Abstract
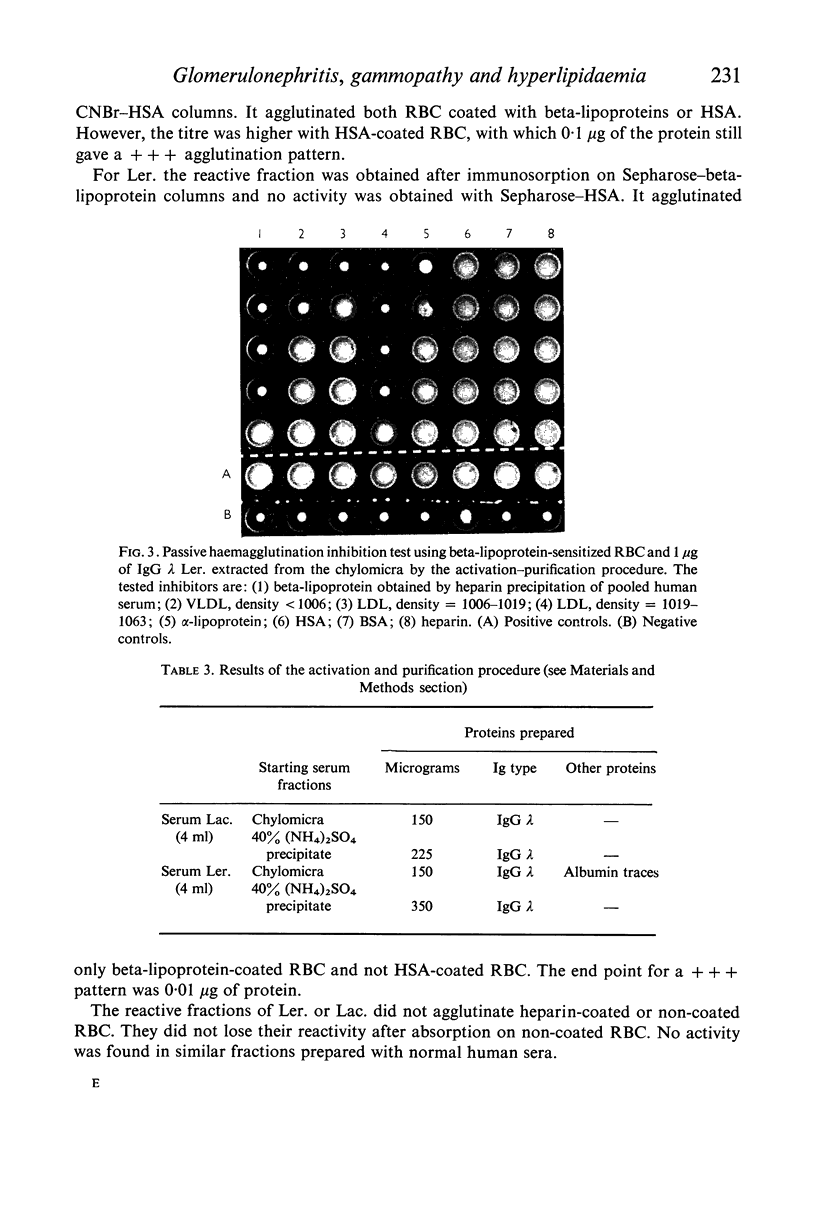
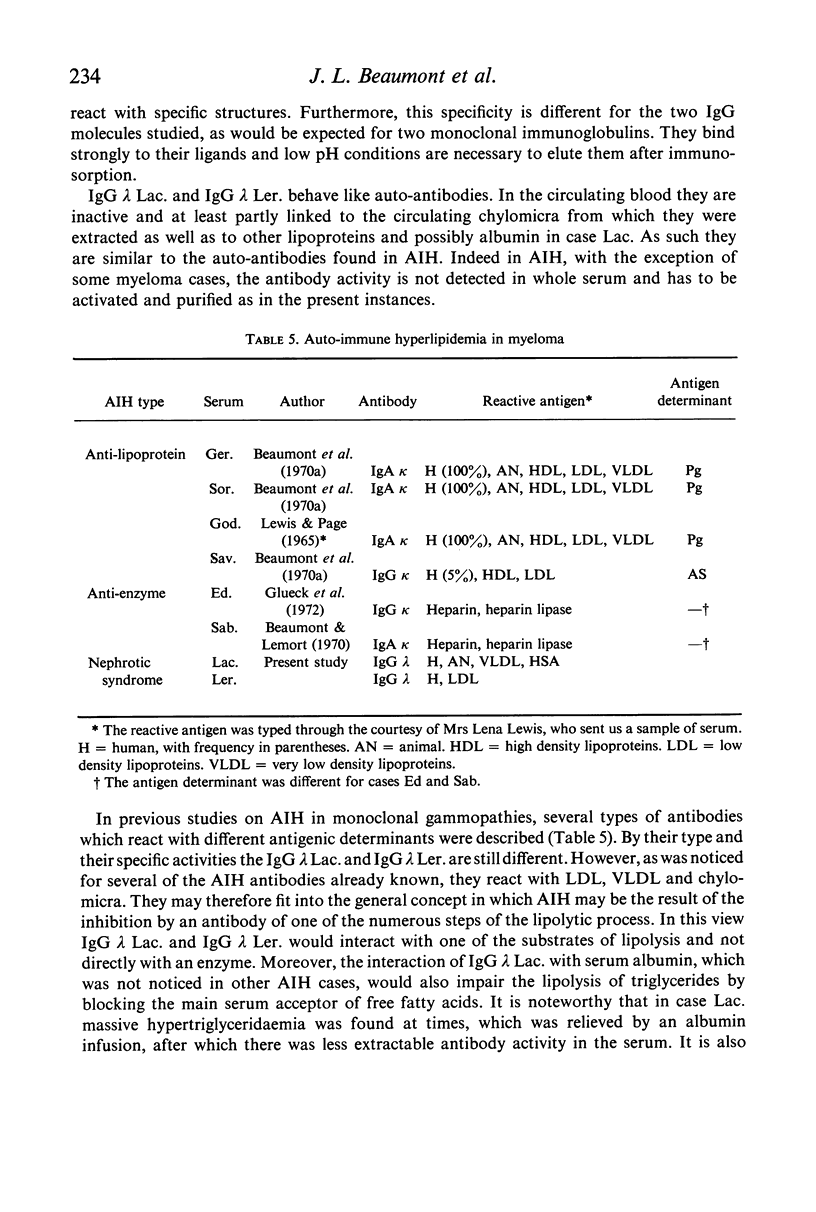
Hyperlipidaemia, glomerulonephritis and IgG λ monoclonal gammopathy were found to be associated in two patients (Ler. and Lac.). A severe atherosclerosis was also present in the former patient. After a purification–activation procedure active IgG λ was obtained from the serum chylomicra and from the ammonium sulphate-precipitated serum gamma-globulins. In passive haemagglutination tests, including inhibition tests, the IgG λ Ler. reacted specifically with the protein moiety of human low density lipoproteins (LDL) and the IgG λ Lac. reacted with human, rat and rabbit very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) as well as with human serum albumin (HSA). These IgG λ behaved like autoantibodies though no activity was found in whole serum, in which they are probably blocked by the corresponding antigens. They are very similar, although not identical, to the autoantibodies found in auto-immune hyperlipidaemia (AIH) and it is proposed that in these patients the hyperlipidaemia is a variety of AIH. Finally it is suggested that the hyperlipidaemia associated with glomerulonephritis chiefly in the nephrotic syndrome may sometimes be AIH. If this is the case the renal lesions and the hyperlipidaemia may be different expressions of an immune complex disease which may also lead to other tissue lesions such as atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF

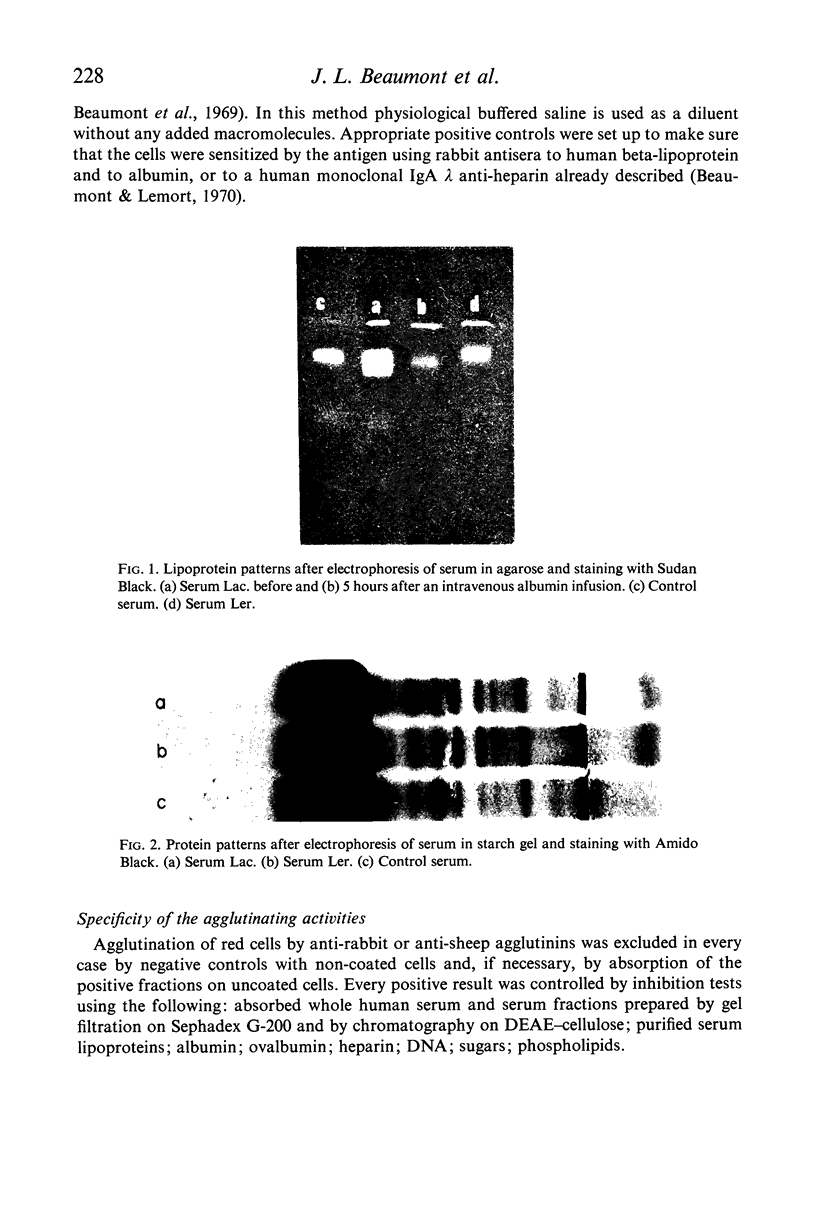






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER J. H., GOODMAN H. C., HAVEL R. J. Serum lipid and lipoprotein alterations in nephrosis. J Clin Invest. 1960 Mar;39:455–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI104058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAINEY J. D., BREWER D. B., HARDWICKE J., SOOTHILL J. F. The nephrotic syndrome. Diagnosis by renal biopsy and biochemical and immunological analyses related to the response to steroid therapy. Q J Med. 1960 Apr;29:235–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L. Auto-immune hyperlipidemia. An atherogenic metabolic disease of immune origin. Rev Eur Etud Clin Biol. 1970 Dec;15(10):1037–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L., Baudet M. F., Delplanque B., Péron F. L'hemagglutination passive au chlorure de chrome. Son emploi sans diluant macromoléculaire. