Abstract
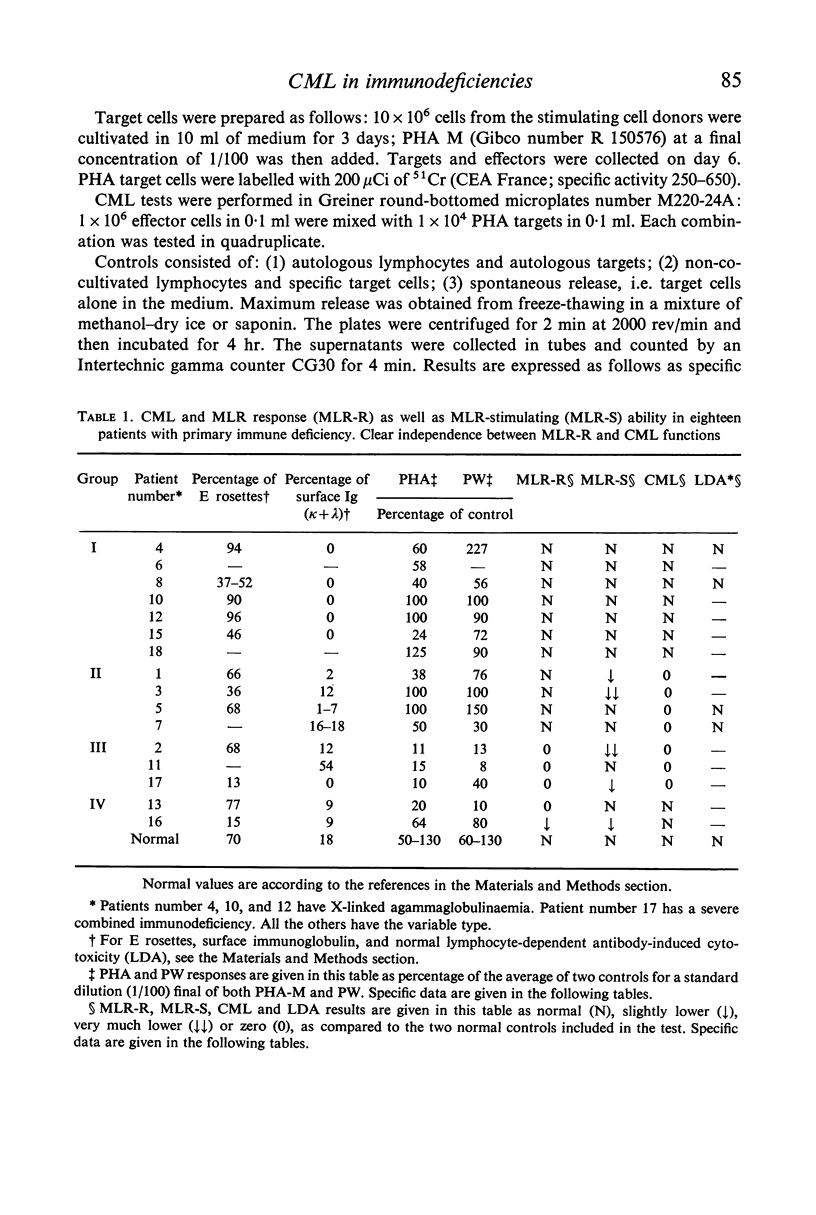
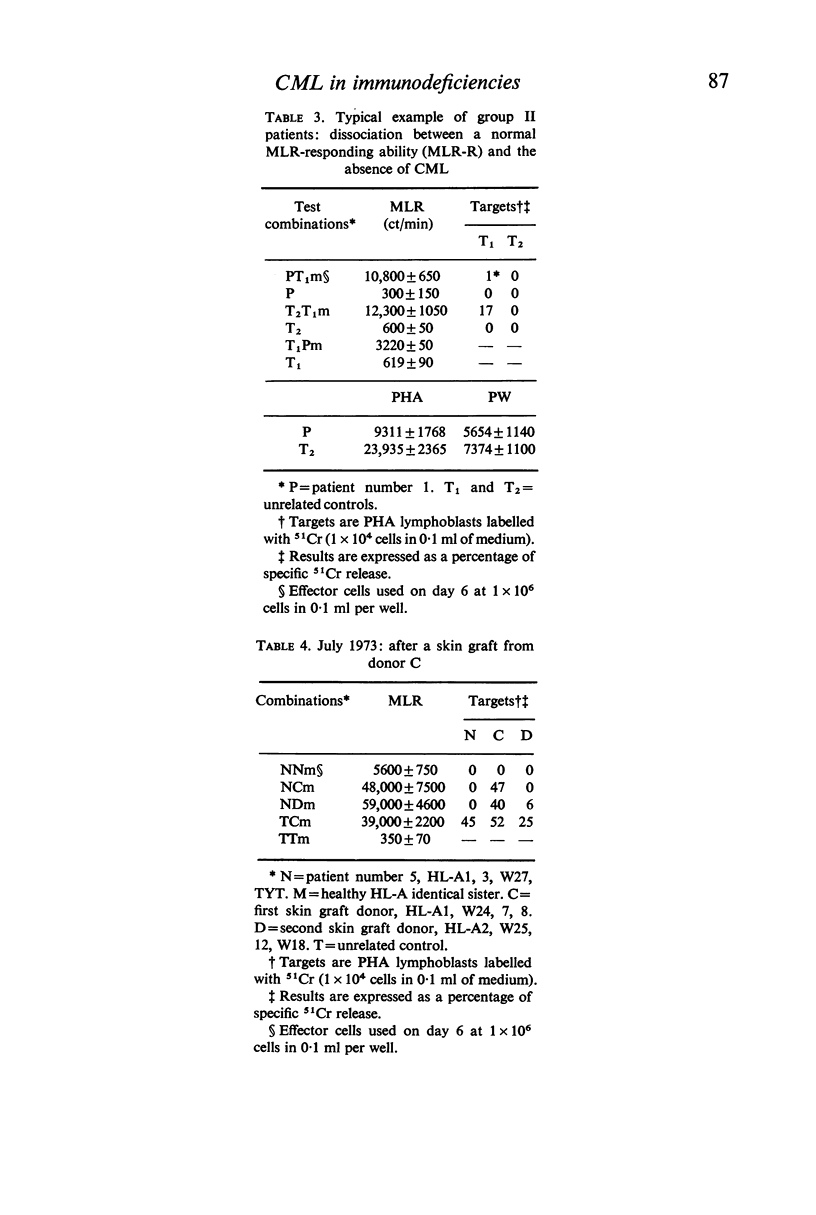
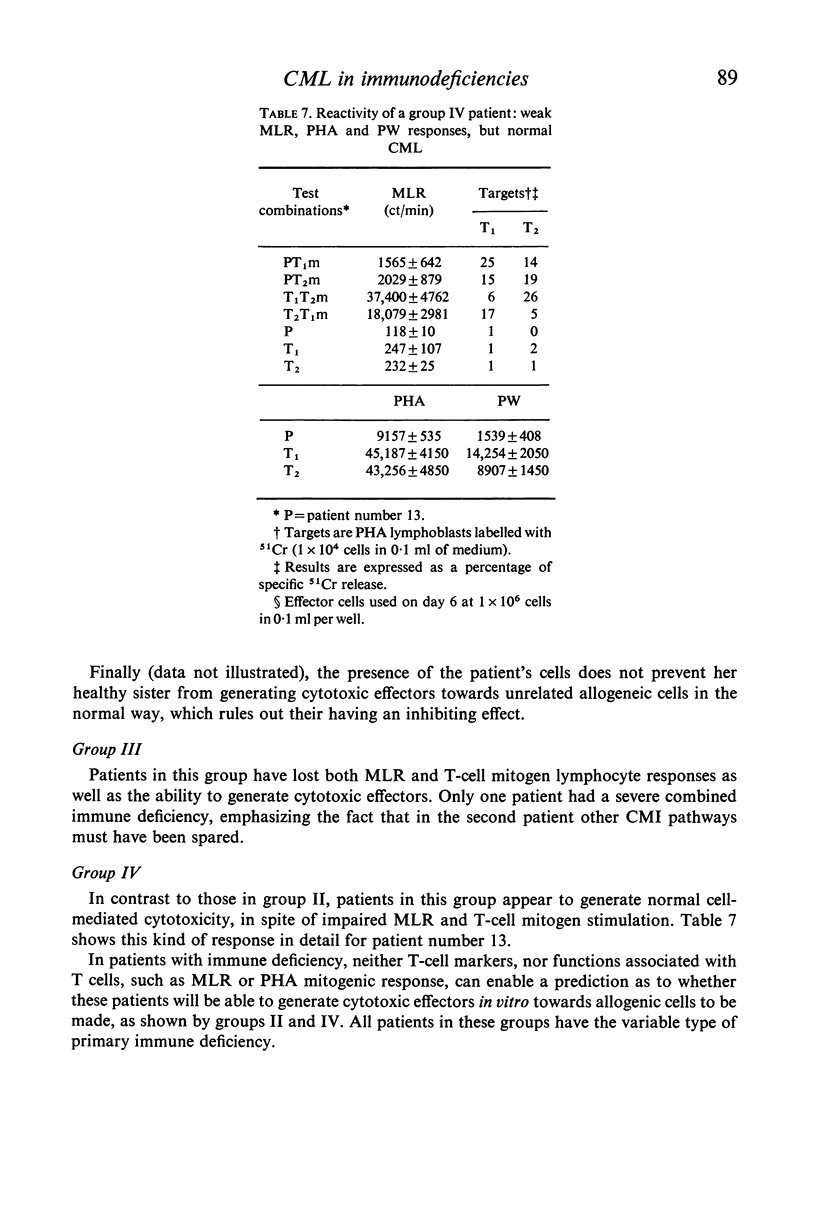
Cell-mediated lympholysis (CML) in eighteen patients suffering from primary immune deficiencies was studied. Fourteen of these patients had the variable type. Mixed lymphocyte response (MLR) and CML were clearly found to be independent: as well as two groups of patients in whom the two functions were either both normal or both deficient, two other groups were found in whom they were definitely separate. In one group MLR and T-cell mitogen responses were normal but no CML occurred against allogenic lymphocytes, and in the other cytotoxic effectors were generated normally but MLR and T-cell mitogen responses were very much lower than normal. These results show that the functions are independent, and are compatible with the theory that more than one subpopulation of T cells is involved. Neither the MLR or T-cell mitogen responses of these patients can predict their ability to generate cytotoxic effectors.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter B. J., Schendel D. J., Bach M. L., Bach F. H., Klein J., Stimpfling J. H. Cell-mediated lympholysis. Importance of serologically defined H-2 regions. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1303–1309. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., Segall M., Zier K. S., Sondel P. M., Alter B. J., Bach M. L. Cell mediated immunity: separation of cells involved in recognitive and destructive phases. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):403–406. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner K. T., Mauel J., Cerottini J. C., Chapuis B. Quantitative assay of the lytic action of immune lymphoid cells on 51-Cr-labelled allogeneic target cells in vitro; inhibition by isoantibody and by drugs. Immunology. 1968 Feb;14(2):181–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Asofsky R. Synergy among lymphoid cells mediating the graft-versus-host response. 