Abstract
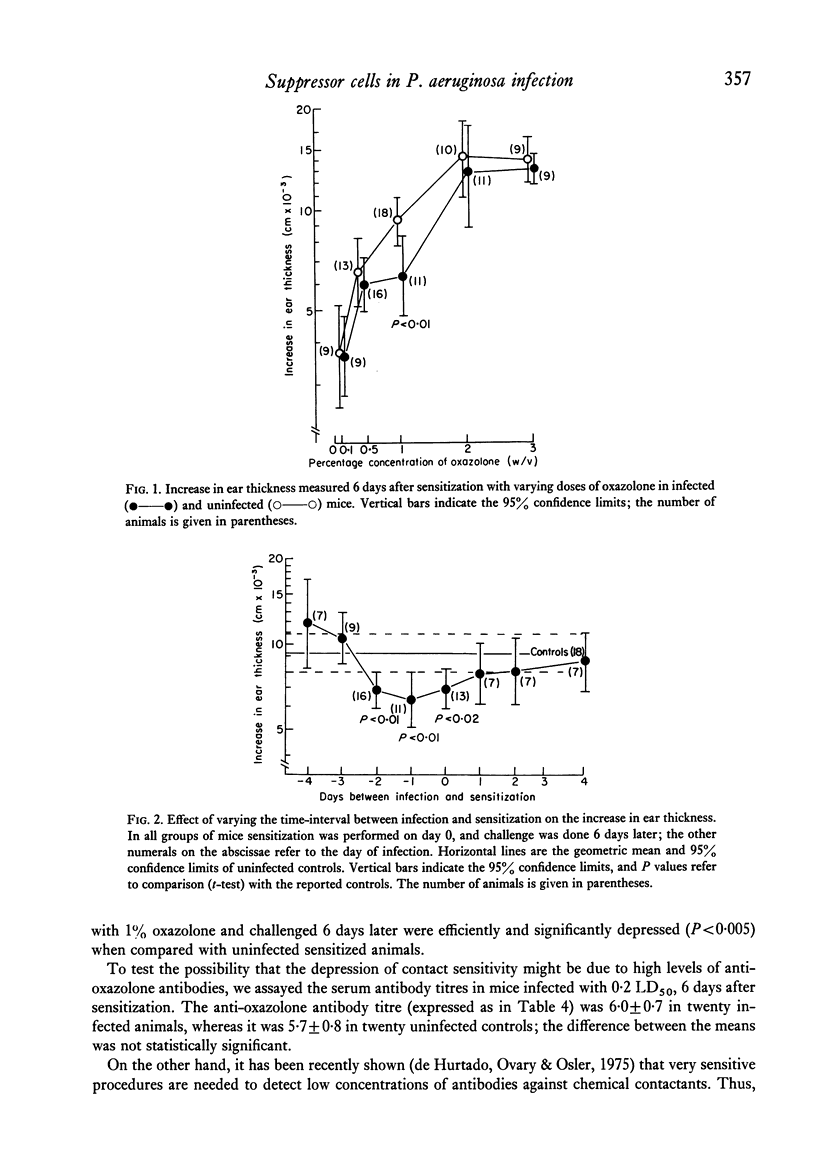
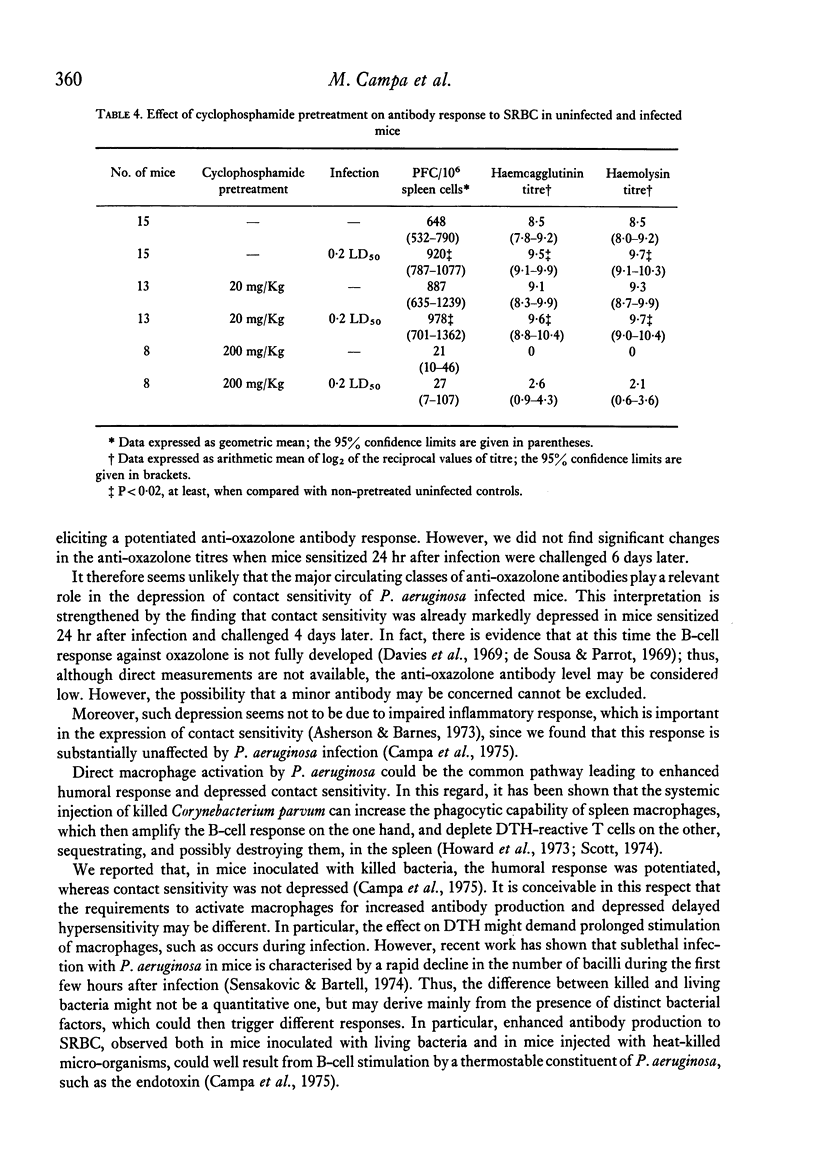
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection depresses contact sensitivity to 2-phenyl-4-ethoximethylene-oxazolone (oxazolone), and enhances the antibody response to sheep erythrocytes (SRBC) in the mouse. Anti-oxazolone antibody titres were found not to be significantly different in infected and uninfected animals; thus, the major circulating classes of antibodies do not seem to be responsibile for the observed depression of skin reactivity. Low dose (20 mg/Kg) cyclophosphamide (CY) pretreatment induced a further potentiation of antibody response to SRBC, and prevented depression of contact sensitivity in infected mice. On the other hand, when infected animals were pretreated with high doses (200 mg/Kg) of CY, antibody production was completely suppressed, whereas contact sensitivity was unaffected. Since CY treatment is known to selectively inhibit B lymphocytes, and since it can abrogate the infection-induced depression of reactivity to oxazolone, it is suggested that suppressor cells, which may have B-cell characteristics, are stimulated during P. aeruginosa infection in the mouse.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asherson G. L., Barnes R. M. Contact sensitivity in the mouse. IX. The role of immunological and non-immunological inflammation in the movement of lymphocytes to immunized lymph nodes. Immunology. 1973 May;24(5):885–894. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askenase P. W., Asherson G. L. Contact sensitivity to oxazolone in the mouse. VIII. Demonstration of several classes of antibody in the sera of contact sensitized and unimmunized mice by a simplified antiglobulin assay. Immunology. 1972 Sep;23(3):289–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askenase P. W., Hayden B. J., Gershon R. K. Augmentation of delayed-type hypersensitivity by doses of cyclophosphamide which do not affect antibody responses. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):697–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendinelli M., Toniolo A., Campa M. Immunodepression by Rowson-Parr virus in mice: effect of Rowson-Parr virus and Friend leukemia complex infections on background antibody-forming cells to various erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1024–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1024-1030.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campa M., Garzelli C., Falcone G. Depression of contact sensitivity and enhancement of antibody response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1252–1257. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1252-1257.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. J., Carter R. L., Leuchars E., Wallis V. The morphology of immune reactions in normal, thymectomized and reconstituted mice. II. The response to oxazolone. Immunology. 