Abstract
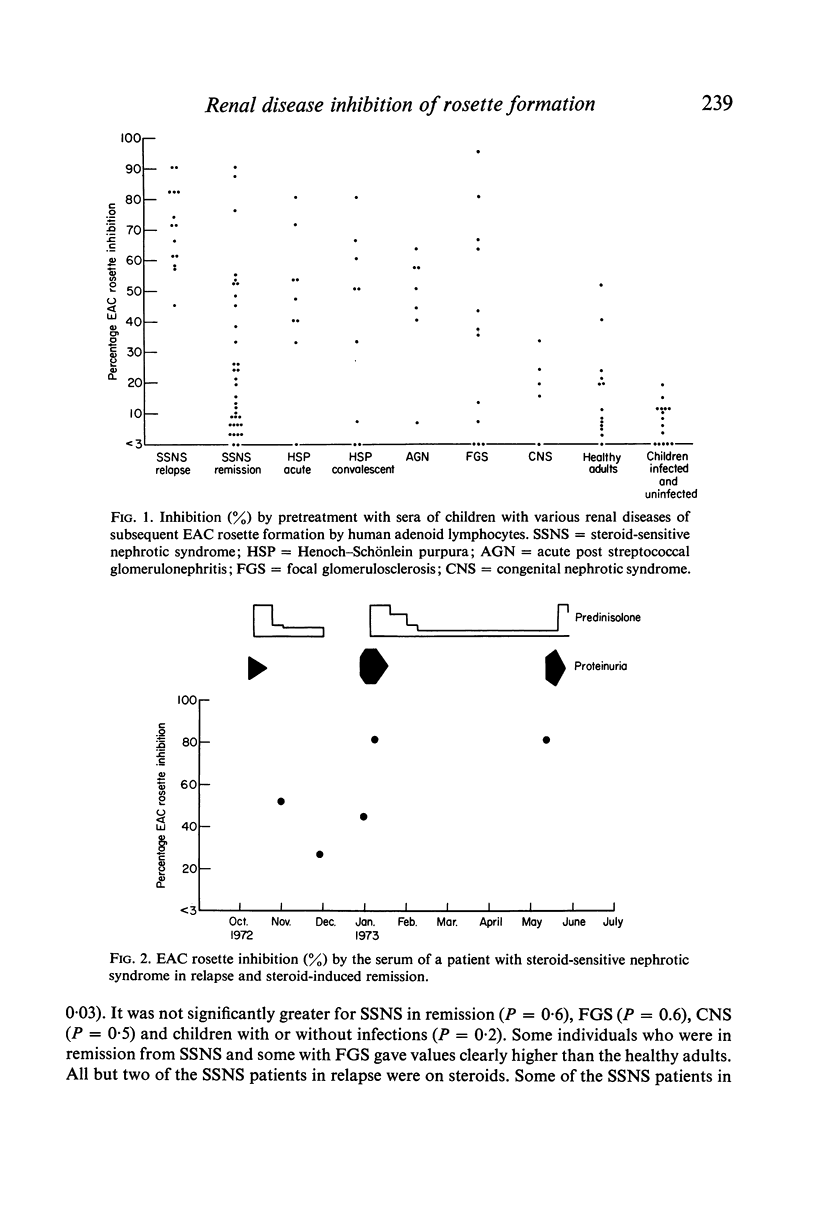
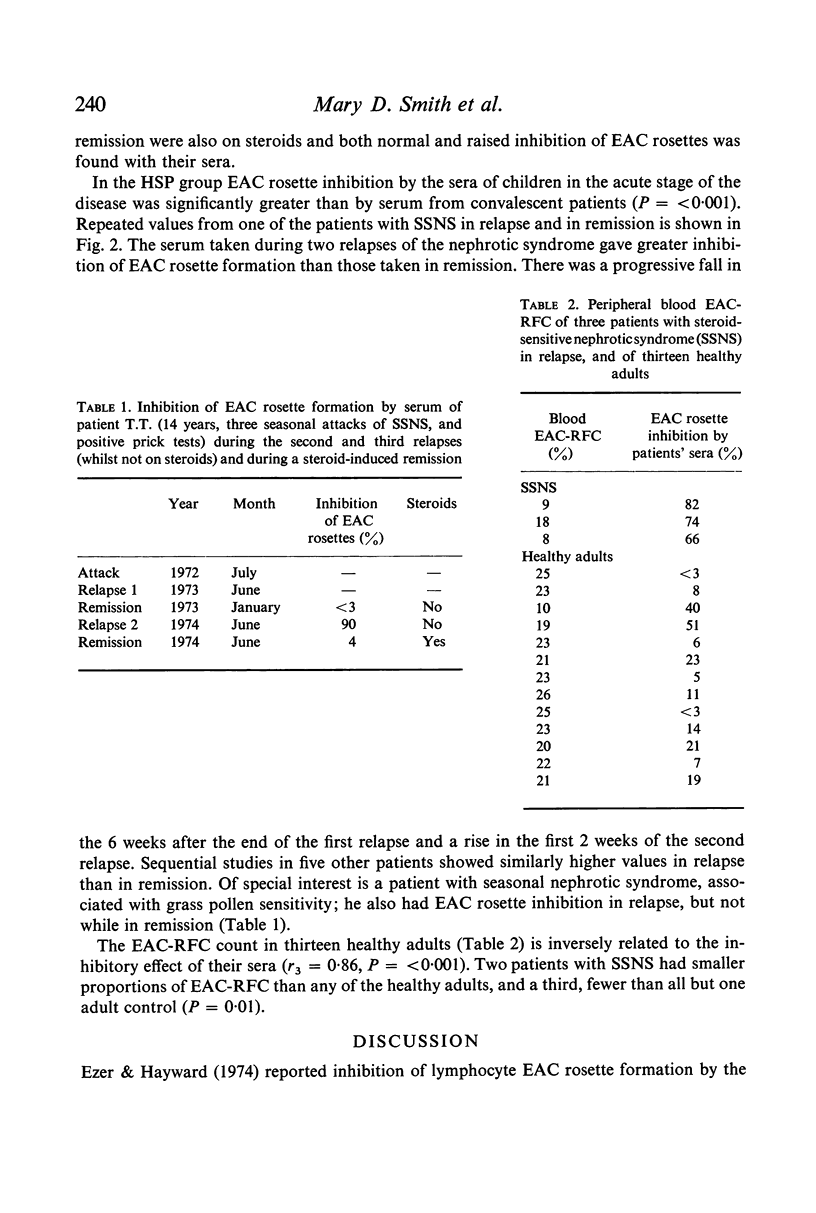
Sera from patients with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SSNS) in relapse, Henoch-Schonlein purpura with nephritis (HSP) and acute post-strptococcal glomerulonephritis inhibited EAC rosette formation by normal human lymphocytes; a similar effect was seen in some patients with focal glomerulosclerosis, but not in patients with congenital neophrotic syndrome. There was significantly less inhibition by sera of SSNS and HSP patients in remission. There were fewer EAC rosette-forming cells (EAC-RFC) in the blood of three patients with SSNS in relapse, suggesting that such blockade occurred in vivo. These findings, interpreted as evidence of circulating activated C3 in the sera, provide further indirect evidence of the immunopathogenesis of these diseases. Sera of healthy adults inhibited EAC rosette formation to a small extent which correclated inversely with the numbers of EAC-RFC in their blood. The EAC rosette inhibition test may be sensitive enough to detect normal variations of complement activation in healthy individuals.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAINEY J. D., BREWER D. B., HARDWICKE J., SOOTHILL J. F. The nephrotic syndrome. Diagnosis by renal biopsy and biochemical and immunological analyses related to the response to steroid therapy. Q J Med. 1960 Apr;29:235–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond K. N., Michael A. F., Good R. A., Vernier R. L. The nephrotic syndrome of childhood: immunologic, clinical, and pathologic correlations. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):620–630. doi: 10.1172/JCI105376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden A., Bianco C., Nussenzweig Mechanism of binding of soluble immune complexes to lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jun;7(3):459–473. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezer G., Hayward A. R. Inhibition of complement-dependent lymphocyte rosette formation: a possible test for activated complement products. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Feb;4(2):148–150. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Paronetto F. IgE in glomeruli of patients with nephrotic syndrome. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1097–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91838-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDWICKE J., SOOTHILL J. F., SQUIRE J. R., HOLTI G. Nephrotic syndrome with pollen hypersensitivity. Lancet. 