Abstract
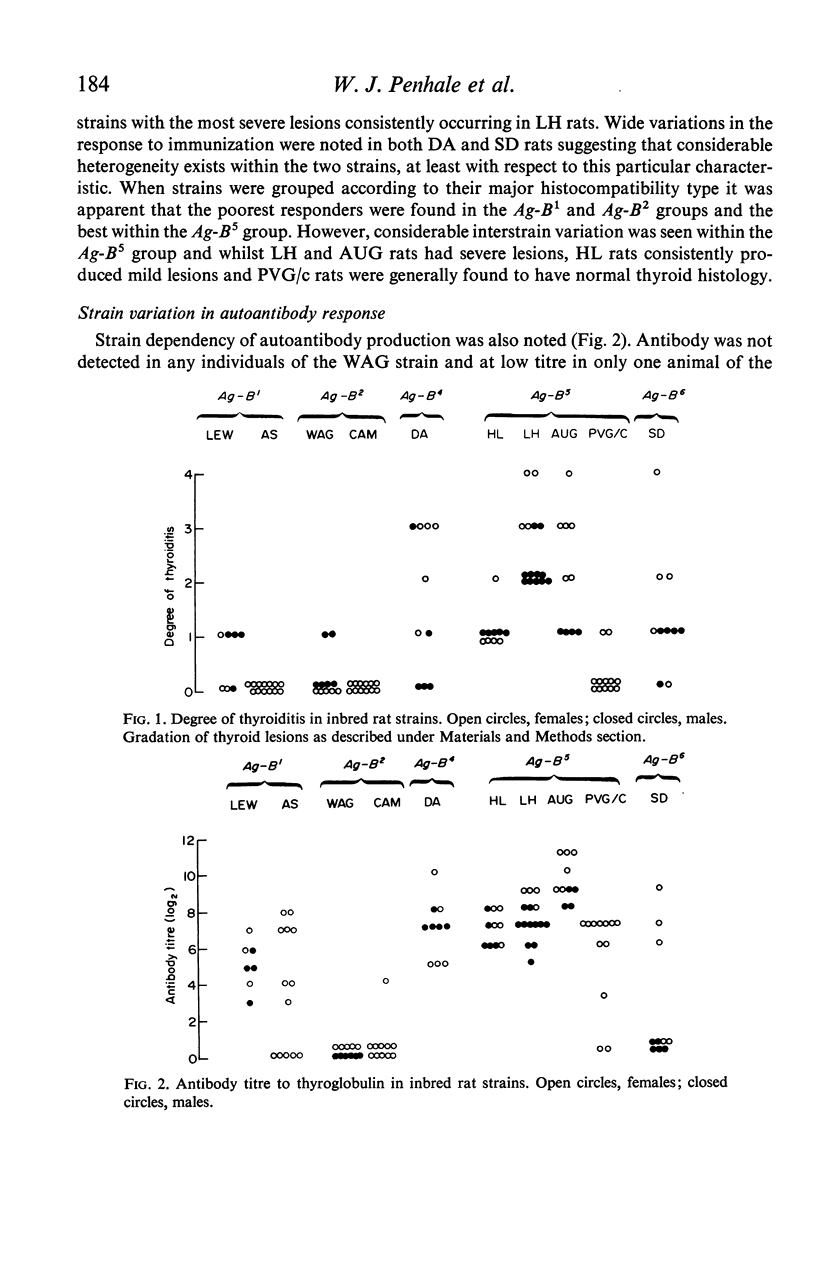
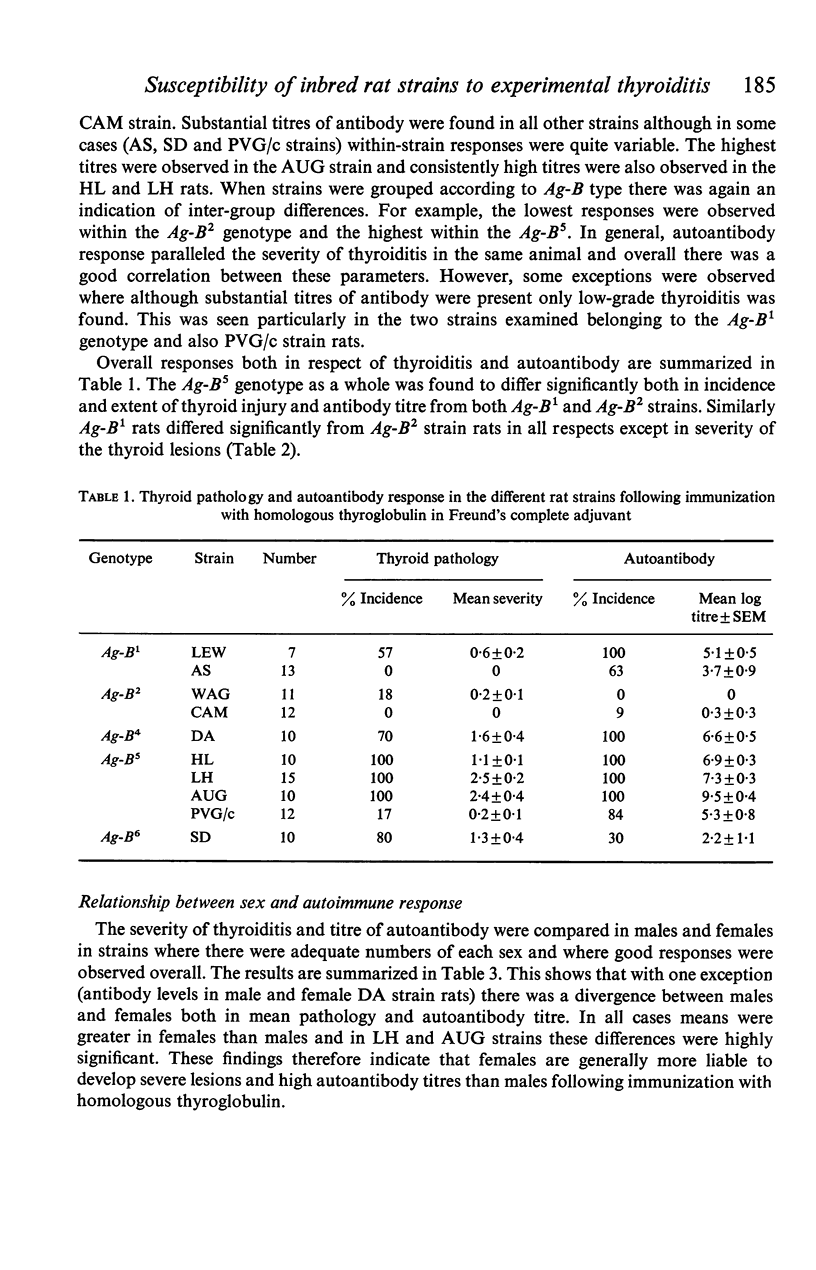
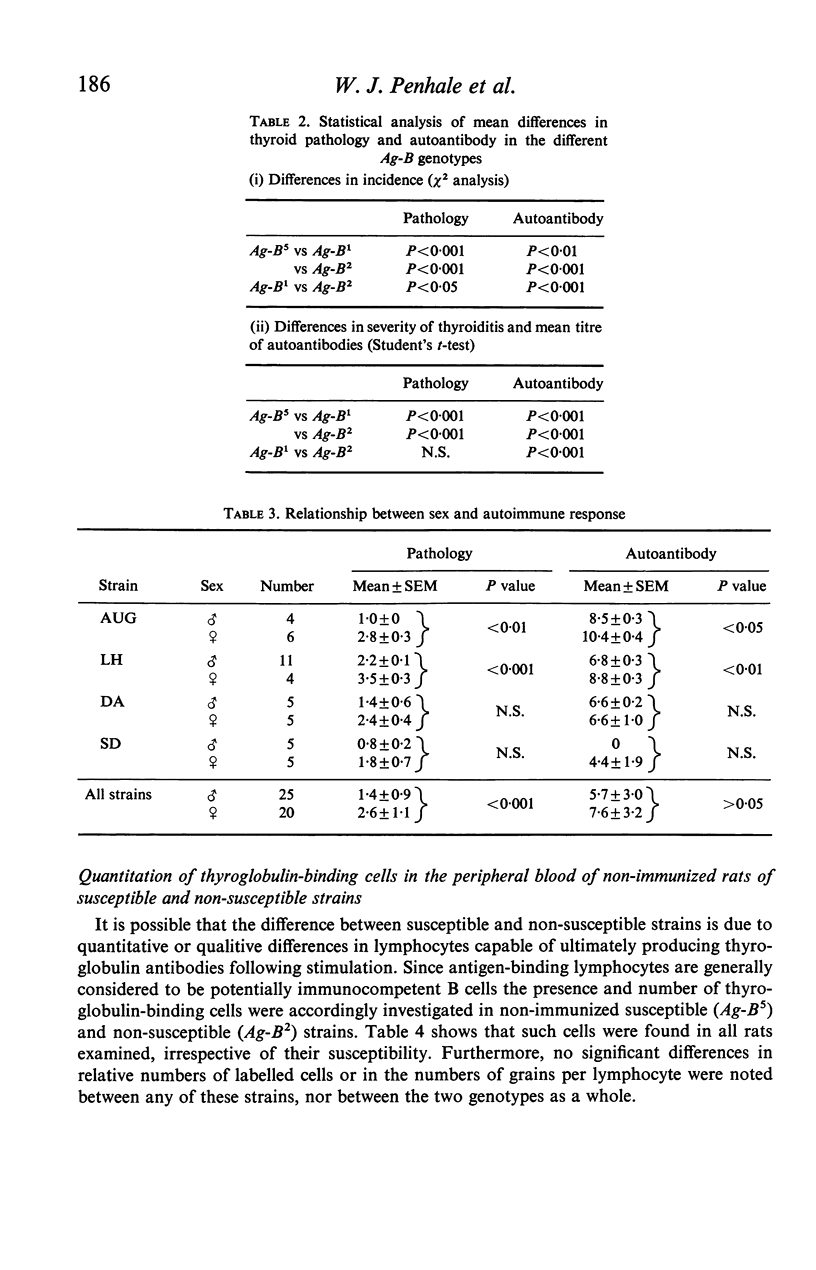
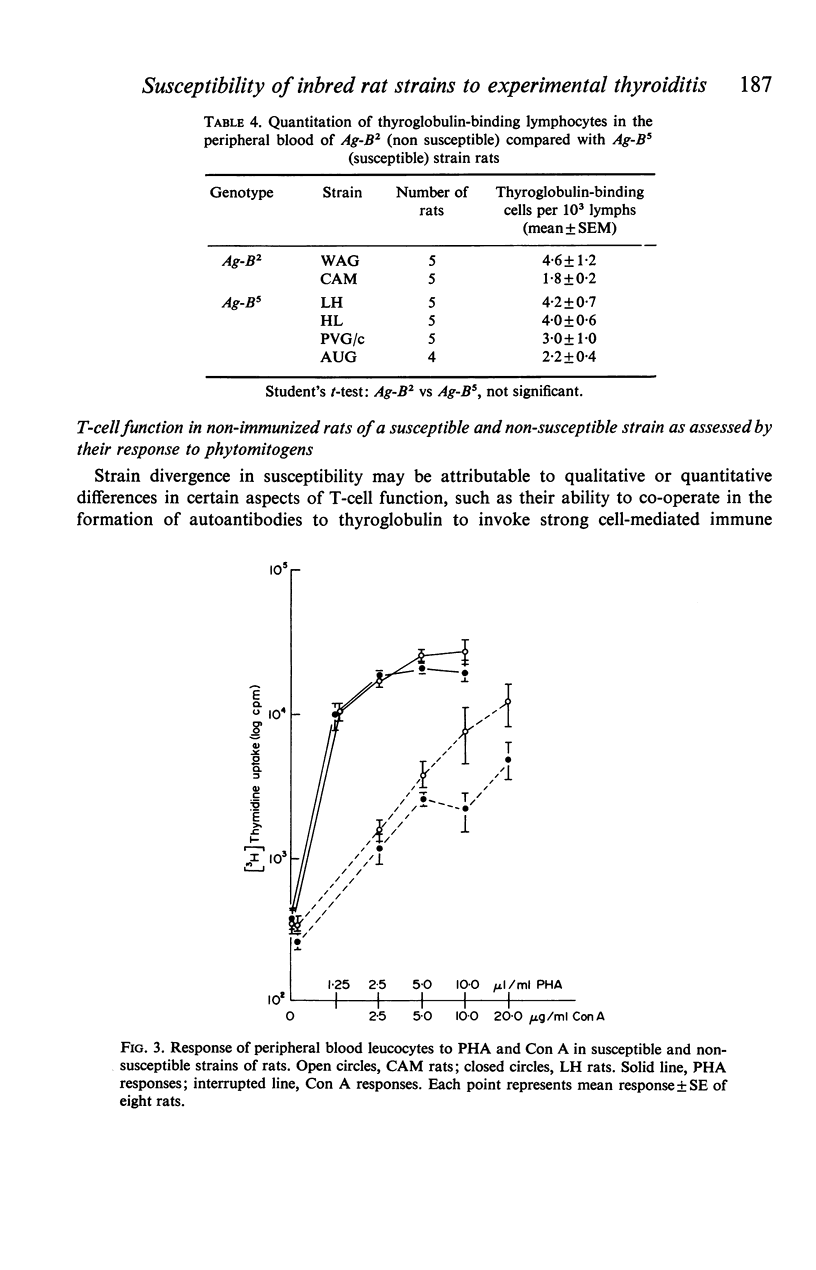
Ten inbred strains of rats were immunized with crude homologous thyroglobulin emulsified in Freund's complete adjuvant in order to investigate strain susceptibility to the induction of both thyroiditis and antibody to thyroglobulin. Two strains (LH and AUG) were found to be extremely susceptible and had 100% incidence of thyroid lesions which in general varied from moderate to very severe (mean index of pathology+/-SE, 2-5+/-0-2 and 2-1+/-0-4 respectively). One other strain (HL) also had 100% incidence of lesions but there were consistently mild in character (1-1+/-0-1). Two strains (DA and SD) were variable, with thyroid change varying from negative to severe. Three strains (LEW, WAG and PVG/c) had occasional lesions and the remaining two strains (AS and CAM) showed no thyroid change. Four strains (LH, AUG, HL and DA) consistently produced good antibody responses to thyroglobulin (mean titres+/-SE 7-3+/-0-3, 9-5+/-0-4, 6-9+/-0-3 and 6-6+/-0-5 respectively). In contrast WAG and CAM rats failed to develop autoantibody and the responses of AS, PVG/c and SD strain rats were quite variable. Although the autoantibody response generally correlated well with the presence of thyroiditis in a particular strain, LEW, AS and PVG/c rats often had good antibody levels with minimal thyroid lesions. Females of the most susceptible strains (LH and AUG) were found to have significantly more severe thyroid lesions and higher antibody titres to thyroglobulin than males. The most susceptible strains were all found to be of the Ag-B5 major histocompatibility genotype whilst the least susceptible were of the Ag-B2 