Abstract
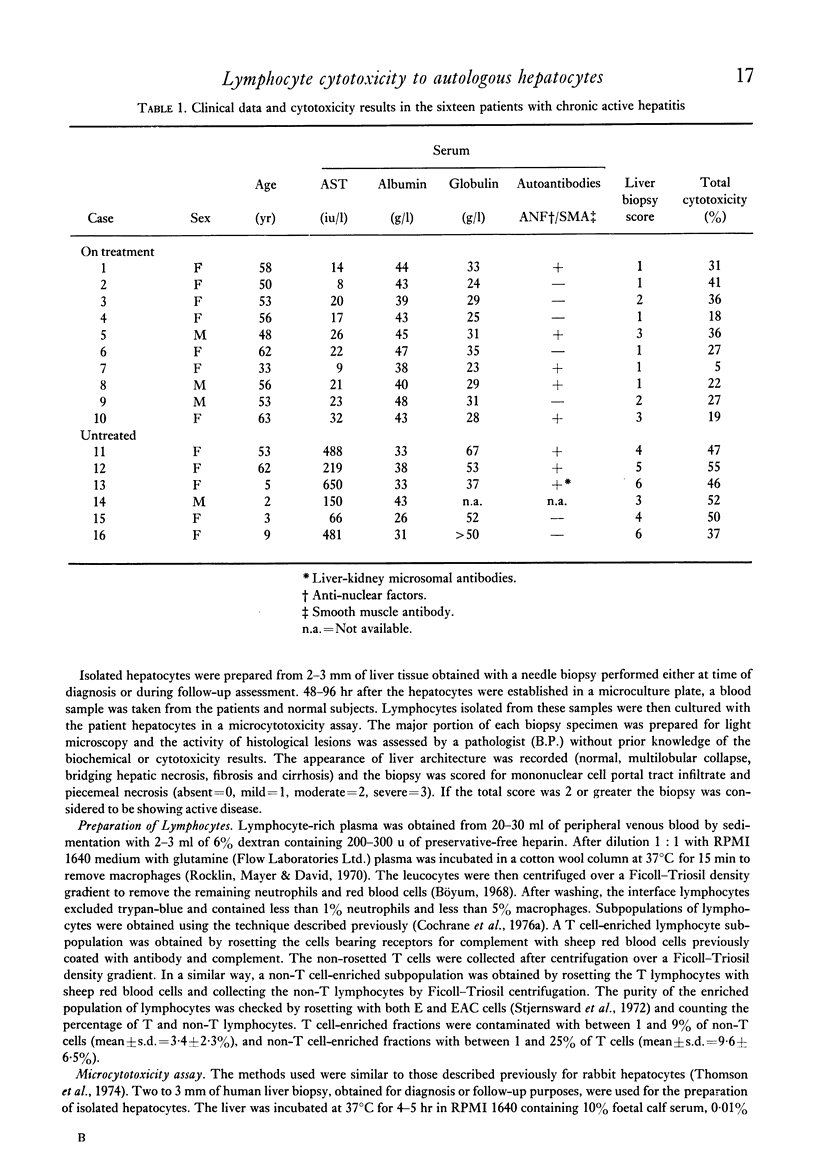
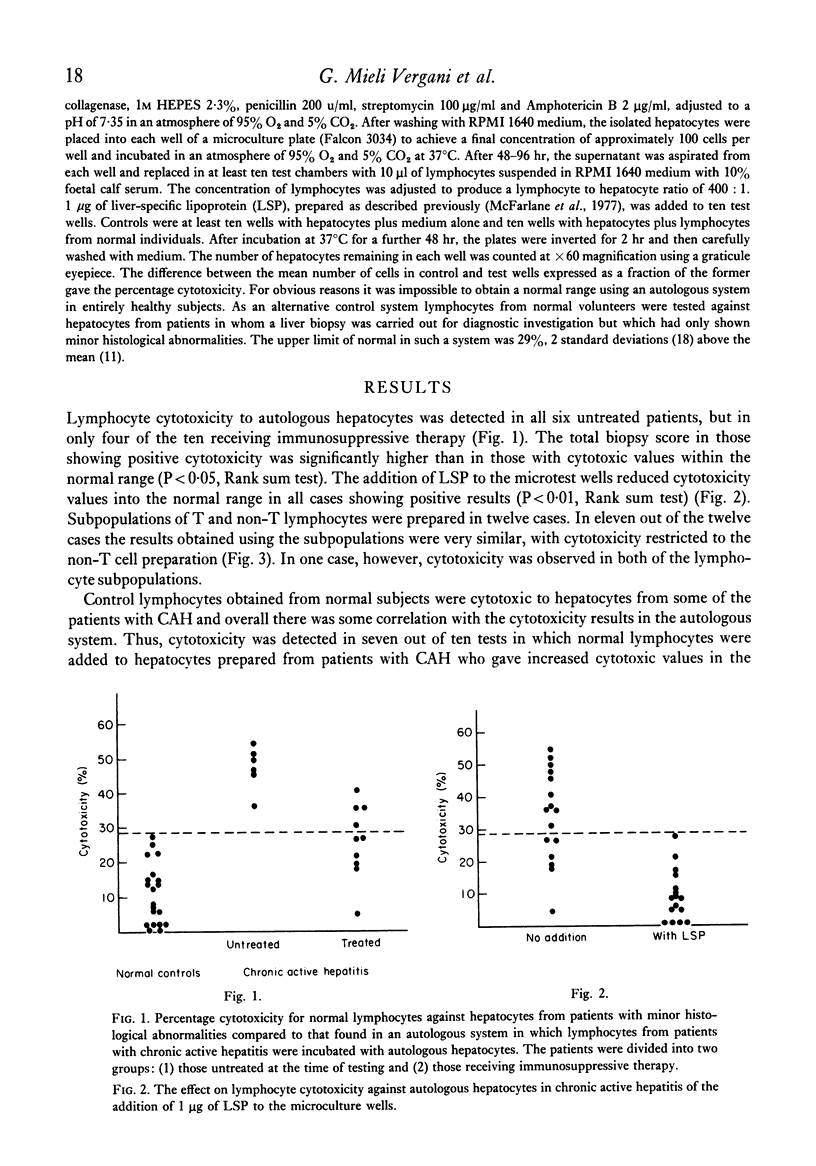
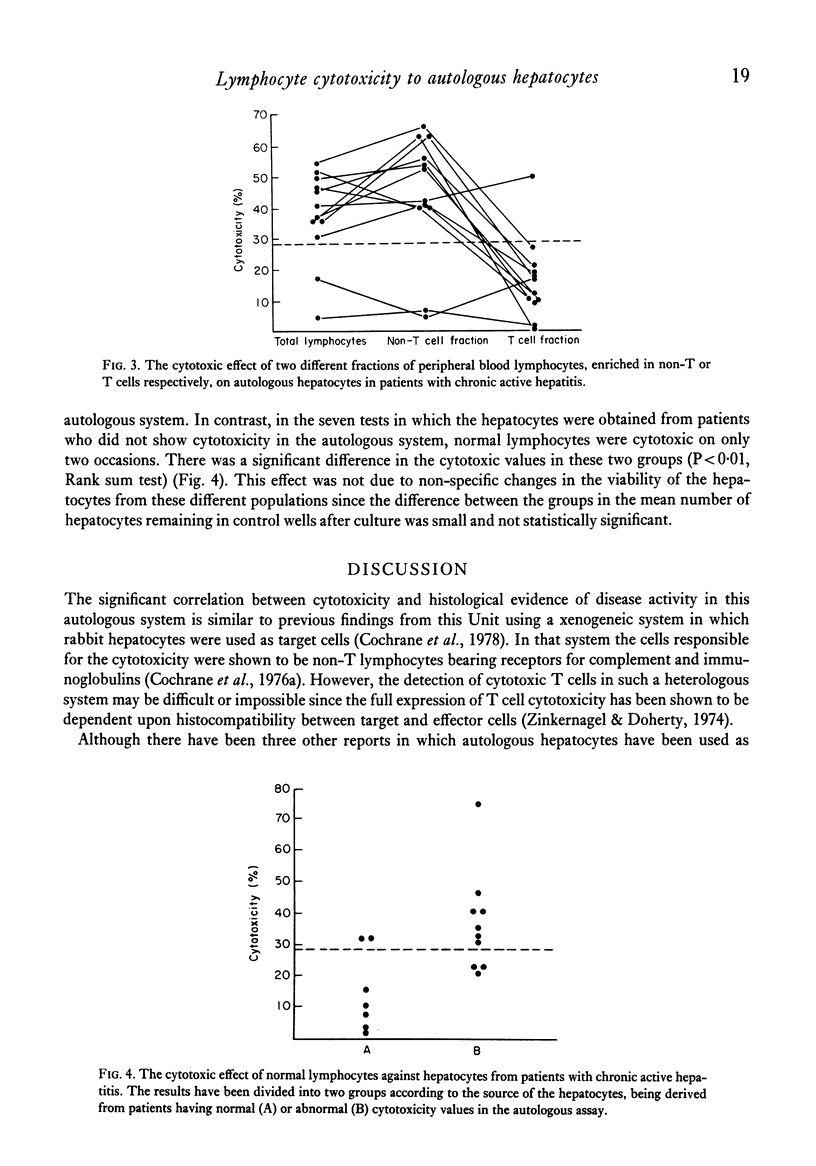
In a micrototoxicity assay, lymphocytes from ten out of sixteen patients with HBsAg-negative chronic active hepatitis have been shown to be cytotoxic to autologous hepatocytes isolated from percutaneous liver biopsies. This cytoxicity was demonstrable in all six untreated patients but in only four out of ten receiving immunosuppressive treatment, the presence of cytotoxicity showing a significant association with the activity of the disease assessed histologically. The addition of excess purified lipoprotein (LSP), derrived from the hepatocyte plasma membrane, blocked the reaction in all cytotoxic cases, indicating that LSP was the major target antigen. Enriched fractions of T cells were cytotoxic in only one case, whereas non-T cell fractions were cytotoxic in the other ten cases investigated in this way. For optimum T cell cytotoxicity, effector and target cells must share histocompatibility determinants and the results of this study using an autologous system show conclusively that the lymphocyte cytotoxicity found in HBsAg-negative chronic active hepatitis is mediated by a non-T cell population.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J. Innate cytotoxicity of CBA mouse spleen cells to Sendai virus-infected L cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):608–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.608-612.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Smith A., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity in chronic active hepatitis: effect of therapy and correlations with clinical and histological changes. Gut. 1978 Apr;19(4):308–314. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.4.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Thomsom A. D., Eddleston A. L., Wiiliams R. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated (K cell) cytotoxicity against isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):441–444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geubel A. P., Keller R. H., Summerskill W. H., Dickson E. R., Tomasi T. B., Shorter R. G. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity and inhibition studied with autologous liver cells: observations in chronic active liver disease and the primary biliary cirrhosis syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1976 Sep;71(3):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumors. II. Characterization of effector cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):230–239. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Arnold W., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Förster E., Bolte J. P. Studies on the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory liver diseases. I. Membrane-fixed IgG on isolated hepatocytes from patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Studies on the pathogenesis of experimental chronic active hepatitis in rabbits. II. Demonstration of immunoglobulin on isolated hepatocytes. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Oct;55(5):509–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Pross H., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):117–121. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Petranyi G., Kärre K., Jondal M., Tracey D., Wigzell H. Killer cells: a functional comparison between natural, immune T-cell and antibody-dependent in vitro systems. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):772–780. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane I. G., Wojcicka B. M., Zucker G. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Purification and characterization of human liver-specific membrane lipoprotein (LSP). Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):381–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronetto F., Vernace S. Immunological studies in patients with chronic active hepatitis. Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes to autochthonous liver cells grown in tissue culture. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jan;19(1):99–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter H. H., Pavie-Fischer J., Fridman W. H., Aubert C., Cesarini J. P., Roubin R., Kourilsky F. M. Cell-mediate cytotoxicity in vitro of human lymphocytes against a tissue culture melanoma cell line (igr3). J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):539–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Meyers O. L., David J. R. An in vitro assay for cellular hypersensitivity in man. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):95–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Moretta L., Zmijewski C. M., Koprowski H. Spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity in humans. Distribution and characterization of the effector cell. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Aug;33(2):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Zmijewski C. M., Koprowski H. HLA-related control of spontaneous and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity in humans. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):765–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjernswärd J., Jondal M., Vánky F., Wigzell H., Sealy R. Lymphopenia and change in distribution of human B and T lymphocytes in peripheral blood induced by irradiation for mammary carcinoma. Lancet. 1972 Jun 24;1(7765):1352–1356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D., Zmijewski C. M., Koprowski H. Functional correlation between antibody-dependent and spontaneous cytotoxic activity of human lymphocytes and possibility of an HLA-related control. Transplant Proc. 1977 Mar;9(1):881–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Perrotto J. L., Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J. Cell-mediated immunity in acute and chronic hepatitis. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):921–929. doi: 10.1172/JCI108021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands K. R., Isselbacher K. J. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous liver cells in chronic active hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1301–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):701–702. doi: 10.1038/248701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