1969 Jul;17(1):111–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Parker D., Sommer G., Turk J. L. Suppressor cells in normal immunisation as a basic homeostatic phenomenon. Nature. 1974 Apr 12;248(449):612–614. doi: 10.1038/248612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phanupak P., Moorhead J. W., Claman H. N. Tolerance and contact sensitivity to DNFB in mice. 3. Transfer of tolerance with "suppressor T cells". J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1230–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak L., Turk J. L. Reversal of immunological tolerance by cyclophosphamide through inhibition of suppressor cell activity. Nature. 1974 Jun 14;249(458):654–656. doi: 10.1038/249654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Depression of delayed-type hypersensitivity by Corynebacterium parvum: mandatory role of the spleen. Cell Immunol. 1974 Aug;13(2):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensakovic J. W., Bartell P. F. The slime of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: biological characterization and possible role in experimental infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):101–109. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Parker D. Further studies on B-lymphocyte suppression in delayed hypersensitivity, indicating a possible mechanism for Jones-Mote hypersensitivity. Immunology. 1973 Apr;24(4):751–758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Parker D., Poulter L. W. Functional aspects of the selective depletion of lymphoid tissue by cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1972 Oct;23(4):493–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W., Möller G. Regulatory effect of antibody on the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:81–127. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembala M., Asherson G. L. Depression of the T cell phenomenon of contact sensitivity by T cells from unresponsive mice. Nature. 1973 Jul 27;244(5413):227–228. doi: 10.1038/244227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembala M., Asherson G. L. The effect of cyclophosphamide and irradiation on cells which suppress contact sensitivity in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Mar;23(3):554–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hurtado I., Ovary Z., Osler A. G. The humoral response to DNCB: its detection by different techniques. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jul;149(3):604–609. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa M. A., Parrott D. M. Induction and recall in contact sensivitity. Changes in skin and draining lymph nodes of intact and thymectomized mice. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):671–690. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


