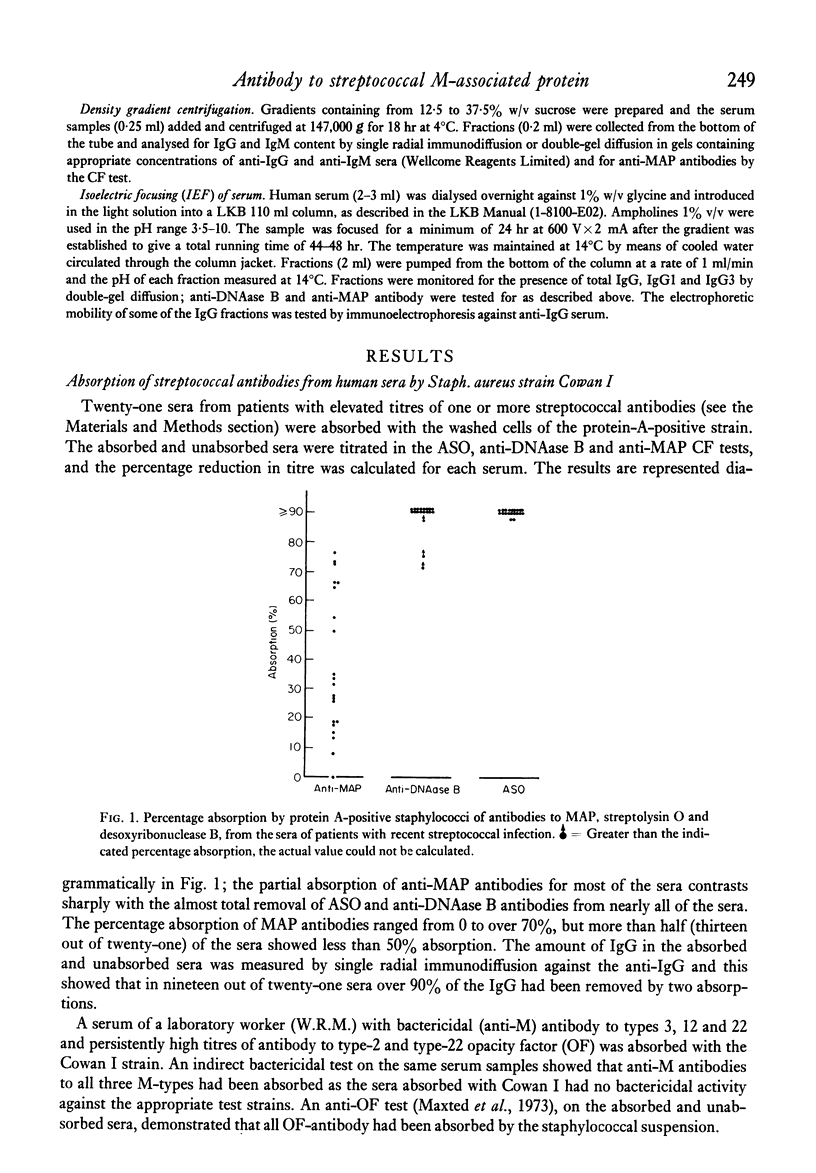
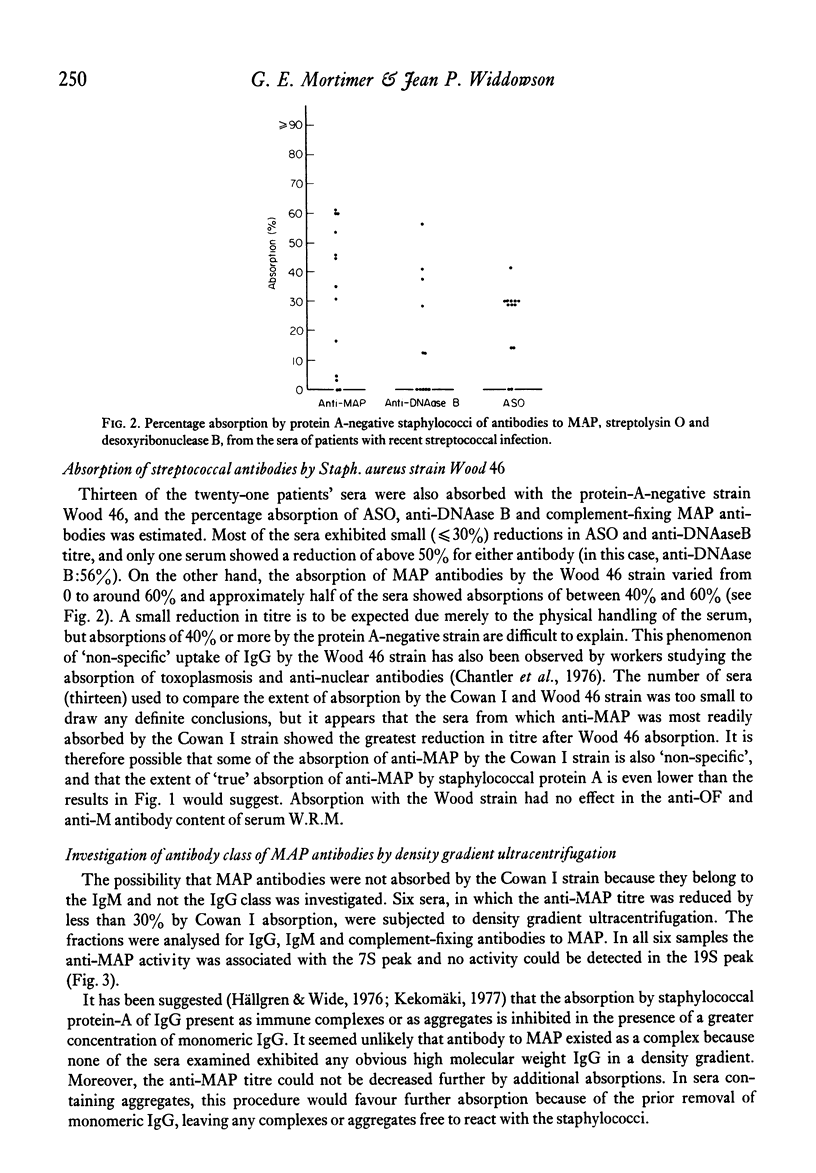
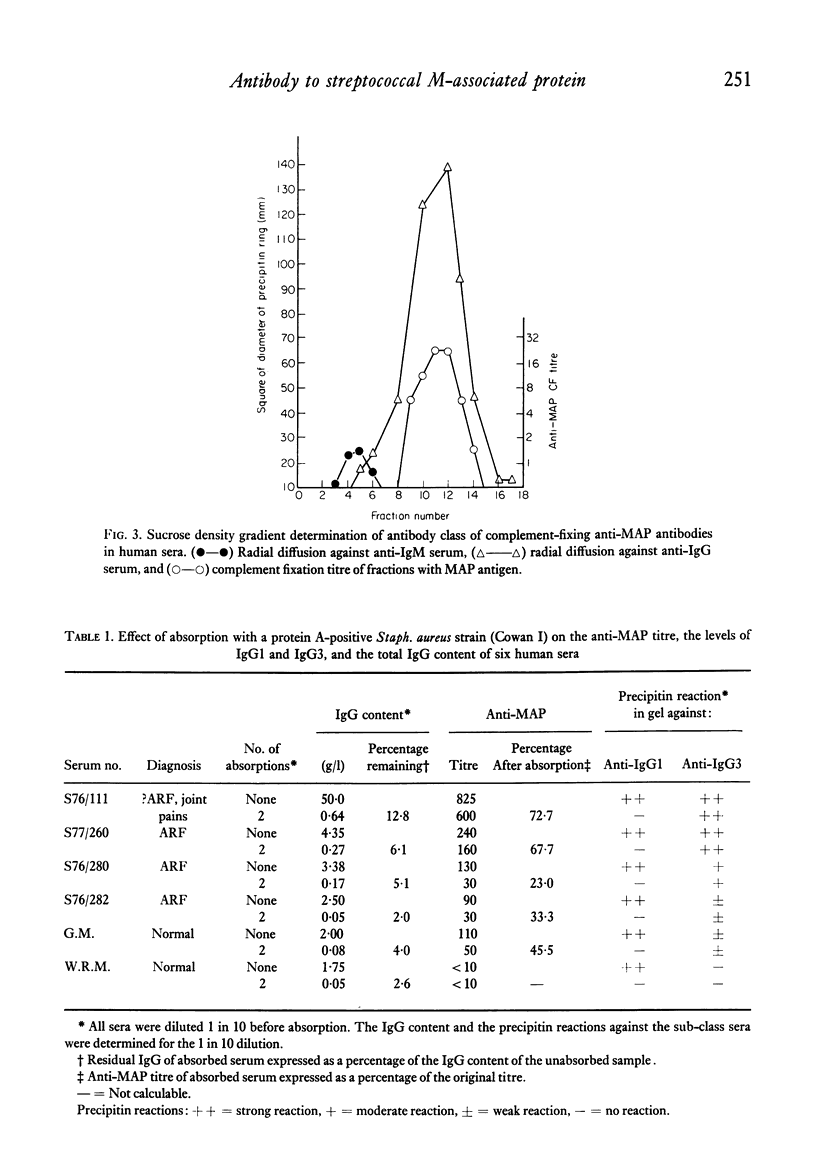
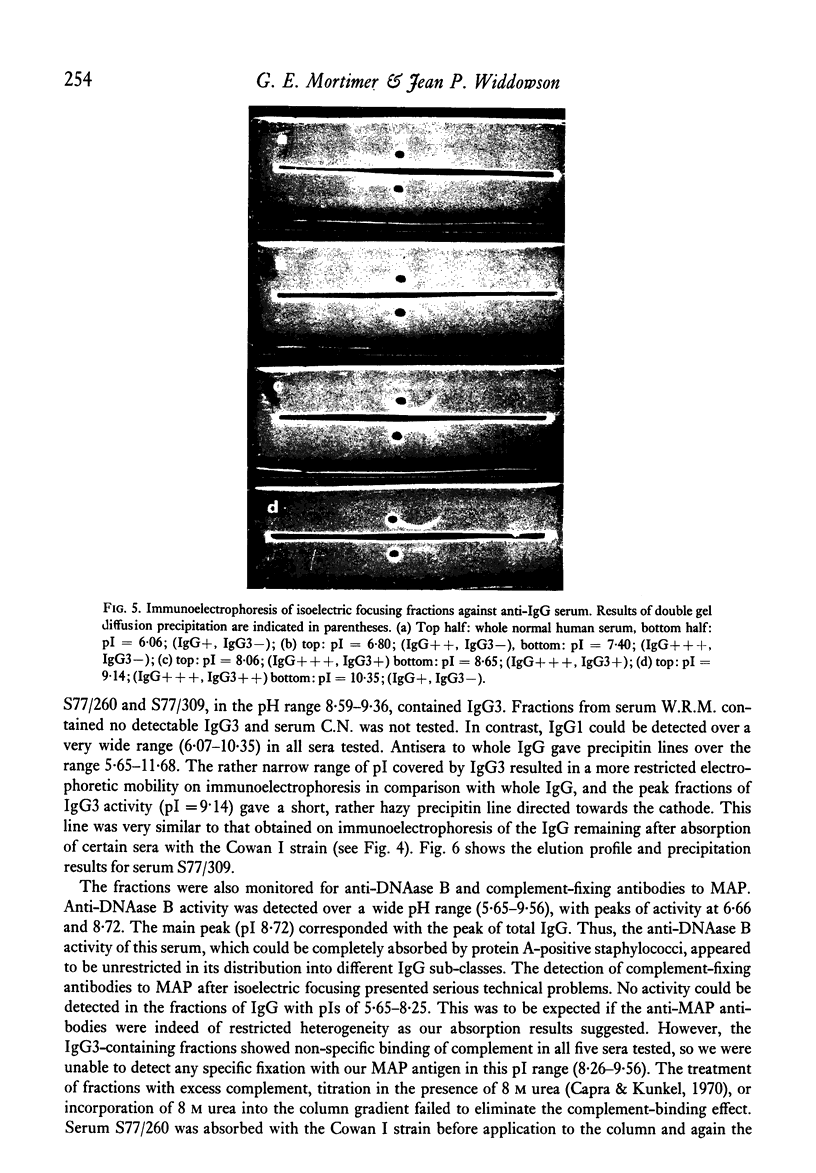
During investigation of the absorption of group-A streptococcal antibodies from human sera by a protein A-positive Staphylococcus aureus strain, we found that the complement-fixing antibodies to M-associated protein (MAP) were only partially absorbed from the majority of sera tested, although they were shown to belong to the immunoglobulin G (IgG) class by density gradient centrifugation. In contrast, other streptococcal antibodies: anti-streptolysin O (ASO), anti-deoxyribonuclease B (anti-DNAase B), 'bactericidal' M antibody and anti-opacity factor (anti-OF), were completely absorbed from all but a minority of sera. We suggest that the complement-fixing antibodies to MAP may be of restricted heterogeneity and have an abnormal IgG sub-class distribution, with a marked predominance of IgG3 (the only sub-class that does not interact with protein A) over the IgG1 and IgG2 sub-class; IgG4 does not participate in complement fixation. The concentration and relative porportions of IgG sub-classes are believed to be genetically influenced, so our findings may have some bearing on the immune responsiveness of different individuals to streptococcal infection, and possibly have important implications in the development of the secondary sequelae.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankerst J., Christensen P., Kjellén L., Kronvall G. A rountine diagnostic test for IgA and IgM antibodies to rubella virus: absorption of IgG with Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):268–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I., Bismo A. L. Studies of antibodies to non-type-specific antigens associated with streptococcal M protein in the sera of patients with rheumatic fever. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1361–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Stollerman G. H. Toxic effects of streptococcal M protein on platelets and polymorphonuclear leukocytes in human blood. J Exp Med. 1971 Aug 1;134(2):351–365. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kunkel H. G. Aggregation of gamma-G3 proteins: relevance to the hyperviscosity syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):610–621. doi: 10.1172/JCI106272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler S., Devries E., Allen P. R., Hurn B. A. A rapid immunofluorescent procedure for the detection of specific IgG and IgM antibody in sera using Staphylococcus aureus and latex-IgG as absorbents. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):367–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen K. K., Christensen P., Mårdh P. A., Weström L. Quantitation of serum antibodies to surface antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with radiolabeled protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):317–323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudding B. A., Ayoub E. M. Persistence of streptococcal group A antibody in patients with rheumatic valvular disease. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1081–1098. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. V. Reaction with guinea pig gamma-globulins. J Immunol. 1968 May;100(5):921–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällgren R., Wide L. Detection of circulating IgG aggregates and immune complexes using 125I protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):306–313. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekomäki Detection of platelet-bound IgG with 125I-labelled staphylococcal protein A. Med Biol. 1977 Apr;55(2):112–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Persistence of type-specific antibodies in man following infection with group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1959 Aug 1;110(2):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxim P. E., Mathews H. L., Mengoli H. F. Single-tube mixed agglutination test for the detection of staphylococcal protein A. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):418–422. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.418-422.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Widdowson J. P., Fraser C. A. Antibody to streptococcal opacity factor in human sera. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Mar;71(1):35–42. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., Steinberg A. G., Van Loghem E., Terry W. D. Correlations between the concentrations of the four sub-classes of IgG and Gm Allotypes in normal human sera. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Chemistry and reaction mechanisms of complement. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:1–80. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Human immunoglobulins: classes, subclasses, genetic variants, and idiotypes. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J., Ayoub E. M., Wannamaker L. W. Streptococcal anti-desoxyribonuclease B: microtechnique determination. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):867–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Shimizu H., Kampa D., Doerr H. W. Rapid method to detect rubella immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin A antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Feb;1(2):132–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.2.132-135.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonozaki H., Takizawa S., Torisu M. Immunoglobulin analysis of anti-streptolysin-O antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Oct;7(4):519–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L., Johnson R. H., Dillon M. F. Further characterization of purified fractions of M protein from a strain of group A, type 12 Streptococcus. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):104–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Newrick C. W., Parkin D. An outbreak of streptococcal sore throat and rheumatic fever in a Royal Air Force training camp; significance of serum antibody to M-associated protein. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Feb;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Notley C. M., Pinney A. M. The antibody respones in man to infection with different serotypes of group-A streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Nov;7(4):483–496. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-4-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Pinney A. M. An M-associated protein antigen (MAP) of group A streptococci. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Dec;69(4):553–564. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie J. B., Hsu K. C., Seegal B. C. Heart-reactive antibody associated with rheumatic fever: characterization and diagnostic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):147–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