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1969 Apr;17(7):429–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L., Beaumont V., Antonnucci M., Lemort N. Les auto-anticorps antilipoprotéines de myélome. Etude comparée de deux types: l'Iga anti-Lp P.G. et l'IgG anti-Lp A.S. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1970;28(5):387–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L. L'hyperlipidémie par auto-anticorps anti-beta-lipoprotéine. Une nouvelle entité pathologique. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 Nov 22;261(21):4563–4566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L., Lemort N. Purification de l'alpha-1-lipoprotéine du sérum. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1969 Mar-Apr;27(3):237–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L., Lemort N. Une immunoglobuline anti-héparine dans un sérum hyperlipidémique. (Une nouvelle variété d'hyperlipidémie par auto-anticorps) C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Dec 21;271(25):2452–2454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L., Lorenzelli L., Delplanque B. Emploi d'un detergent pour la purification d'anticorps antilipoproteines. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jan;7(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L., Lorenzelli L. Le phénomène d'agglutination des particules lipidiques. Son intérêt en séro-immunologie. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1972 Apr;20(7):357–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanza M. E., Pinn V., Schwartz R. S., Nathanson L. Carcinoembryonic antigen-antibody complexes in a patient with colonic carcinoma and nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 6;289(10):520–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309062891007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon F. J. Comments on immunopathology. Mil Med. 1966 Sep;131(9 Suppl):1233–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lees R. S. Fat transport in lipoproteins--an integrated approach to mechanisms and disorders. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 5;276(1):34–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701052760107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTMAN A., SHAFRIR E. ADIPOSE TISSUE IN EXPERIMENTAL NEPHROTIC SYNDROME. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:702–706. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germuth F. G., Jr, Senterfit L. B., Pollack A. D. Immune complex disease. I. Experimental acute and chronic glomerulonephritis. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1967 Apr;120(4):225–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glueck H. I., MacKenzie M. R., Glueck C. J. Crystalline IgG protein in multiple myeloma: identification effects on coagulation and on lipoprotein metabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 May;79(5):731–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Chromic chloride: a coupling reagent for passive hemagglutination reactions. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS L. A., PAGE I. H. AN UNUSUAL SERUM LIPOPROTEIN-GLOBULIN COMPLEX IN A PATIENT WITH HYPERLIPEMIA. Am J Med. 1965 Feb;38:286–297. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODA M., PUCK T. T. The interaction of mammalian cells with antibodies. I. J Exp Med. 1961 Mar 1;113:599–610. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poullin M. F., Vilain C., Beaumont J. L. Une méthode de purification des beta-lipoprotéines sériques. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1967 May-Jun;25(5):645–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENMAN R. H., FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O. The causal role of plasma albumin deficiency in experimental nephrotic hyperlipemia and hypercholesteremia. J Clin Invest. 1956 May;35(5):522–532. doi: 10.1172/JCI103305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Kibukamusoke J. W. Evidence for soluble immune complexes in the pathogenesis of the glomerulonephritis of quartan malaria. Lancet. 1969 Feb 8;1(7589):283–285. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Matsuda I. Lipoprotein lipase in clinical and experimental nephrosis. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Dec;30(3):787–794. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]