3. Evidence for interaction between two types of thymus-derived cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):764–779. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. C., Stites D. P., Fudenberg H. H. Dissociation of responses to phytohaemagglutinin and adult allogeneic lymphocytes in human foetal lymphoid tissues. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):279–281. doi: 10.1038/newbio241279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity, allograft rejection, and tumor immunity. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:67–132. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G., Wu A. Y., Waksman B. H. Cellular differentiation in the thymus. 3. Surface properties of rat thymus and lymph node cells separated on density gradients. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1107–1121. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eijsvoogel V. P., Du Bois R., Melief C. J., Zeylemaker W. P., Raat-Koning L., de Groot-Kooy L. Lymphocyte activation and destruction in vitro in relation to MLC and HL-A. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):415–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eijsvoogel V. P., du Bois M. J., Meinesz A., Bierhorst-Eijlander A., Zeylemaker W. P., Schellekens P. T. The specificty and the activation mechanism of cell-mediated lympholysis (CML) in man. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1675–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fudenberg H., Good R. A., Goodman H. C., Hitzig W., Kunkel H. G., Roitt I. M., Rosen F. S., Rowe D. S., Seligmann M., Soothill J. R. Primary immunodeficiencies. Report of a World Health Organization Committee. Pediatrics. 1971 May;47(5):927–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P., Wigzell H., Blomgren H., Svedmyr E. A. Cells mediating specific in vitro cytotoxicity. II. Probable autonomy of thymus-processed lymphocytes (T cells) for the killing of allogeneic target cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):890–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häyry P., Defendi V. Mixed lymphocyte cultures produce effector cells: model in vitro for allograft rejection. Science. 1970 Apr 3;168(3927):133–135. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3927.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightbody J., Bernoco D., Miggiano V. C., Ceppellini R. Cell mediated lympholysis in man after sensitization of effector lymphocytes through mixed leukocyte cultures. G Batteriol Virol Immunol. 1971 Sep-Dec;64(9):243–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawas C., Christen Y., Legrand L., Sasportes M., Dausset J. Cellular and humoral response against determinants other than the classical HL-A specificities. Evidence for at least one system independent of the major histocompatibility complex. Transplantation. 1974 Sep;18(3):256–266. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197409000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawas C., Sasportes M., Christen Y., Bernard A., Dausset J., Alter B. J., Bach M. L. Cell-mediated lympholysis (CML) in the absence of LD2 mixed lymphocyte reaction and CML in the presence of SD1-SD2 identity in two HL-S-genotyped families. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1683–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen H. J., Bach F. H., Hong R., Good R. A. Lymphocyte studies in congenital thymic dysplasia: The one-way stimulation test. J Pediatr. 1968 Feb;72(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabholz M., Vives J., Young H. M., Meo T., Miggiano V., Rijnbeek A., Shreffler D. C. Cell-mediated cell lysis in vitro: genetic control of killer cell production and target specificities in the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1974 May;4(5):378–387. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasportes M., Bernard A., Dausset J. Abnormal mixed leucocyte reaction in bone marrow aplasia. Br Med J. 1973 Oct 6;4(5883):48–49. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5883.48-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasportes M., Lebrun A., Rapaport F. T., Dausset J. Studies of skin allograft survival and mixed lymphocyte culture reaction in Hl-A-genotyped families. Transplant Proc. 1972 Jun;4(2):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solliday S., Bach F. H. Cytotoxicity: specificity after in vitro sensitization. Science. 1970 Dec 25;170(3965):1406–1409. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3965.1406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Paul W. E. Functional heterogeneity of murine lymphoid cells. 3. Differential responsiveness of T cells to phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A as a probe for T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):362–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Paul W. E., Henney C. S. Functional heterogeneity of murine lymphoid cells. IV. Allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reactivity and cytolytic activity as functions of distinct T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):652–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Röllinghoff M., Nossal G. J. T-cell-mediated immune responses induced in vitro: a probe for allograft and tumor immunity. Transplant Rev. 1973;17(0):3–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H. The correlation between the proliferative and the cytotoxic responses of mouse lymphocytes to allogeneic cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):630–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis E. J., Amos D. B. Three closely linked genetic systems relevant to transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3031–3035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