1959 Mar 7;1(7071):500–502. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Vernier R. L., Najarian J. S., Raij L., Simmons R. L., Michael A. F. Recurrence of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome after renal transplantation. Lancet. 1972 Aug 19;2(7773):343–348. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91734-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOUVALAINEN K., VAINIO T., HJELT L., HALLMAN N. Behaviour of skin grafted from infant to mother in congenital nephrosis families. Ann Paediatr Fenn. 1962;8:173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H. Serum complement component levels in human glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Oct;75(4):555–560. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngu J. L., Barratt T. M., Soothill J. F. Immunoconglutinin and complement changes in steroid sensitive relapsing nephrotic syndrome of children. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):109–116. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. G., Cameron J. S., Johansson S. G., Ogg C. S., Peters D. K., Weller R. O. Seasonal nephrotic syndrome. Description and immunological findings. Clin Allergy. 1975 Jun;5(2):121–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy L. P., Westberg N. G., Michael A. F. Nephrotic syndrome--no evidence for a role for IgE. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Apr;13(4):553–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman S. T., Barratt T. M., Soothill J. F. Immunoconglutinin and complement studies in congenital nephrotic syndrome and nephritis of Henoch-Schönlein purpura in children. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Dec;46(250):838–841. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.250.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F. Altered complement component C3A (beta-1C--beta-1A) in patients with glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jan;2(1):83–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Iverson G. M., Oppenheim J. J. Induction of guinea pig B-cell lymphokine synthesis by mitogenic and nonmitogenic signals to Fc, Ig, and C3 receptors. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1631–1645. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