genotype. However, wide interstrain variability was noted within the Ag-B5 genotype particularly with respect to the induction and extent of thyroid lesions. It was not found possible to relate the divergence in susceptibility between rat strains of Ag-B5 and Ag-B2 genotypes to differences in respective numbers of thyroglobulin-binding cells within the circulation of the non-immunized animal. Similarly, there were no differences in response between a susceptible (LH) and non-susceptible (CAM) strain to the phytomitogens PHA and Con A.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ada G. L. Antigen binding cells in tolerance and immunity. Transplant Rev. 1970;5:105–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1970.tb00358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Denman A. M., Barnes R. D. Cooperating and controlling functions of thymus-derived lymphocytes in relation to autoimmunity. Lancet. 1971 Jul 17;2(7716):135–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOEHME D. RESPONSE OF RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM TO EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ORCHITIS IN A GENETICALLY SUSCEPTIBLE AND RESISTANT MOUSE GENOTYPE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Feb;118:374–376. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankhurst A. D., Torrigiani G., Allison A. C. Lymphocytes binding human thyroglobulin in healthy people and its relevance to tolerance for autoantigens. Lancet. 1973 Feb 3;1(7797):226–230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrt P., Ada G. L. An in vitro reaction between labelled flagellin or haemocyanin and lymphocyte-like cells from normal animals. Immunology. 1969 Oct;17(4):503–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., McLeman D., Irvine W. J. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity induced by pre-incubation with serum from patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Nov;15(3):467–470. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Penhale W. J., McLeman D., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. Lymphocyte-dependent antibody-mediated cytotoxicity in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):153–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clagett J. A., Weigle W. O. Roles of T and B lymphocytes in the termination of unresponsiveness to autologous thyroglobulin in mice. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):643–660. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton B. A., Weigle W. E. Cellular events during the induction of experimental thyroiditis in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1605–1615. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East J., De Sousa M. A., Parrott D. M., Jaquet H. Consequences of neonatal thymectomy in New Zealand black mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Mar;2(2):203–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser D. L., Newlin C. M., Palm J., Gonatas N. K. Genetic control of susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. Science. 1973 Aug 31;181(4102):872–873. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4102.872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green I., Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Histocompatibility-linked genetic control of the immune response to hapten guinea pig albumin conjugates in inbred guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. A., Stedronska J. The susceptibility of rat strains to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Immunology. 1973 May;24(5):879–884. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J., McDevitt H. O. Frequency and characteristics of antigen binding cells in genetic high and low responder mice. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):179–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE J. M., OLITSKY P. K., SCHNEIDER H. A., ZINDER N. D. Role of heredity in experimental disseminated encephalomyelitis in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Mar;85(3):430–432. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Tanaka Y., Sakakura T., Kojima A. Murine thyroiditis induced by neonatal thymectomy. Experientia. 1973 Nov 15;29(11):1396–1398. doi: 10.1007/BF01922839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhale W. J., Farmer A., Maccuish A. C., Irvine W. J. A rapid micro-method for the phytohaemagglutinin-induced human lymphocyte transformation test. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):155–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhale W. J., Farmer A., McKenna R. P., Irvine W. J. Spontaneous thyroiditis in thymectomized and irradiated Wistar rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Oct;15(2):225–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H. Strain differences in the immune responses of mice. 3. A raised tolerance threshold in NZB thymus cells. Immunology. 1971 Dec;21(6):1037–1043. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts I. M., Whittingham S., Mackay I. R. Tolerance to an autoantigen-thyroglobulin. Antigen-binding lymphocytes in thymus and blood in health and autoimmune disease. Lancet. 1973 Oct 27;2(7835):936–940. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose N. R., Vladutiu A. O., David C. S., Shreffler D. C. Autoimmune murine thyroiditis. V. Genetic influence on the disease in BSVS and BRVR mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Oct;15(2):281–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague P. O., Friou G. J. Antinuclear antibodies in mice. II. Transmission with spleen cells; inhibition or prevention with thymus or spleen cells. Immunology. 1969 Nov;17(5):665–675. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbaniak S. J., Penhale W. J., Irvine W. J. Circulating lymphocyte subpopulations in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Nov;15(3):345–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladutiu A. O., Rose N. R. Autoimmune murine thyroiditis relation to histocompatibility (H-2) type. Science. 1971 Dec 10;174(4014):1137–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4014.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch P., Rose N. R., Kite J. H., Jr Neonatal thymectomy increases spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):575–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick G., Kite J. H., Jr, Cole R. K., Witebsky E. Spontaneous thyroiditis in the obese strain of chickens. 3. The effect of bursectomy on the development of the disease. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):45–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. M., Moore M. J. Linkage of susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis to the major histocompatibility locus in the rat. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):775–783. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Quantitative studies on the mixed lymphocyte interaction in rats. I. Conditions and parameters of response. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):625–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


