Abstract
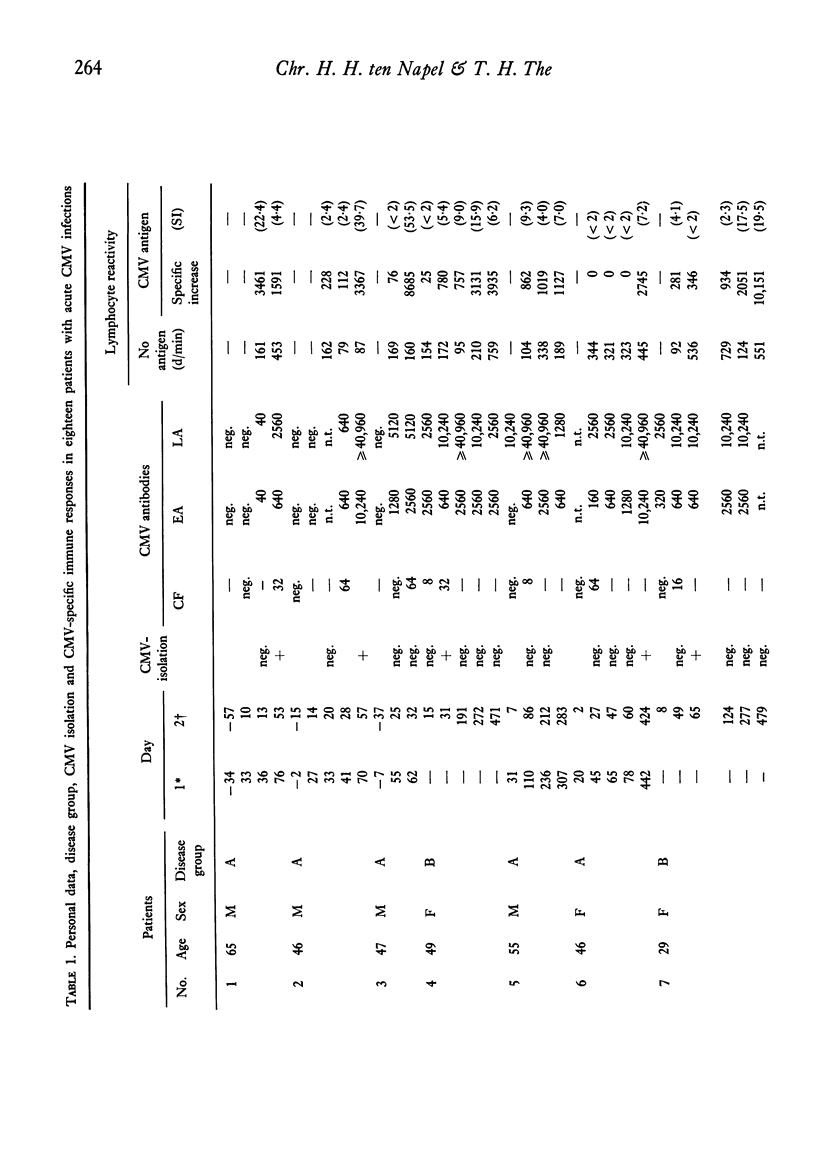
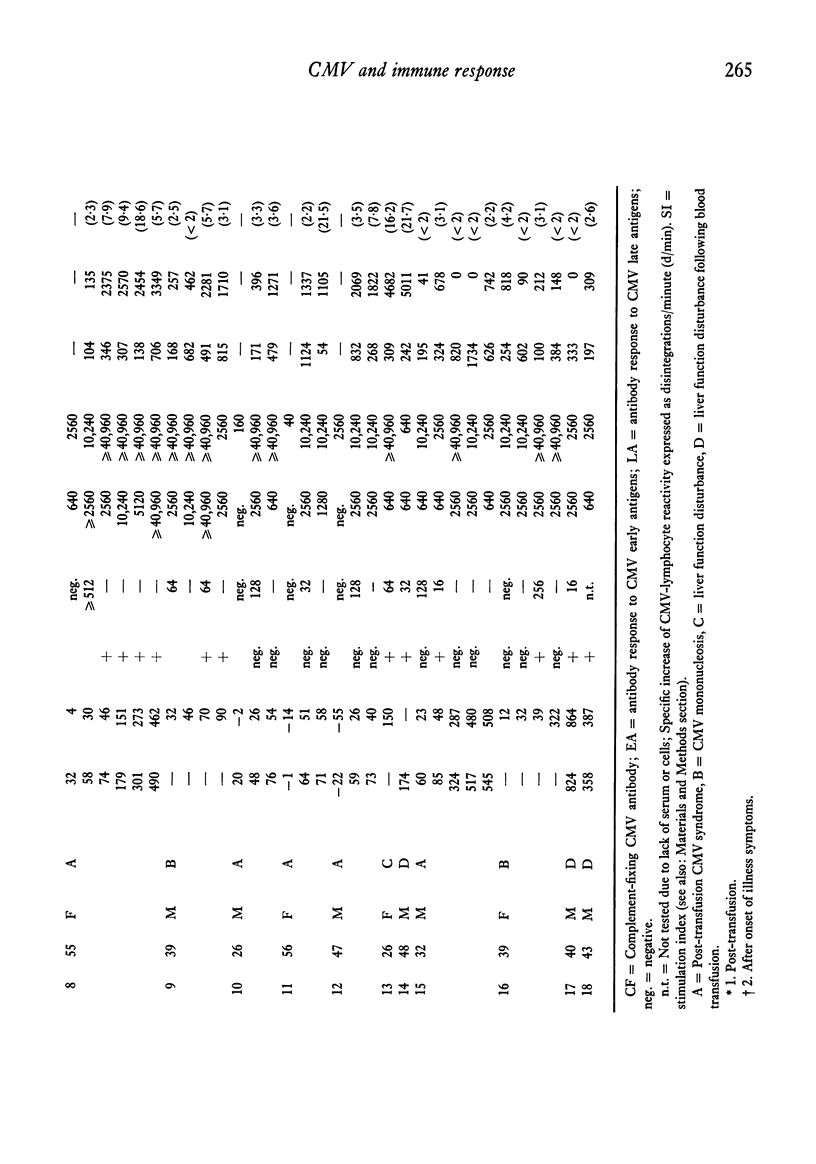
Cytomegalovirus-induced lymphocyte reactivity (CMV-LR) of peripheral blood lymphocytes and antibodies against CMV-early (EA) and late (LA) antigens were studied in eighteen patients with documented acute CMV infections and seventy-six healthy persons. The development of a positive CMV-LR test lagged far behind the appearance of virus-specific antibodies. Positive CMV-LR tests were shown in all fourteen patients who could be tested twice or more. The median value of twenty-two tests in the acute phase (<50 days) was 269 d/min and the median of thirty tests in the post-illness phase (>50 days) was 1301 d/min (P<0·02). Once positive CMV-LR remained so during the follow-up period, up to 479 days after the onset of illness symptoms. In the meantime the LA and EA antibody response remained positive. Only two patients studied once showed negative CMV-LR responses while their serum contained high CMV-EA antibody titres. In CMV-LA seropositive healthy individuals who also possessed CMV-EA antibodies (LA+EA+) CMV-LR was higher (P<0·01) than in the LA seropositives who lacked EA antibodies (LA+EA−). The young LA+EA+ individuals, however, showed better (P<0·02) CMV−LR test results than the aged ones while their CMV antibody levels—especially the EA antibodies (P<0·02)—were lower. This phenomenon of increased CMV antibody production in relation to depressed CMV-LR is possibly caused by age-associated impairment of T lymphocyte function. The combined CMV-LR and EA antibody tests may provide useful means to study the specific immunological host/virus relationship in different clinical situations.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutner K. R., Morag A., Deibel R., Morag B., Raiken D., Ogra P. L. Strain-specific local and systemic cell-mediated immune responses to cytomegalovirus in humans. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.82-87.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. II. Antigen triggering of T and B cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1122–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Payne J. E., Berne T. V., Moore T. C., Henle W., Montgomerie J. Z., Chatterjee S. N., Guze L. B. Epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infection after transplantation and immunosuppression. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):421–433. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrz R. C., Marker S. C., Knorr S. O., Kalis J. M., Balfour H. H., Jr Specific cell-mediated immune defect in active cytomegalovirus infection of young children and their mothers. Lancet. 1977 Oct 22;2(8043):844–847. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Cereda P. M., Cattaneo E., Achilli G., Revello M. G. Immunoglobulin G to virus-specific early antigens in congenital, primary, and reactivated human cytomegalovirus infections. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):833–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.833-841.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto S., Tomino S., Inomata K., Kotegawa S., Saito T., Kuroki M., Mitsuya H., Hisamitsu S. Age-related changes in the subsets and functions of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1773–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., Käriäinen L. Cytomegalovirus as a possible cause of a disease resembling infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1965 Nov 6;2(5470):1099–1102. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5470.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Klemola E., Paloheimo J. Rise of cytomegalovirus antibodies in an infectious-mononucleosis-like syndrome after transfusion. Br Med J. 1966 May 21;1(5498):1270–1272. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5498.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenhuysen M. M., The T. H., Nieweg H. O., Kapsenberg J. G. Demonstration of IgM cytomegalovirus-antibodies as an aid to early diagnosis in adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Mar;6(3):387–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller-Larsen A., Andersen H. K., Heron I., Sarov I. In vitro stimulation of human lymphocytes by purified cytomegalovirus. Intervirology. 1975;6(4-5):249–257. doi: 10.1159/000149479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morag A., Morag B., Bernstein J. M., Beutner K., Ogra P. L. In vitro correlates of cell-mediated immunity in human tonsils after natural or induced Rubella virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):409–416. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Aguilar-Torres F. G., Balay J., Heim L. R. Assessment of the status of cell-mediated immunity in cytomegalovirus-infected renal allograft recipients. Cell Immunol. 1978 Apr;37(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Andersen H. K., Spencer E. S., Klein G. Antibodies against cytomegalovirus-induced early antigens (CMV-EA) in immunosuppressed renal-allograft recipients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jun;28(3):502–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Klein G., Langenhuysen M. M. Antibody reactions to virus-specific early antigens (EA) in patients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jan;16(1):1-7,9-12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waner J. L., Budnick J. E. Blastogenic response of human lymphocytes to human cytomegalovirus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):44–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


